Displaying items by tag: X302
Successful Youth Sailor Introduction to Irish Half Ton Cup & X302 Championships at Howth Yacht Club
Despite only four boats in each class making it to the start line, the small fleets enjoyed very close racing in 12-20 knots on Saturday and only 3 – 8 knots on Sunday.
Nigel Biggs’ Half Tonner Checkmate sealed the deal on Saturday with three wins when Mata was forced to retire with a bust guard rail and a few swimmers (all collected safely) in the last race.
ICRA overall champion Dux led the X302s on Saturday evening with a two-point lead but Sunday’s very light airs meant they took the prize by just one point overall from Paddy Kyne’s Maximus.
The “normal” Half Ton Cup has a separate trophy for the offshore race and whilst Sunday felt like an offshore in such light airs, the day was won by King One.
The runaway success for the weekend was the initiative for every boat to take an under 18 junior which introduced a number of youngsters into yacht racing, all of whom reported enjoying it immensely.
At least six Half Tonners and six X302s are expected for a newly devised Championships at Howth Yacht Club later this month.
The Irish Half Ton Cup and X302 Challenge will be sailed over three windward-leeward courses and a coastal race from August 21 & 22nd.
With July's Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta cancelled and leaving a void in the season, the two classes came together to produce the pop-up event.
The championships will also serve as a warm-up for September's ICRA National Championships at the National Yacht Club.
Under 18 sailors
The Half-Ton Class says it is keen to promote junior sailing and so have agreed that each boat will take an under 18 sailor as part of the crew for the event. Event rules will permit IRC crew number plus one to encourage same.
The Notice of Race and the Sailing Instructions are downloadable below. Online entry is here.
Half–Tonners, Sigma 33s, X302s, J97s & Corbys Mean ICRA Class Two Title Is Wide Open
Class Two is certainly heating up and expanding this year writes Dave Cullen, Skipper of championship winning half–tonner Checkmate XV. The quality of the fleet must make it one of the most competitive with boats ranging from €15k to €150k all in with a fighting chance of the podium.
At the bottom of the rating band, Sigma 33s make up the numbers and the top end is dominated by J97s and Elan 333s.
