Displaying items by tag: Mixed Two Person Keelboat
Offshore Mixed & Double Handed Sailing is Exciting Addition to Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta 2021
An exciting addition to Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta is its offshore double-handed and mixed keelboat component to the July 2021 event.
Offshore Mixed Doubles is the fastest-growing segment of offshore sailing that is also set to become an Olympic sport in 2024 as Afloat previously reported here.
As outlined in the Irish regatta's Notice of Race published last week, Dun Laoghaire Regatta is open to Offshore Double Handed & Mixed Two Person boats with an IRC rating between .800 and 1.030. Boats outside these limits may be accepted at the sole discretion of the OA.
While the VDLR race may not be a true offshore, it does provide the opportunity for serious competitors to sharpen their boat to boat skills while allowing newcomers to the discipline to try it out without the commitment required by full-on offshore.
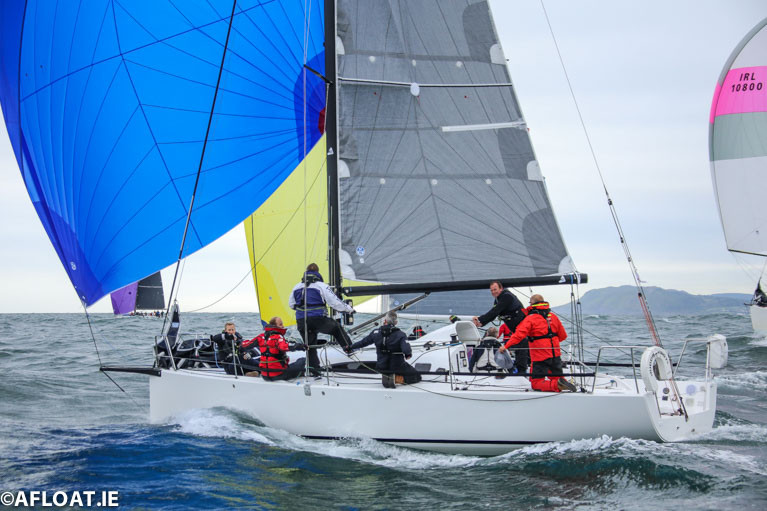
 Conor Fogerty's Silver Shamrock is one of the first entries into VDLR's 2021 double-handed division Photo: Afloat
Conor Fogerty's Silver Shamrock is one of the first entries into VDLR's 2021 double-handed division Photo: Afloat
As far as Ireland is concerned, there is significant interest in the new Olympic discipline with currently up to three (or maybe four) possible contenders already for the single berth at the Paris 2024 Olympics even though a final decision on the new class has been deferred until next Summer. These include Tom Dolan who has not yet announced a 2024 sailing partner, Kenny Rumball and Pamela Lee from Dun Laoghaire and Greystones and Conor Fogerty and Susan Glenny from Howth. Fogerty has been an early entry into the VDLR and will sail double-handed with Suzanne Ennis in his classic half tonner Silver Shamrock.
Dun Laoghaire Regatta organisers say automatic and wind-vane devices for steering may be used in the Two Person Class.
Boats shall hold and carry aboard a valid 2021 IRC rating certificate issued no later than 1700 on Friday 25 June 2021 and shall be compliant with World Sailing Offshore Special Regulations 2020.
Paris 2024 Mixed Two Person Keelboat Offshore Equipment Call Receives 12 Responses from Classes & Manufacturers
Following a request for information to allow for a Paris 2024 Mixed Two Person Keelboat Offshore Equipment market assessment, World Sailing has received a positive industry response from Manufacturers and Class Associations. In December 2019, World Sailing issued a Request for Information (RFI) to engage manufacturers and classes in the discussions around the Equipment.
The Paris 2024 Olympic Sailing Competition will, for the first time ever, feature a Mixed Two Person Keelboat Offshore Event that will test the mental resolve and physical attributes of the sailors competing. The plans for the new Olympic class have met with great interest in Ireland where a number of teams are already aiming to contest the single 2024 berth.
