Displaying items by tag: survey
Survey to Assess Value of Irish Angling
#ANGLING - Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI) has appointed Tourism Development International (TDI) to undertake a Socio-Economic Survey of Recreational Angling in Ireland.
The overall objective of the survey, which will run over the course of 2012, is to establish the current volume and value of domestic and overseas recreational angling in the country.
Pike, coarse fish, bass, salmon, sea trout, brown trout and sea anglers will all be invited to participate in what is described as Ireland's most comprehensive angling survey undertaken in decades.
The survey will inform IFI and its tourism partners in relation to the business of angling in Ireland and also enable improved strategic planning and decision-making in terms of product development and marketing.
"Anglers are the key to this survey," commented Minister of State for Natural Resources Fergus O'Dowd. "They know the resource and they understand the importance of sustainability. What anglers contribute to Ireland’s economy is unknown but I am certain that it is significant.
"Angling takes place in every river and lake in Ireland and all around our coastline. There is no town or village in Ireland that doesn’t have anglers."
He added: "It is imperative that the inland fisheries and sea angling resources are managed in the best way possible to ensure enjoyment for our local and visiting anglers, sustainable jobs in rural communities and maximising its potential to add to Ireland’s economy.
"Getting the right information from those most involved will greatly assist in improving the angling product."
The survey comprises two parts: a household survey and a survey of recreational anglers which will commence in April. Anglers will be met at fishing locations throughout Ireland and invited to participate there and then, or later by phone or online. IFI says that every effort will be made to accommodate participation.
- angling
- Inland Fisheries Ireland
- IFI
- Tourism Development International
- TDI
- survey
- SocioEconomic Survey of Recreational Angling in Ireland
- Pike
- Salmon
- Sea Trout
- brown trout
- coarse angling
- sea angling
- tourism
- business
- marketing
- development
- Minister of State for Natural Resources
- Fergus O'Dowd
- sustainability
- inland waterways
- jobs
River Barrow Has Potential for Tourism
#INLAND WATERWAYS - A new study on the River Barrow and its environs recommends the development of "activity hubs, tourist trails and new angling and boat facilities", The Irish Times reports.
Waterways Ireland and Fáilte Ireland commissioned the Barrow Corridor Recreational, Tourism and Commercial Identification Survey to find ways to exploit the area's "undeveloped potential" for tourism.
The survey covered the river itself as well as its estuary and the Barrow branch of the Grand Canal. Its findings pointed to a number of areas where development is already being actioned, such as in boating and cruising, nature and wildlife, and angling.
Environment Minister Phil Hogan, who launched the study in Carlow yesterday, hailed the co-operation of the agencies and county councils involved.
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
Marine Notice on Pipeline Survey in Celtic Sea
#NEWS UPDATE - The latest Marine Notice from the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport (DTTAS) advises on a pipeline survey in the Celtic Sea next month.
PSE Kinsale Energy Limited will be commencing the survey of the 24" Gas Export Pipeline on 6 March 2012 using the Marine Institute vessel RV Celtic Voyager (call sign EIQN). The survey is expected to last 1 to 2 days, depending on weather conditions.
The survey will take place along the existing pipeline route in the Celtic Sea, between the shoreline at Inch Beach in Co Cork and gas platform 'Alpha'.
The RV Celtic Voyager will display appropriate lights and signals, and will be towing side scan sonar with cables of up to 200m long. A Radio Navigation Warning will be issued via the Irish Coast Guard (schedule Bravo, four times a day) prior to the vessel's arrival at the survey area. The vessel will also keep a listening watch on VHF Channel 16.
All vessels, particularly those engaged in fishing, are requested to give the RV Celtic Voyager and her towed equipment a wide berth and keep a sharp lookout in the relevant areas.
Further details for seafarers, including relevant co-ordinates, are included in Marine Notice No 7 of 2012, a PDF of which is available to read and download HERE.
Special Angling Event Produces First Salmon of 2012
#ANGLING - The first wild Atlantic spring salmon of 2012 was caught Sunday on the River Liffey in exceptional circumstances, The Irish Times reports.
Though the river is closed for salmon fishing as stocks are currently below sustainable levels, Inland Fisheries Ireland sanctioned a special catch-and-release club event for survey reasons at Islandbridge in the capital.
Declan Briggs – a 47-year veteran of the Dublin and District Salmon Anglers' Association - landed the 8.5lb beauty using a wooden Devon lure at 9.50am.
“This is my first time to catch the first fish. I’m absolutely delighted," he said.
Elsewhere in Ireland, Briggs' catch was mirrored by Tyrone man Ian Martin, who caught the northern region's first salmon on the year on the River Drownes near Bundoran.
