Displaying items by tag: Lee Overlay
Irish Sailors Up For It In RORC Caribbean 600
For those reared in the simple certainties of the course in the offshore classics like the Rolex Fastnet Race and the even more clearly defined Volvo Round Ireland Race, the multi-island RORC Caribbean 600 which starts tomorrow (Monday) morning at Antigua is a strange beast writes W M Nixon.
Set against the straight-line austerity of other long-established classics such as the Newport-Bermuda and the Rolex Sydney-Hobart, its weaving course makes it seem almost fussy. But in a typical February in the Northern Hemisphere, people will happily race round as many islands as are required to make the magic 600 miles total. Just so long as it’s in those marvellous Caribbean sailing and climatic conditions which contrast so totally with what many other areas of the Northern Hemisphere are experiencing in this dank dark cold month.
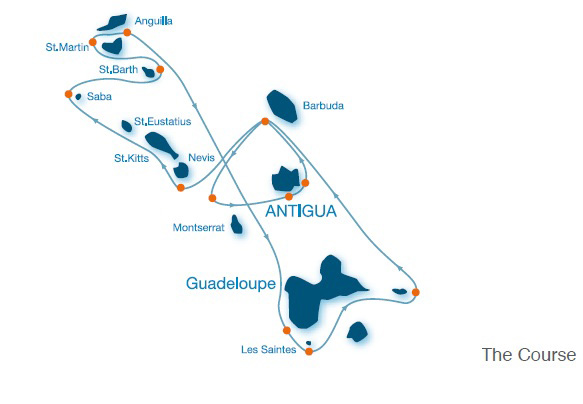
It’s a busy course – with so many islands to be ticked off, navigators could usefully employ the services of a continuity director…
Eleven islands are required to act as race marks in order to put sufficient mileage in the course. But with 77 boats – many of them noted superstars – tuned up and ready to go, it’s clear that the huge variety of legs both long and short which have to be sailed is no deterrent, and Irish interest is high both in terms of participation, and in the presence of international contenders expected for the Volvo Round Ireland Race in June.
Then too we’ve a certain proprietorial interest. The Caribbean 600 having been inaugurated as recently as 2009, it’s a modern classic. And the fact that on its first staging, it was won overall by Adrian Lee’s Cookson 50 Lee Overlay Partners from Dun Laoghaire, makes it extra special. For in her previous life as Ger O’Rourke’s Chieftain, the Lee ship had been overall winner in the Rolex Fastnet Race 2007, providing the rare if not unique situation that the same Irish boat won two classics in the space of just 18 months.
Six years later, the ever-green Cookson 50 is such a good all-rounder that she’s still very much in the hunt, and Lee Overlay Partners is in the listings for tomorrow’s start, the smallest boat in the six strong canting-keel division which includes such giants as Jim and Kristy Hinze Clark’s mega-powerful hundred footer Comanche.
We’ve interest throughout the race, as in addition to Lee Overlay Partners, the fleet includes two Howth Yacht Club crews. Howth sailors with the likes of Kieran Jameson on the strength have already got involved in past seasons in the Rolex Middle Sea Race with a Performance Yacht Charter’s First 40, and now with two of PWC’s boats of this proven marque on the other side of the Atlantic, there with PYC’s Lucy Johnson on Southern Child are Howth men raring to go Caribbean island-rounding. Much of the Howth team assembled by Darren Wright for the 2014 Rolex Middle Sea Race are re-joining the same boat, Southern Child, and their lineup incudes Kieran Jameson, Frank Dillon, Rick de Neve, Jonny White, Colm Bermingham, while new talent in the form of Michael Wright, recently-retired HYC Commodore Brian Turvey, and young Howth K25 squad member Luke Malcolm are also on the strength.
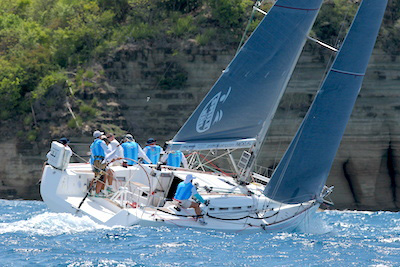
One of the two Howth crews will be racing the First 40 Southern Child, which they’ve already campaigned in the Rolex Middle Sea Race

Howth Yacht Club Headquarters for the RORC 600: Villa Touloulou
Up against them to provide a spot of in-club competition is HYC’s Conor Fogerty who is doing an Atlantic circuit as a mix of racing and cruising with his new Sunfast 3600 Bam, a boat which might have been designed with RORC Caribbean 600 enjoyment in mind. Bam’s racing crew coming out from home include Simon Knowles, Daragh Heagney, Paddy Gregory, Roger Smith and Anthony Doyle. After Bam sister-ship Red Shift’s success in last year’s race, Conor Fogerty has great hopes for his stylish boats showing once tomorrow has seen the start – usually a very challenging business in itself – get cleanly away.

