Displaying items by tag: sharks
One Week Left to Catch 'Shark Week' at Sea Life Bray
#MARINE WILDLIFE - There's still a week left to check out the Shark Week celebrations at Sea Life Bray.
Till 4 November the centre on the promenade in Bray, Co Wicklow will be hosting events that take a closer look at one of nature's most magnificent but misunderstood creatures.
In an urgent bid for shark conservation, Sea Life is supporting the UK-based Shark Trust by throwing the spotlight on sharks - raising awareness about the wide range of shark species in British and Irish waters, and the challenges they and other marine wildlife are facing.
Kids can get involved with badge making, puzzles and games, shark-related quizzes and activity sheets, and even see the centre's sharks - which include bonnet head shark, leopard shark and blacktop reef shark - get their dinner at the shark feeding times!
The full timetable for Shark Week related events at Sea Life Bray is available HERE.
Tall Ships, Galway Volvo Ocean Race, European Tour, Sharks and More
An unforgettable experience on a tall ship, Galway and the Volvo Race, the MOD70 European Tour in Dublin, protection for seafarers after 92 years, Wi-Fi and sharks, topics in your TIN this week.
Read on ....
UNFORGETTABLE EXPERIENCE" ON A TALL SHIP
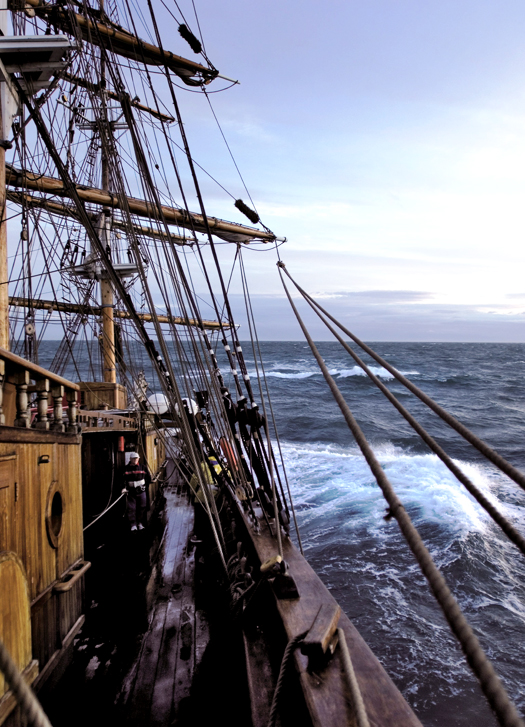

Sailing the Jeanie Johnston
With the Tall Ships Race in Dublin, Captain Michael Coleman has answered my question as to what it is like to command one of these vessels:
"Sailing in good weather on a clear and starry night is an unforgettable experience. The distractions of the land are left far behind and you become at one with nature and the elements."
Captain Coleman of Cobh sailed the Jeanie Johnston in the 2005 Tall Ships Race out of Waterford. "An unforgettable experience never to be repeated," he says and he is right, because at the start of that race Ireland had three tall ships and they led the fleet down the Waterford Estuary to the sea – Asgard, Dunbrody and Jeanie Johnston.
"The distractions of the land are left behind and you become at one with nature and the elements," aboard a tall ship says Capt. Coleman. "No TV or mobile phones or the pressure of modern living, just the ship, the wind and the sea and yourself."
His description is in a new book about the tall ship from Kerry, published by Collins Press of Cork to mark the Tall Ships Race in Dublin. Michael English, who was born in Liverpool and studied art in Cork, then worked in advertising in Dublin, made a photographic record of his voyage aboard the Jeanie Johnston in 2005. This forms the new book: 'Jeanie Johnston – Sailing the Irish Famine Tall Ship.'
The Jeanie Johnston has been berthed for some years as a floating museum on the Liffey in Dublin. As tall ships from around the world gather this week in the capital, while there will be smaller Irish vessels taking part, this island nation does not have an active, sailing tall ship providing training for Irish young people.
VOLVO RACE AND GALWAY
Will we see another race village in Galway again?