Such are the numbers that a number of boats might find themselves unhappy participants in Class One which happened in Sovereigns Cup two years ago.
The fleet is diverse and includes a sizeable X302 fleet from Howth YC including the stalwart podium winner DUX, Maximus and Viking to name but a few.
 Stephen Quinn’s J/97 Lambay Rules is at the top of the Class Two Rating Band Photo: Afloat.ie
Stephen Quinn’s J/97 Lambay Rules is at the top of the Class Two Rating Band Photo: Afloat.ie
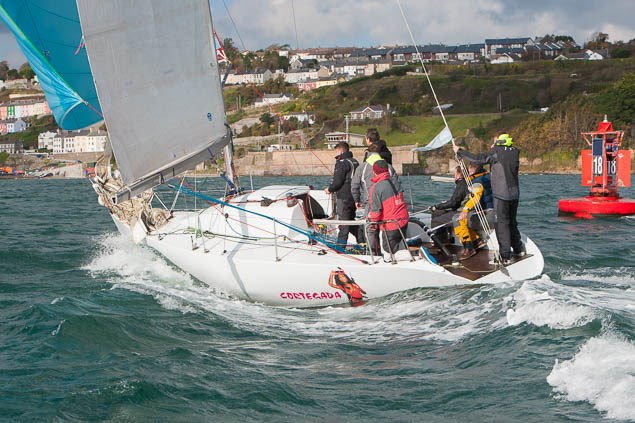 Cork's George Radley adds his latest 'half' Half Tonner Cortegada to the Class Two fleet this season. Photo: Bob Bateman
Cork's George Radley adds his latest 'half' Half Tonner Cortegada to the Class Two fleet this season. Photo: Bob Bateman
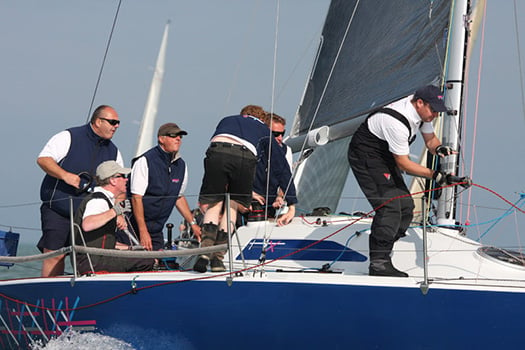 David Cullen's Checkmate from Howth Yacht Club is the 2015 Half Ton champion
David Cullen's Checkmate from Howth Yacht Club is the 2015 Half Ton champion
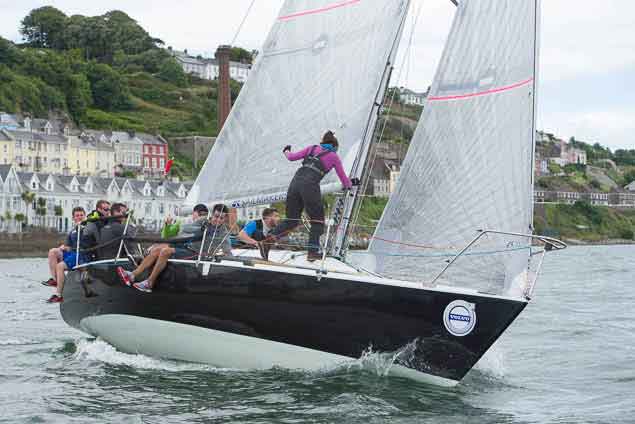 Popular Half tonner Harmony from Howth (Jonny Swan) is on the Class Two circuit Photo: Bob Bateman
Popular Half tonner Harmony from Howth (Jonny Swan) is on the Class Two circuit Photo: Bob Bateman
 Another quality Half tonner campaign from HYC, The Big Picture (Michael and Richard Evans). Photo: Afloat.ie
Another quality Half tonner campaign from HYC, The Big Picture (Michael and Richard Evans). Photo: Afloat.ie
The Half Ton class is formidable and apart from the locals of Checkmate XV, Harmony, King One and The Big Picture, visiting boats planning on basing campaigns here include Nigel Biggs latest Checkmate XVIII ex Dick Dastardly, Paul Wayte from Swansea's HB31 Headhunter and the highly optimised Miss Whiplash returns to Dublin owned by Paul Pullen visiting from Swansea. Demolition from Falmouth is also likely to appear. George Radley adds his latest 'half' Cortegada to the pile of quality competitors.
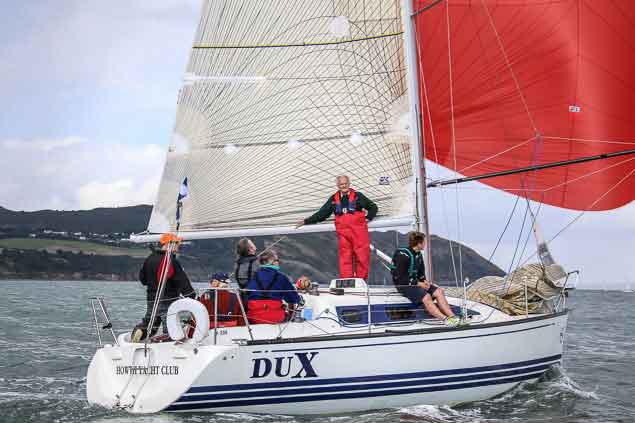 The X302 fleet from Howth YC includes stalwart DUX Photo: Afloat.ie
The X302 fleet from Howth YC includes stalwart DUX Photo: Afloat.ie
Throw in DB1s, J80s, Corby 25 & 26s and the start line really shapes up with a sharp competitive fleet.
It's easy to predict the half tonners as dominating with light to medium conditions suit them for sure. The same applies with the Corbys. Throw in an extra few knots and the X302s pick up their heels as do the Sigma 33s which are never too far behind. Movistar Blue and Lambay Rules like a breeze too so the field is really wide open.