Conor Fogerty’s Sunfast 36 Bam from Howth is doing the RORC Caribbean 600 as part of an Atlantic odyysey
Ireland’s own RORC Commodore Michael Boyd of the RIYC, who won the Gull Salver for best-placed Irish boat in last year’s Fastnet Race with the Grand Soleil 43 Quokka 8, is helping to pass the time while waiting for delivery of his new JPK 10.80 by racing the Caribbean as navigator on Andy McIrvine’s Grand Soleil 46 Bella Donna.
As for pointers towards the Volvo Round Ireland Race in June, the two MOD 70 trimarans already signed up for it, Lloyd Thornburg’s Phaedo 3 and Concise 10 (Tony Lawson & Ned Collier Waefield) are both g0ing for the Caribbean 600.
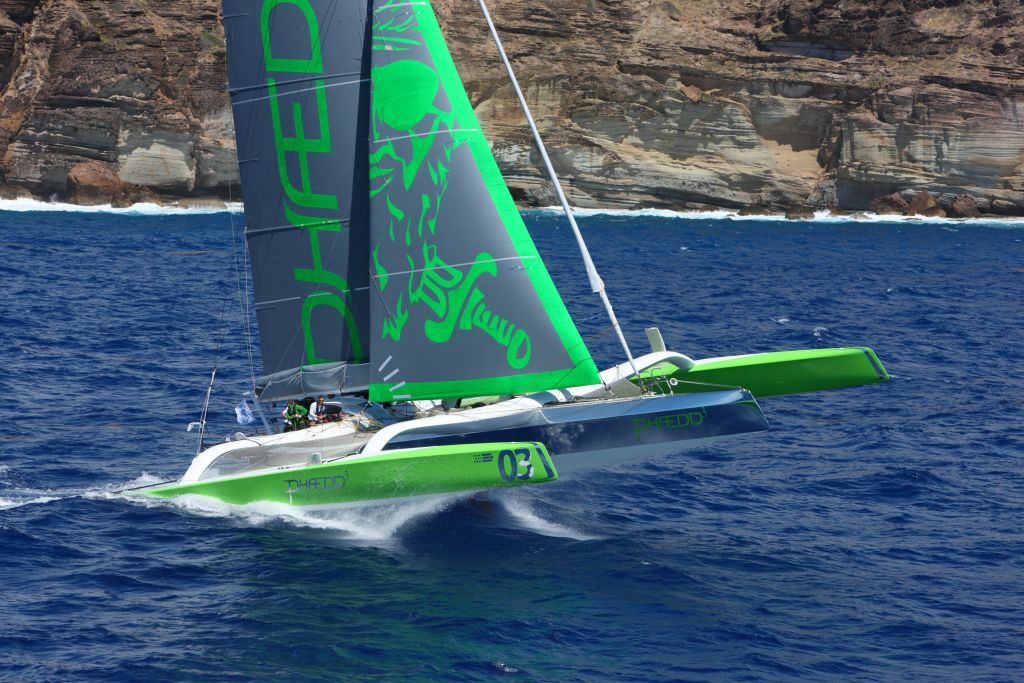

Lloyd Thornburg’s MOD 70 Phaedo 3 is one of two sister-ships entered for the Volvo Round Ireland Race 2016 which are also doing the Caribbean 600, the other being Concise 10.
In fact it’s a very eclectic fleet, as Eric de Turckheim’s noted Commodore’s Cup contender of 2014, Teasing Machine from France, has somehow got herself to the Caribbean after being far away to cut a successful swathe through the recent Rolex Sydney-Hobart Race. And up towards the top of the fleet, the 72ft mini-maxi Momo, which was best of the bigger boats in last summer’s Fastnet, find herself up against Hap Fauth’s similarly-sized superstar Bella Mente, which had to scratch from the 2015 Fastnet Race for personal reasons after a blisteringly successful Cowes Week, but is now set to go in a race in which she is the defending champion.

Back to the fray. Having been forced to scratch from the Rolex Fastnet 2015 in which she was a favourite, Hap Fauth’s 72ft mini-maxi Bella Mente is very much in the hunt in tomorrow morning’s RORC Caribbean 600, in which she is defending champion.
The 72ft mini-maxis seem to be the favoured size of boat o the most recent peformances, as Nik Zennstrom’s Ran won in 2012, George Sakellaris’s Shockwave won in 2014, and Bella Mente won in 2015. But the evergreen Cookson 50 is a good steady bet, with Lee Overlay Partners; win in 2009, and Ron O’Hanley’s with Privateer in 2013.
The RORC Caribbean 600 starting process gets under way at 1030hrs local time tomorrow morning off Antigua, and there are going to be 77 very busy crews having more than a few dry-mouth moments before they get clear away around this island’s beautiful east coast.
#d2d – The canting-keel Cookson 50 Lee Overlay Partners skippered by Dun Laoghaire's Adrian Lee is the latest high profile entry into this June's Dun Laoghaire to Dingle race. The Royal St. George yacht is a proven offshore winner, taking the inaugural 2009 RORC Caribbean 600 race and overall victory (as Chieftain) in the 2007 Fastnet Race.
