Displaying items by tag: RV Celtic Explorer
2020’s Irish Groundfish Survey Gets Under Way
This year’s Irish Groundfish Survey (IGFS 2020) of the North, West and South Coasts of Ireland is set to commence today, Sunday 25 October.
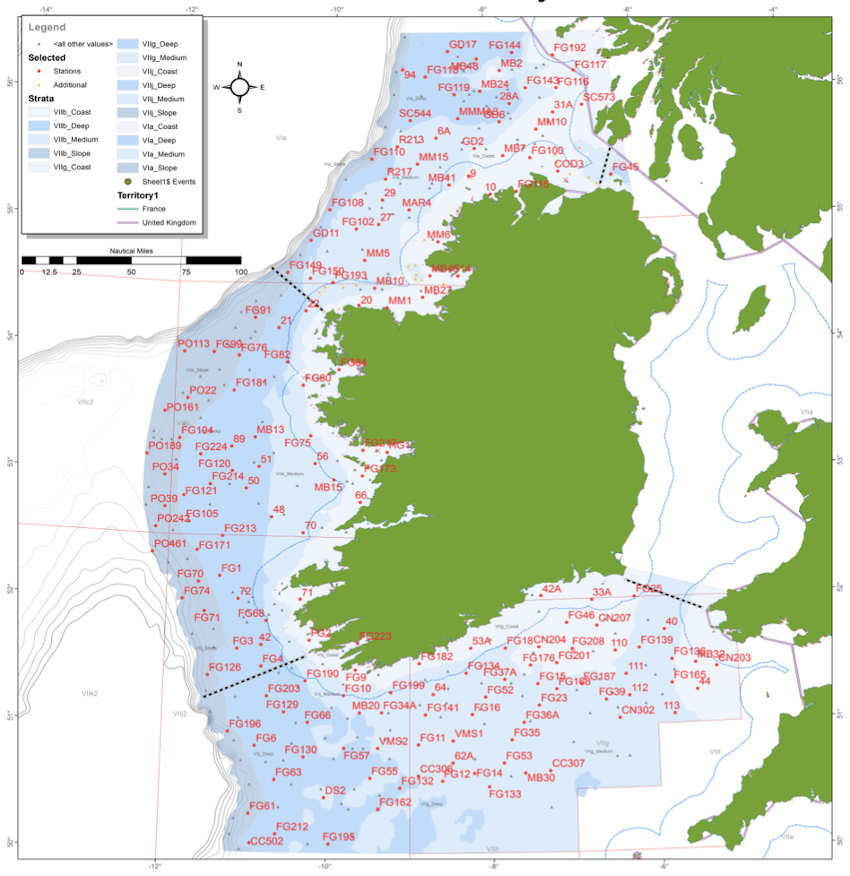
Carried out by the Marine Institute, the IGFS is a demersal trawl survey consisting of around 170 fishing hauls, each of of 30 minutes’ duration, in ICES areas VIa, VIIb, VIIg and VIIj.
As part of the requirements for the 2020 survey, fishing will take place within a two-nautical-mile radius of indicated positions.
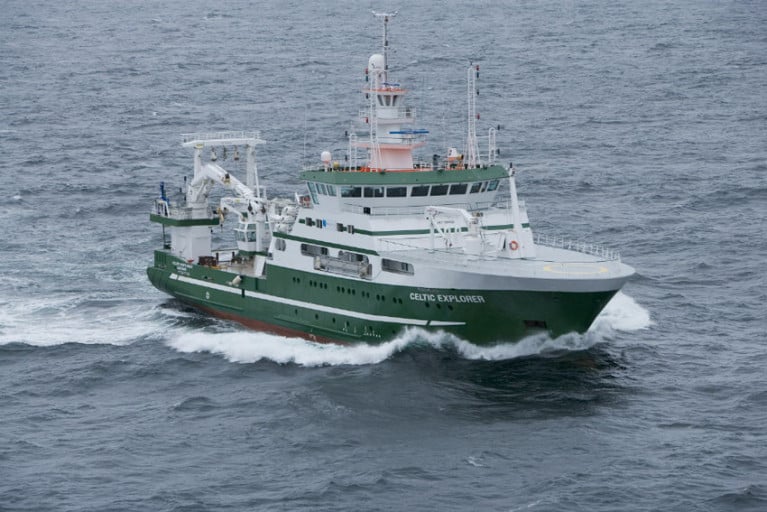
The survey will be conducted by the RV Celtic Explorer (callsign EIGB) which will display appropriate lights and signals.
The vessel will be towing a high headline GOV 36/47 demersal trawl during fishing operations.
Co-ordinates and approximate locations of these hauls are included in Marine Notice No 48 of 2020, a PDF of which is available to download below.