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
Sonar Survey Reveals Torpedoed Guinness Ship
The detailed seabed images, which include deck features and complex sand wave structures, were recorded by towed sidescan sonar provided by the Moore Marine Group, and give a visual insight into the defensively armed ship that was sunk by a German torpedo in 1917, seven miles east of the Kish Bank off Dublin.
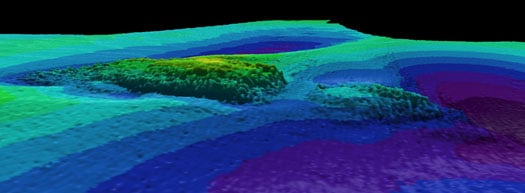
Photos above and below show topographic seafloor images in 3D, showing the partially buried wreck of the W M Barkley lying at a water depth of 56 metres; with deeper scouring around it down to 72 metres (darker colours indicate greater depths). The images were created from sonar data acquired onboard the Marine Institute's research vessel RV Celtic Voyager, during INFOMAR Programme mapping in 2010 and 2011 with data processed by INFOMAR's Fabio Sacchetti (University of Ulster) and Charise McKeon (Geological Survey of Ireland).
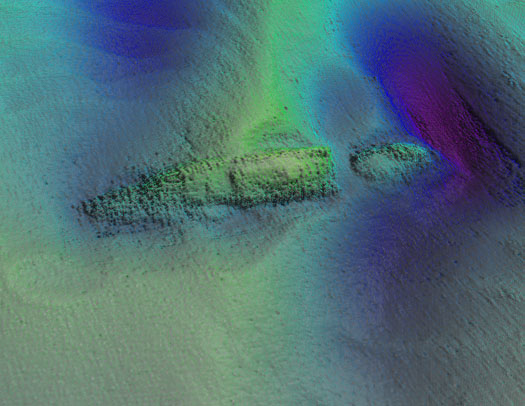

In May 2010, during a large scale mapping survey in the Irish Sea by INFOMAR, a national marine study run by the Marine Institute and the Geological Survey of Ireland, identified a seabed feature which, to the trained eye, was discernable as a potential shipwreck lying in the same position recorded on the Admiralty Chart, the EU wreck site and UK Hydrographic Office wreck site directories, as well as a survey conducted in the 1980s as the last known position of the W.M.Barkley.
Viewing the spectacular imagery of the shipwreck Minister for Communications, Energy & Natural Resources, Pat Rabbitte, said "I am delighted to note the continued excellence of the valuable work being carried out under the INFOMAR project. These images from the deep reveal a unique view of part of Ireland's marine heritage and I am delighted to announce details of INFOMAR''s annual seminar to be held in Galway on November 16 and 17th."

Eibhlin Roche - Guinness Archivist, Guinness Storehouse with the model of the W.M. Barkley. Photo: Jason Clarke Photography
Ninety four years ago on the dark night of October 12th 1917 the W.M.Barkley was torpedoed without warning by the German submarine UC-75. Within minutes the ship, which was owned and operated by the Guinness Company of Dublin, broke in two and sank, taking with her to the bottom four men including her Captain and leaving the rest of her crew to face the sea in an open lifeboat. Now, the darkness where the ship has lain in pieces has been disturbed, probed by fingers of sound that are mapping the seabed in incredible details and bringing to light the position of this famous Irish shipwreck.
"As the first Guinness owned ship, the W.M. Barkley played an important role in the story of the transportation of GUINNESS beer overseas," said Eibhlin Roche, Guinness Archivist. The events of the night of 12th October 1917 are very much part of the history of Guinness that is recorded in the Guinness Archive. It is exciting to finally know the exact resting place of the W.M. Barkley."
A scale model of the W.M. Barkley is on display in the Transport Gallery of Guinness Storehouse remembering the lives of the Guinness men who both perished and survived the events of 12th October 1917. These are stories of tragedy and bravery portraying Irish traditional values, and how they were brought to light with the application of cutting-edge technology.

Koen Verbruggen (GSI), Minister Pat Rabbitte, Dr. Peter Heffernan (CEO, Marine Institute), Eibhlin Roche (Guinness Archivist, Guinness Storehouse) and David Smith (Country Director, Diageo Ireland) Photo: Jason Clarke Photography
Plan to Power Edinburgh with Giant Windfarm
Plans are afoot to power Edinburgh with a giant offshore windfarm, the Edinburgh Evening News reports.
The £1.2 billion (€ 1.37 billion) project proposed by Irish group Mainstream Renewable Power could see as many as 130 turbines generate power for up to 335,000 homes.
The turbines would be installed 30km north of Dunbar, East Lothian, though a number would be visible from the coastline.