At least three of the marques that will sail in Ireland in 2020 feature in the list of 12 including the new J99, the Figaro 3 and the brand new Sunfast 3300 that is due into Kinsale next month.
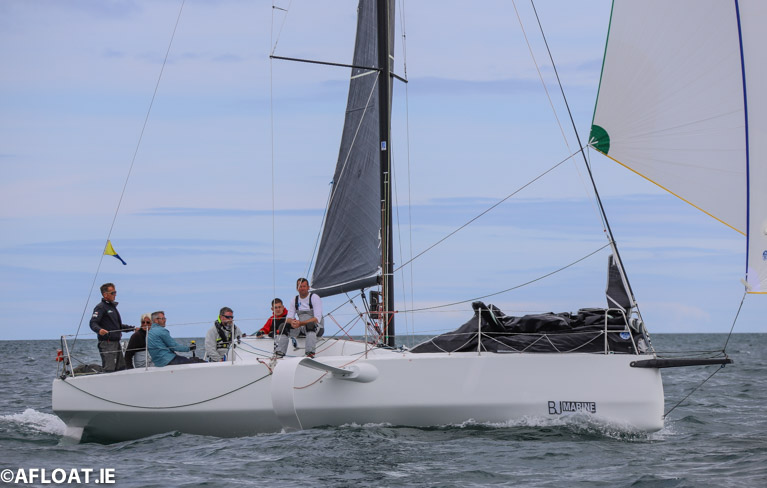 Beneteau's foiling Figaro 3 is one of the models proposed
Beneteau's foiling Figaro 3 is one of the models proposed
World Sailing received 12 responses from manufacturers and designers who provided information such as technical data including production capacity, handicap certificates, statements of suitability for double-handed sailing, sailors endorsements and existing fleet sizes.
The following manufacturers and classes responded to the RFI:
- Dehler 30 OD
- Django 8s
- FarEast 28 R
- Figaro 3
- J88
- J99
- J105
- JPK1030
- L30
- Sunfast 3300
- TEN2
- Vector6.5
At World Sailing's 2019 Annual Conference in Bermuda, World Sailing's Council, the main decision-making body of World Sailing, approved the decision-making process for the selection of Equipment for the Event.
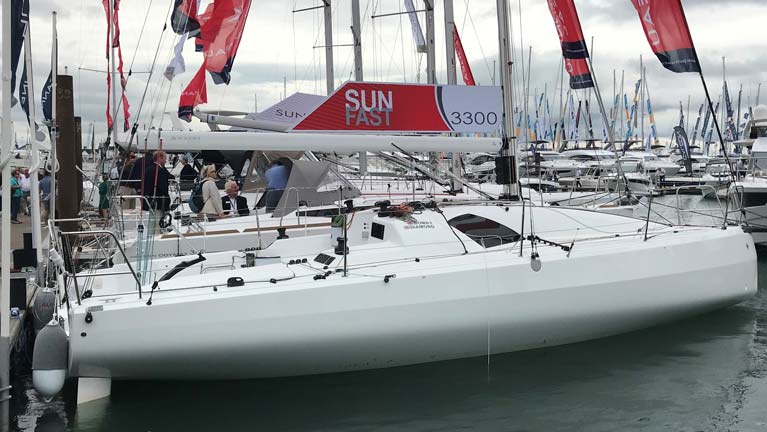 The new Sun Fast 3300 on the dock
The new Sun Fast 3300 on the dock
The criteria for suitable Equipment for the Olympic Offshore Event will be published no later than 31 December 2020 and the Equipment will be selected no later 31 December 2023. With regards to the qualification events, a list of Equipment that meets the qualification criteria shall be published no later than 31 December 2020. It is expected that the criteria will give the widest possible choice of suitable equipment, giving many manufacturers the opportunity for their equipment to be selected.