The Marine Institute requests that commercial fishing and other marine operators keep a 2nm area around the tow mid-points clear of any gear or apparatus during the survey period between now and October and Thursday 10 December.
This survey follows the annual Irish Anglerfish and Megrim Survey which was conducted off the West, South West and South Coasts this past February and March.
Irish-Led Marine Science Mission Studies Past Climate Change To Predict The Future
An Irish-led team of marine scientists on board the RV Celtic Explorer returns to Galway Harbour today (Wednesday 16 September) after more than three weeks investigating historic climate change in the Arctic region.
Scientists from NUI Galway, University of Southampton, University of Bremen and Bergen University had been capturing data in the Nordic and Greenland Seas as part of the CIAAN survey (Constraining the Impact of Arctic Amplification in the Nordic Sea: A biogeochemical approach).
This survey aims to provide new insight into how essential climate variables are recorded in geologic archives.
Assessing the impact and magnitude of past (pre-industrial) climate changes is critical to further our understanding of how the climate system will respond to a rapidly changing Arctic ecosystem, the scientists explain.
‘One of the key challenges in climate change science is assessing the magnitude of future climate change’
Lead scientist Dr Audrey Morley, from the School of Geography and Archaeology at NUI Galway, says: “One of the key challenges in climate change science is assessing the magnitude of future climate change, due to our short observational records which are limited to the past 150 years.
“Our research is unique, as we are not only observing modern essential climate variables, but we will also look into the past to assess how essential climate variables have evolved since before pre-industrial conditions.
“This long-term perspective is crucial and will help us to better understand our environment and the environmental consequences of human activities.”
Dr Morley notes that the Arctic is an especially sensitive and vulnerable environment with regards to contemporary climate change.
“The North Atlantic and Nordic Seas are a key region for the formation of North Atlantic deepwater and the uptake of atmospheric carbon dioxide. Whether or not this region will remain a carbon sink during rapidly warming climates is a question that remains to be answered,” she says.
As part of this research survey, the RV Celtic Explorer travelled to 79 degrees north in the Greenland Sea, which is the highest latitude reached by the marine research vessel.
‘The RV Celtic Explorer is crucial to facilitate this type of international research’
In order to operate in the Arctic region, the RV Celtic Explorer was required to obtain a Polar Code Certification — becoming the first Irish vessel to achieve this status, which greatly increases its ocean research capabilities.
“The RV Celtic Explorer is crucial to facilitate this type of international research,” says Marine Institute chief executive Dr Paul Connolly.
“This research in the Arctic region will deepen our knowledge of the region and will improve models that can forecast changes to our oceans and climate. This will inform effective policy and management decisions to meet the challenges posed by climate change.”
Connect With The Ocean Wilderness Via Art Project ‘Aerial/Sparks’ On Inis Oírr & Online
An art project involving multiple collaborators and many years in the making will soon invite the public to connect, both in person and online, with one of the last unknown spaces on earth — the ocean wilderness.
Aerial/Sparks was created by artist Louise Manifold as part of Galway’s European Capital of Culture programme for 2020, as previously reported on Afloat.ie.
Manifold brought together seven artists, writers and composers from across Europe who produced a series of standalone artworks for exhibition and radio broadcast, inspired by their experiences on research expeditions aoard the Marine Institute’s RV Celtic Explorer.
Inis Oírr, the smallest of the Aran Islands and with a deep-rooted maritime culture, is the setting for the Aerial/Sparks Art Trail from 11-27 September.
At just 3km long by 3km wide, the island can easily be traversed by foot to discover sound works housed in a lighthouse, the local church, an old handball alley and Áras Éanna, Europe’s most westerly arts centre.
Louise Manifold created Aerial/Sparks to explore the potential of radio communication to reimagine our relationship with the ocean
‘Garden Galway’ — a virtual programme of events for Ars Electronica 2020, the world-renowned festival for art, technology and society — will accompany the main exhibition from 9-13 September, and will include a series of conversations between artists and marine science experts.
Manifold created Aerial/Sparks to explore the potential of radio communication to reimagine our relationship with the ocean.
And each artist’s experience of ocean and water masses around Ireland and Europe has informed the production of individual works for audio and radio listening.
Highlights include author Kevin Barry’s ‘Island Time’, a monologue in nine chapters for a lovelorn lighthouse keeper as he dreams of distant lands, sited at Inis Oírr Lighthouse.
German composer David Stalling’s ‘Palace of Ships’ was created in collaboration with seismologist Sergei Lebedev, while visual artist Carol Anne Connolly’s acoustic portrayals of the ocean were inspired by the use of sound waves in acoustic mapping to create visuals of the sea bed.
Meanwhile, UK radio artist Magz Hall’s ‘Waves of Resistance’ is a broadcast created in the spirit of transnationalism, relaying a message of peace, hope and unity across all borders.