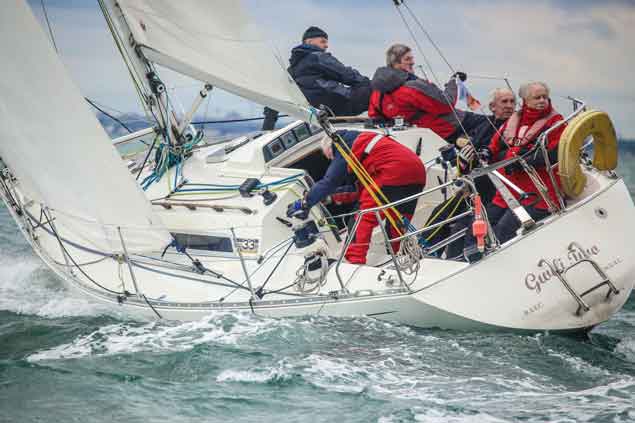 The Sigma 33 class, formerly a stand alone one design class, have joined DBSC Cruisers Two division this year, boosting numbers on Dublin Bay to 19 Photo: Afloat.ie
The Sigma 33 class, formerly a stand alone one design class, have joined DBSC Cruisers Two division this year, boosting numbers on Dublin Bay to 19 Photo: Afloat.ie
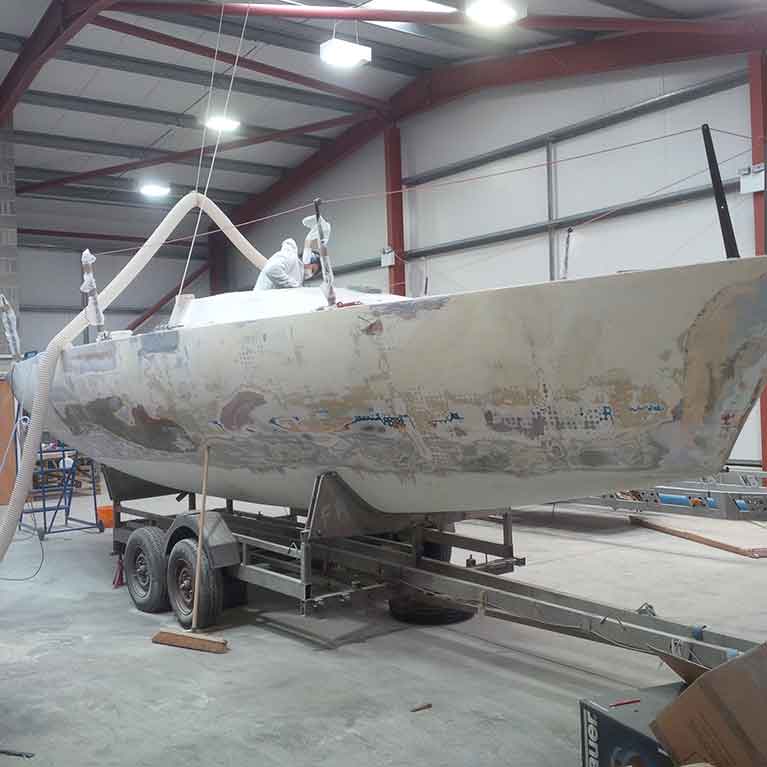 Checkmate XVIII – the old Emiliano Zapata, ex Dick Dastardly, ex French Beret, ex Concorde from 1985 is undergoing a refit in North Wales, launching early May
Checkmate XVIII – the old Emiliano Zapata, ex Dick Dastardly, ex French Beret, ex Concorde from 1985 is undergoing a refit in North Wales, launching early May
On Dublin Bay, there will be a reported 19 boats in this year's DBSC Cruisers two fleet boosted by eight Sigma 33s who join the division.
As to predictions, any of the boats in the class can win but need to arrive on the line in good shape and well prepared. Rub your hand over the bum of any of the Class leaders and you will see the efforts put in as the best winning ingredient for race wins is boat speed.
I think a prediction is futile without a weather forecast so I would say for lighter traditional Dublin summer conditions, any of the half tonners or the Corby 25 will feature in a windward–leeward race, Lambay Rules (J97) prefers a reach round the cans races whilst a well sailed Sigma 33 has a real chance if they can stop the mighty Dux in breezy conditions.
Having answered the question like a politician would, if it was predictable none of us would bother, so place your bets and see how it fared out in October. I'll put a tenner on Biggsy though!
Dave Cullen of Howth Yacht Club is Skipper of Half–Tonner Checkmate XV and won the 2015 Half Ton Classics Cup with a race to spare





























