Concerns have been raised by East Lothian residents at a consultation hearing regarding the environmental impact of the project, dubbed Neart na Gaoithe (might of the wind), though wildlife and environmental surveys are still being carried out.
Any final go-ahead on the windfarm scheme would have to be given by the Scottish government.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, Mainstream Renewable Power - headed by Eddie O'Connor - has signed deals for windfarms in South Africa and Alberta province in Canada.
The Evening News has more on the story HERE.
Bremore Survey Indicates New Push for Port Development
Drogheda Port Company is seeking tenders to carry out geological investigations off Bremore Head near Balbriggan, the Sunday Business Post reports.
The port company and partner Treasury Holdings had been working with Hong Kong-based Hutchison Whampoa on plans for a new port in the north Co Dublin area, set to have a starting freight capacity of 10 million tons per year.
Treasury Holdings says the survey is intended to help avoid developing on a location that could interfere with historic sites, after An Taisce voiced its opposition to any port scheme that would impact on an archaeologial site running from Bremore to the mouth of the River Delvin.
An Taisce is also opposed to another proposed site at Gormanston.
Drogheda Port Company CEO Paul Fleming could not be contacted by the Sunday Business Post to comment on whether the tender indicates a decision to move forward with plans for a port at Bremore.
Minister for Transport Leo Varadkar said he supported the bid to develop a new facility at Bremore, after a previous move to extend the boundaries of Drogheda port were halted by legislative limits that have since been amended.
The Sunday Business Post has more on the story HERE.
Underwater Survey at Portumna Castle Harbour
Waterways Ireland says the survey area is defined by coordinates:
|
Point |
Lat |
Long |
|
A |
53.083405 |
-8.220102 |
|
B |
53.082973 |
-8.21993 |
|
C |
53.08289 |
-8.219533 |
|
WGS84 decimal degrees |
||
The International Dive flag “A” (Blue / White) will be flown from the dive boat and marine vhf channel 16 will be monitored. The dive boat may also be contacted on 353-86-3859251.
Ireland's First Biodiversity Audit Launched
Ireland's first ever biodiversity audit has revealed that our mountains, woodlands and waterways are home to more than 31,000 different species of plants and animals. For all the latest news on Irish marine animals click here.
Ireland's waters boast more than 560 different species of marine fish, most of which are perch-like or ray finned fish, while 29 different fish species inhabit Irish inland waterways.
The state of knowledge report also found that popular species of plants, birds or mammals make up just one in ten of all species in Ireland.
Dr Liam Lysaght of the National Biodiversity Data Centre told the Irish Independent that the report "will for the first time allow us to accurately describe Ireland's biological resources and identify the knowledge gaps that exist".
http://www.independent.ie/national-news/irelands-wildlife-audit-revealed-2591440.htmlScientists joined with State bodies, NGOs and third-level institutions last August to conduct the survey of Ireland's plantlife and wildlife.
Minister for Arts, Heritage and Gaeltacht Affairs Jimmy Deenihan said that the protection of Ireland's biodiversity "is not a luxury".
The report is available online at biodiversity.biodiversityireland.ie
Ireland's first ever biodiversity audit has revealed that the country's mountains, woodlands and waterways are home to more than 31,000 different species of plants and animals.
The survey reveals that Ireland's waters boast more than 560 different species of marine fish, most of which are perch-like or ray finned fish, while 29 different fish species inhabit Irish inland waterways.
The state of knowledge report also found that popular species of plants, birds or mammals make up just one in ten of all species in Ireland.
Dr Liam Lysaght of the National Biodiversity Data Centre told the Irish Independent that the report "will for the first time allow us to accurately describe Ireland's biological resources and identify the knowledge gaps that exist".
Scientists joined with State bodies, NGOs and third-level institutions last August to conduct the survey of Ireland's plantlife and wildlife.
Minister for Arts, Heritage and Gaeltacht Affairs Jimmy Deenihan said that the protection of Ireland's biodiversity "is not a luxury".
The report is available online at biodiversity.biodiversityireland.ie
Aerial Survey of Whales Begins
The first ever Air Corps marine animal survey of whale and dolphin activity in Irish waters is set to begin today, the Irish Times reports.
A survey team accompanied by members of the Irish Whale and Dolphin Group (IWDG) were scheduled to take off from Casement Aerodrome this morning headed for the southeast coast, where humpback whales have recently been sighted near Curracloe and Hook Head.
According to the IWDG, 19 whale and dolphin species have been recorded in Irish waters since 1948, the most common sightings being harbour porpoises.
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.






































































