Displaying items by tag: Fionn Leyden
Just fifteen places in a fleet of 112 sailors from 44 countries separated the three Irish sailors competing at the 2016 Laser Standard Men’s World Championship in Mexico yesterday.
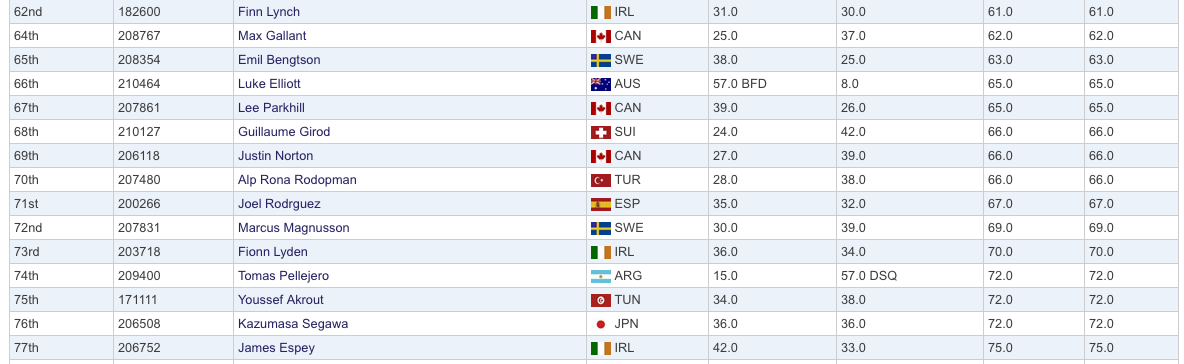
Britain's Nick Thompson has opened his Laser title defence with a perfect 1,1 score and in the final Irish selection trial being sailed as part of the championships, Finn Lynch leads James Espey and Fionn Lyden, although results in the 60s and 70s will not be the kind of performance Ireland is hoping for in Rio in August. Lynch is 62nd, Lyden 73rd and Espey 77th. Read more about the Irish trialists final battle here.
Competitors enjoyed sparkling conditions of 12 to 15 knots in the waters off Nayarit on the west coast of Mexico. The total fleet is sailing in two groups during the qualifying series to determine the gold and silver fleets.
The first fleet was a little jumpy in the lighter conditions at the beginning of the day and needed 3 attempts to start before getting away on fourth start. In the process, 7 boats were taken out by the black flag for breaking the start line, including 9 times world champion, Robert Scheidt from Brazil.
On the final start in a building breeze Croatia’s Tonci Stipanovic tacked quickly on to port off the start line and headed for the starboard side of the course on a two-tack first beat. His tactic helped him to round the first mark in the lead, a position he held to the finish ahead of Milivoj Dukic from Montenegro. Behind him Philipp Buhl from Germany pulled through from 9th to 4th and then to 3rd by the finish.
The blue fleet started on the first attempt with Mark Spearman (AUS) rounding the first mark in the lead but was soon overtaken by Nick Thompson (GBR). “I had a good start and protected the right-hand side and rounded in fifth behind the guys who went further right” said Thompson. “I managed to gain places on the downwind second leg to get the lead at the bottom of the run and then hold on to the finish”.
In spite of a large swarm of bees landing on the Race Committee signal boat and pin boat, both fleets got away first time with clean starts for the day’s second race. In the yellow fleet race Scheidt made up for his previous black flag start to lead the fleet to a comfortable win ahead of Jean-Baptiste Bernaz of France and Andy Maloney from New Zealand.
In the blue fleet, Thompson got another good start from a slightly favoured pin and was able to cross over to the right side of the course to round the first mark just behind Julio Alsogarey ARG and ahead of Matthew Wearn AUS. Thompson pulled through to first on the second windward leg to take the gun ahead of Alsogarey and Wearn.
Qualifying racing continues today with two more races scheduled in the 14 race series. Overall results after 2 races without discard.
Nick Thompson GBR 2 pts
Tonci Stipanovic CRO 5 pts
Matthew Wearn AUS 7 pts
Jean- BaptisteBernaz FRA 9 pts
Millivoj Dukic MNE 13 pts
Andy Maloney NZL 14 pts
Philipp Buhl GER 15 pts
Kacper ZieminskiPOL 16 pts
Jesper Stalheim SWE 17 pts
Lorenzo Brando Chiavarini GBR 17 pts
#laserworlds – Ireland's James Espey has completed the 2015 Kingston Laser Standard World Championships in 43rd place from 53. It's a gold fleet performance but not the elusive break through in to the top 20 the London 2012 representative may have wisheds for. In a similar sized silver fleet, West Cork's Fionn Lyden was 20th. Three races were completed yesterday in winds of 6-10 knots from the North East, for a total of six races in the final series. Nick Thompson representing Great Britain, went into the day with a 20 point lead, and was able to stay on top, winning the 2015 Laser Standard World Championship. Nick Thompson had a strong regatta, as he remained one of the top 5 competitors for the entire event.
The next Laser event of Irish interest Laser Radial European Championships in Denmark. Annalise Murphy will be competing for a title she won in 2013. Racing starts there on July 19th.