Applications from ports around the world to stage the next Volvo Race must be lodged with Volvo by next month and the 'Let's Do It Global' group which ran the event in Galway is not, so far, preparing one it seems, despite the great success of twice staging the event there, this year and in 2009.
Raising the money needed is the problem.
900,000 people attended the race festival in Galway this year, the organisers said and there was a major economic spin-off for the city. A study of the 2009 stopover estimated the economic impact at €55.8 million with more than 650,000 visitors.
The €4 million fee for hosting this year's event was paid directly to the Volvo Ocean Race organisation as the price for bringing it to Galway by Fáilte Ireland. The Galway organisers found it difficult to secure sponsorship in the current economic climate. Galway Harbour Company, which closed the port for the nine-day festival and Galway City Council were major backers. The event had huge voluntary effort. A number of State agencies hosted events and provided logistical support.
Galway Chamber of Commerce called on the Government to provide the necessary support to secure a third successful bid for Galway.
John Killeen one of the leading forces in getting the race to Galway has said the event would have to be underwritten by a bigger entity than just a voluntary group.
As a host port in this year's event, Galway received an automatic invitation for inclusion in the next race in 2014/2015, with the final decision on port selection to be made by the race organisers in December.
EUROPEAN TOUR FOR IRELAND
The MOD70 is coming to Ireland
Ireland continues to gain a reputation as one of the best sailing locations in the world. The new global sailing championship series, the MOD70 European Tour will be in Dun Laoghaire from Wednesday, September 5 to Sunday, September 9, hosted by the National Yacht Club and Dun Laoghaire Harbour Company. Many of the world's top sailing events have been held in Ireland this year.
The high speed MOD70 class of trimarans are a new innovation in sailing. Each MOD70 is identical, built from the same moulds. That should reflect the skills of the sailing crew in performance and not technological advantage.
The MOD70s coming to Dublin Bay will be - Race For Water, FONCIA, Groupe Edmond de Rothschild, Spindrift Racing and Musandam Oman Sail.
On Friday, September 7 and Saturday, September 8, they will sail the Dublin City Race and Speed Match Races. The trimarans will leave Dun Laoghaire at 3 p.m. on Sunday, September 9, for the start of the second leg of the European Tour from Dun Laoghaire to Cascais.
AFTER 92 YEARS – SEAFARERS TO GET WORK PROTECTION
The labour rights of the world's 1.2 million seafarers are to be protected in a new charter – the Maritime Labour Convention. Following its ratification by 30 countries it will go into effect in a year's time – ninety-two years after it was first proposed.
The International Labour Organisation is the United Nations' agency for internationally-recognised labour rights. The Convention was adopted back in 2006 but could not be put into effect until 30 countries adopted it. They represent nearly 60 per cent of the world's shipping tonnage, meaning that seafarers working on more than 50 per cent of the world's international shipping will be covered by the new Convention. Ireland is a member of the ILO but has not yet signed the Convention.
• A safe and secure workplace that complies with safety standards
• Fair terms of employment
• Decent working and living conditions on board ship
• Health protection, medical care, welfare measures and other forms of social protection
TRACKING WHITE SHARKS

Marine researchers are using "ocean WiFi hotspots" in their latest attempts to track the movements of white sharks. The species is under threat. Sharks take several years to reach maturity and spawn. An unmanned 'Wave Glider' robot is the latest development in ocean technology. It has been deployed near San Francisco in US waters. The self-propelled solar-powered glider is part of a new network including data receivers on fixed buoys that will pick up signals from acoustic tags on animals passing within 1,000 feet and transmit the data to a research team on-shore at Stanford University Marine Sciences Department. These are the result of 12 years development of fixed and mobile ocean transmitters to follow thousands of species. They increase scientific capacity to observe the oceans and marine populations, improve fisheries management models and monitor animal responses to climate change.
• The tracking can be followed in real time on a smartphone and tablet computer app "Shark Net" available free of charge at the Apple app store.