Most recently, in 2013, the globe trotting 50–footer set a course record of 2 days 53 minutes and 40 seconds and the overall win in the 360– mile race from Dubai to Muscat in Oman. In what is looking like a potent line-up for the 12th edition of the National Yacht Club race, this Dun Laoghaire entry joins the Commodore's Cup winning Ker 40, Catapult skippered by Anthony O'Leary of Cork, Afloat's 2014 Sailor of the Year.
Dublin Yacht Claims Middle East Sailing Record in Dubai to Muscat Race
#offshore – As Afloat.ie reported earlier this morning, Adrian Lee's Cookson 50, Lee Overlay Partners, has claimed line honours for the IRC Racing Division in the 2013 Dubai to Muscat Race writes Louay Habib
The Irish canting keel racing yacht crossed the finish line at Muscat on Tuesday, 5 November at 11:58 40 seconds (local time). Lee Overlay Partners elapsed time for the race was 2 Days 53 Mins at 40 Secs, setting a new course record for the 360-mile race.
Adrian Lee was full of praise for his crew, after breaking the monohull record for the longest offshore yacht race in the Arab region that has lasted for 13 years.
"The crew have been absolutely first class, we have sailed together for many years and beating the course record is a very special moment for us. We think we have done well on handicap but we will just have to see how the competition does before we will really know. I think we made some excellent tactical decisions and if we had to run the same race again, I doubt if we would have changed much. What has really surprised me about the race is the 30 knots of wind we experienced for most of yesterday. It was not forecast and seemed to just come from nowhere. The boat was sitting at 16 knots for long periods and flying down the beautiful Omani coast line was very special. We have received a very warm welcome at Bandar Al Rowdha Marina"
Lee Overlay Partners for the Dubai to Muscat Race: Adrian Lee, James Hemingway, Ilya Lee Paveliev, Scott Wilson, Emmet Kerin, James Gunne, Tim Corney, Neil Harrison, Ruairi Herraghty, Robert Witte and Daniel McKeown, who took the photo as the team crossed the finish line.
The 22nd Dubai to Muscat Race is organised under the auspices of the Royal Ocean Racing club. HH Sheikh Khaled Bin Zayed Al Nehayan was the guest of honour for the start. The 360-mile race is the longest offshore yacht race in the region and is organised by The United Arab Emirates Sailing and Rowing Federation in association with the Ministry of Sports Affairs, the Sultanate of Oman.
#muscat – An Irish yacht looks set to break the monohull record for the longest offshore yacht race in the Arab region writes Louay Habib. The record has stood for 13 years. Yesterday afternoon, the wind speed picked up significantly in the Gulf of Oman, propelling Adrian Lee's Cookson 50, Lee Overlay Partners at record breaking pace.
"The Strait of Hormuz was an impressive sight with the mountains of Musandam in clear view, it was a spectacular exit from the Arabian Gulf and what followed was a dramatic introduction to the Indian Ocean." reported Adrian Lee via satellite phone. "A storm blew in from astern and with the wind speed touching 30 knots, we were often at over ten knots of boat speed and surfing down waves at over 16 knots, what a ride! The storm seemed to pass but the wind hardly decreased, we are trucking along, but dead down wind, so we have had to put in a few big gybes, which the crew have executed with great precision, morale on board is fantastic."
Race Organisers, GWM Racing have reported that 3 yachts have retired with all the crew safe and well. Fawzi al Sultan's Kuwaiti team on Dolce Vita put into port just after Ras Al Khaimah and the Emirates team on Adel Lootah's Jadi made safe haven at Fujairah.
XS35 catamaran, Blackwater skippered by Matt Vukelich has also retired. "We had a tough beat to leave the Strait of Hormuz, with 18 knots of wind on the nose it was pretty bumpy on board." Reported Matt via Thuraya satellite phone. "We were just looking forward to coming off the wind, for what would have been a fantastic ride, when one of our rudders broke. As required by the rules of the race we had a spare, which we fitted but we decided to retire from the race as a precaution. We are disheartened to say the least but happy no one got hurt and we all had a great time!"
The monohull record for The Dubai to Muscat Race was set in 2000 by Twister, skippered by Marco Graziano. In strong winds and a significant sea state the UAE registered J/105, Twister was often sailing with just a heavily reefed mainsail and completed the course in 2 days 3 hours 52 mins 31 secs.
Lee Overlay Partners need to finish the race by 14:52 and 30 secs to become the first overseas yacht to hold the record for 13 years. Today at 0940 local time, Lee Overlay Partners was 20 miles from the finish but the wind speed was dropping dramatically.
Eric Laing's Beneteau 57, Yours Truly was the first yacht to finish the race in the Club Class. Finishing in the early hours of this morning, the UAE based team have won the class for the second year in a row.
The 22nd Dubai to Muscat Race is organised under the auspices of the Royal Ocean Racing club. HH Sheikh Khaled Bin Zayed Al Nehayan was the guest of honour for the start. The 360-mile race is the longest offshore yacht race in the region and is organised by The United Arab Emirates Sailing and Rowing Federation in association with the Ministry of Sports Affairs, the Sultanate of Oman.































