Final top ten:
1. Nick Thompson, GBR, 67 points
2. Philipp Buhl, GER, 93
3. Tom Burton, AUS, 97
4. Juan Ignacio Maegli, GUA, 105
5. Matthew Wearn, AUS, 106
6. Andy Maloney, NZL, 106
7. Sam Meech, NZL, 107
8. Kacper Zieminski, POL, 110
9. Pavlos Kontides, CYP, 113
10. Lorenzo Brando Chiavarini, GBR, 116
* Of the 46 places available on the Rio 2016 Laser startline, nine were up for grabs at the 2015 Worlds which were held in Kingston, Canada from 2-8 July 2015. The first qualification regatta, the Santander 2014 ISAF Sailing World Championships saw 24 nations secure a spot in Rio.
The nine nations to qualify for Rio 2016 from the 2015 Laser Worlds (in nation order) are:
1. Argentina
2. Chile
3. Estonia
4. Hungary
5. Korea
6. Montenegro
7. Peru
8. South Africa
9. Spain
Amazing Annalise Murphy Counts Five Race Wins to Lead Laser European Championships
#lasereuros2013 – Annalise Murphy wins two more races today to lead the Laser Europeans in Dun Laoghaire by seven points. In bright sunshine, warm temperatures and even an unusual sea breeze, favourite Annalise Murphy remains the only sailor at the Laser European & World Championships to complete the six-race Qualifying Series counting a score line of five race wins.
The satisifed Dun Laoghaire sailor tweeted after racing: 'Wins in both races today @LaserEuros2013 ! I am going to sleep well tonight! #sotired'
The change from the offshore, shifty westerly breezes of the first two days might have been welcomed, but in their place was a difficult, at times frustrating, thermal sea breeze which was often riddled with holes and peppered with puffs which still brought significant changes in wind direction. But the change did not seem to worry Murphy who built a significant lead in both of her races for another two winning guns. But as the Final Series now starts - the business end of the championships - she will face much stiffer competition.
"I'm feeling pretty good. Now it's gold fleet and it will be very different, much harder with twice as many good people in the fleet. I feel good after these last few days but there are three days to go. I am taking nothing for granted. I am just looking to keep sailing well, to get good starts and hopefully it will work out. I don't worry about what the weather forecast might bring, they have been wrong the last three days and so there is no point in speculating" Murphy, who is sailing on her home waters, reported.
She goes forward with a lead of seven points over Belgium's Evi Van Acker, the 2012 Olympic bronze medallist who finished second twice today, whilst the British Sailing Team's Ali Young and Denmark's Sarah Gunni are three points further back on 17 points.
Fionn Lyden drops to second
In the Laser Radial Men's fleet Baltimore's Fionn Lyden dropped to second after a 20th in the second race today but remains only one point behind Australian leader Tristan Brown. "I got everything wrong" Lyden said later, "I had a reasonable start and thought the wind was going to shift left but it didn't. I was in the bottom 15 at the first mark but gained about 15 places on the run. I thought it was going to shift left again on the second beat but it didn't. I then gained a few more places on the reach but finished 20th. It was a weird race".
Last year's European Championships runner-up, Sweden's Jesper Stalheim, goes into the Final Series of the Men's Olympic class with a lead of two points over Brazil's Robert Scheidt who he kept behind him twice today as he sailed to a first and a second, with the five times Olympic medallist taking second and third.
Scheidt confirmed again today that he is racing the Laser not through any sense of obligation but because he loves it, and it is his best option at the moment for him to win a sixth medal. "I think this is my only option in terms of an Olympic class. It is a boat I know, I have the experience, easy to start a campaign. The most important thing is I still enjoy sailing the boat. I would not be doing this if I did not enjoy sailing this boat" he smiled in the Dun Laoghaire sunshine this afternoon.
Of his races today he reported "In the first race I rounded the top mark in 25th and so I was pleased to come back from that. It was pretty difficult with a lot of holes in the breeze. It was very fluky wind, getting up to 16 - 17 knots but then dropping very quickly to four knots. That made the racing very difficult. Also downwind sometimes you were going but sometimes you were stopped. I am happy to have made two results in the top three today. But tomorrow it is like the start of a new regatta. We all start again in the one fleet".
Although Swede Jesper Stalheim sailed to first and second place finishes, he maintained he had found the conditions confounding at times. "It was a game of luck at times and my luck again seemed to work out" said Stalheim, "There were such big pressure differences. You would go from full hiking to no wind in a matter of seconds and just stop. And people would still be going around you. It feels really good to be sailing well though".
"The conditions were weird at the last Europeans where I was second. I must be OK at it. But the standard there was not so high (as many sailors were in Weymouth preparing for the Olympics). I feel I am sailing well. I will have to be good from here."
Stipanovic shares the same raw motivation as Annalise
With a first and a third today Croatia's Tonci Stipanovic is up to third overall. Twice Laser European Champion – in 2010 and 2011 – Stipanovic shares the same raw motivation as Annalise Murphy. He too missed out painfully on an Olympic medal in the Medal Race at Weymouth and Portland just over a year ago.
"It will be difficult as of now. You have to sail well on the first day of the finals, the pressure really is on then. If you don't it becomes complicated. It is not necessary to win races, just get good results" said Stipanovic.
See here for full results































