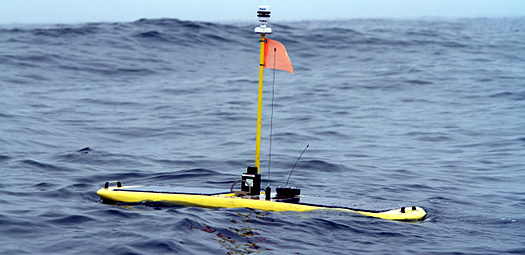
White shark tracking robot
FIRST USA WAVE POWER PLANT
Approval has been given for the building of the first commercial wave-power plant in the USA. The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission has issued a 35-year licence to Ocean Power Technologies Inc. to build the plant, intended to produce 1.5-megawatts of power, 2.5 miles off the coast of Reedsport, Oregon.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
• Email your maritime comments to TIN: [email protected]
Follow me for more maritime news and comment on Twitter: @TomMacSweeney
• And on Facebook – THIS ISLAND NATION page:
Bethany Hamilton: 'I Would Have Been Lost Without Surfing'
Last Saturday's Irish Times features an interview with Hawaiian surfing champion Bethany Hamilton who was in Bundoran for Eurosurf 2011 - where the film of her incredible true life experiences, Soul Surfer, had its gala premiere.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, Soul Surfer tells the story of how Hamilton battled against all odds to become a champion again after losing her arm in a shark attack when she was just 13 years of age.
Most people would be put off surfing for life after such an ordeal, but Hamilton felt she would be lost without it.
"My passion for surfing outweighed my fear of sharks or anything else that might stop me from going in there," she said. "I was so excited to be back in the ocean and once I did it I felt like I was back at home and where I felt comfortable."
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
European Shark Experts Gather in Galway
International experts on sharks, skates and rays will meet at the Marine Institute in Galway for the 14th Annual European Elasmobranch* Association Conference from 10th-13th November 2010.
The waters around Ireland are home to a rich diversity of sharks, skates and rays, with over forty different species regularly recorded. Since 1997 the Irish Elasmobranch Group (IEG) has been promoting the research, conservation and awareness of these animals in Irish waters.
"Ireland is not alone in having a specific body dedicated to the promotion of shark research with many other European countries having similar groups," said conference organiser Dr. Edward Farrell who has spent the last four years studying Smooth Hound Sharks under the supervision of Dr. Stefano Mariani of the University College, Dublin and Dr. Maurice Clarke of the Marine Institute. The European Elasmobranch Association (EEA) is a share-holding organisation for coordinating the activities of all the national shark organisations dedicated to the study, management or conservation of sharks, skates and rays within Europe.
"Irish shark research will feature strongly at the conference," said Dr. Clarke, "with presentations on the satellite tagging of porbeagle sharks and a global population study of blue sharks among the highlights."
The conference this year will cover a wide variety of topics including elasmobranch taxonomy, biology, management and conservation, fisheries and ecology. It will also be preceded by a meeting of the Shark Specialist Group of the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) on Tuesday 9th November in Galway. This group promotes the long term conservation of the world's sharks and related species. Their task will be to assess the status of a number of threatened and endangered Northeast Atlantic species. For more information see http://www.iucnssg.org.
"The annual EEA conference provides a unique opportunity for a diverse range of member organisations to exchange ideas and research, and forge links to promote shark, skate and ray conservation throughout Europe and the rest of the world," said IEG outreach officer Emmet Jackson of BIM. "Galway Atlantaquaria is hosting the welcome reception and delegates are sure to enjoy the elasmobranch exhibits, particularly the impressive ray pool and the world's only captive white skate."
Further details of this conference, a first for Ireland, are available on the Irish Elasmobranch Group website and the EEA website at:
http://www.irishelasmobranchgroup.org/ and http://www.eulasmo.org/
* "Elasmobranch" is a collective name for sharks, skates and rays.
































