Manifold says Inis Oírr is the ideal home for these sound works.
“I wanted to find a place more than a space for this presentation, a place rich with silence, where organic and human sound floats and carries through the wind,” she explains. “I wanted each work to be experienced in a way that would connect with and charge our experience of place.”
Aerial/Sparks is the result of a long-term collaboration with the Marine Institute. Since 2017, artists from Ireland, Germany, England and Slovenia have taken part in seven ocean surveys and a passage from Galway to Hamburg on the RV Celtic Explorer, which the institute says is one of the few marine research vessels with sonic capabilities.
‘An innovative opportunity for artists and marine scientists to connect and engage with the wider community’
These expeditions have opened up "unique opportunities to foster connections between art and science", the Marine Institute says, as artists work side-by-side with scientists monitoring our marine biodiversity and human impact on the ocean environment.
“The collaboration between the Marine Institute and Aerial/Sparks has created an innovative opportunity for artists and marine scientists to connect and engage with the wider community through mediums such as art and music,” says Marine Institute chief executive Dr Paul Connolly.
“Using the concept of sound and the sea is a unique way of showing how both the arts and sciences can come together to highlight the value, opportunities and societal benefits of our ocean.”
Marilyn Gaughan Reddan, head of programme at Galway European Capital of Culture 2020, added: "Aerial/Sparks is a notable example of what a European Capital of Culture can bolster — new ways of thinking, new ways of working, new conversations and new partnerships.”
The Inis Oírr exhibition will be open from 11-27 September, Wednesday to Sunday between 11am and 5pm. For more information visit aerialsparks.org
Surface ocean carbon dioxide observations collected by the Marine Institute’s RV Celtic Explorer have been published in the 2020 version of the Surface Ocean Carbon Atlas (SOCAT).
These data provide scientists, climate researchers and international policy makers with essential information on ocean carbon dioxide measurements.
About 36 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide are added to the atmosphere each year as a result of human activities. The ocean absorbs about one-quarter of these emissions, which helps to slow down climate change by removing CO2 from the atmosphere.
However, absorbing additional CO2 increases the acidity of seawater. This process is known as ocean acidification, and it could have dramatic consequences for marine life.
The impacts of ocean acidification would extend up the food chain, threatening food security for millions of people
If sea water is too acidic, it can make it difficult for marine organisms such as coral, oysters and mussels to form shells and skeletons.
Ocean acidification may impact some plankton species, which form the base of marine food webs and would impact larger animals like fish and whales.
The impacts of ocean acidification would extend up the food chain, affecting fisheries and aquaculture, threatening food security for millions of people, as well as the tourism industry.
Ocean acidification is a global problem. The European Union has committed to cut its greenhouse gas emissions by at least 40% below 1990 levels by 2030 and aims to be climate-neutral — an economy with net-zero greenhouse gas emissions — by 2050.
To understand the Earth’s changing climate, it is essential to collect high-quality data on surface ocean CO2 levels.
Since 2017, the Marine institute has been measuring dissolved carbon dioxide (pCO2) in Irish and Atlantic surface waters using a General Oceanics pCO2 system on board the RV Celtic Explorer. This system enables near-continuous and high-accuracy carbon dioxide measurements in surface water and the atmosphere when the vessel is at sea.
The close collaboration between the Marine Institute and P&O Maritime Services, with support from GEOMAR in Germany, has resulted in the successful collection of this data.
SOCAT has become a milestone in research co-ordination, data access, climate research and in informing policy
The high-quality measurements of CO2 collected by the Marine Institute are now included in the 2020 version of the Surface Ocean Carbon Atlas (SOCAT) and fill “a notable data gap”, according to the Irish State agency for marine research.
The Marine Institute submitted data from nine surveys in 2017 and a further 15 surveys in 2018 to SOCAT, whose data set os used globally by climate researchers and contribute to the work of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
SOCAT has become a milestone in research co-ordination, data access, climate research and in informing policy, the Marine Institute says.
And this work further contributes to collaborative research on ocean carbon and acidification undertaken over the last decade by the institute and NUI Galway.
Margot Cronin, chemist at the Marine Institute, said: “Measuring carbon dioxide in Irish and Atlantic waters provides essential data that increases the understanding of our oceans and climate.
“The Marine Institute is contributing to global science, providing advanced scientific knowledge which will help inform policy and our response to a changing ocean.”
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, the Marine Institute’s latest Oceans of Learning series focuses on our changing ocean climate with videos, interactive activities and downloadable resources.
Irish Anglerfish & Megrim Survey 2020 Set To Begin Next Weekend
The first and second leg of 2020’s Irish Anglerfish and Megrim Survey will be carried out from next weekend off the West, South West and South Coasts of Ireland by the Marine Institute, in fulfilment of Ireland’s Common Fisheries Policy obligations.
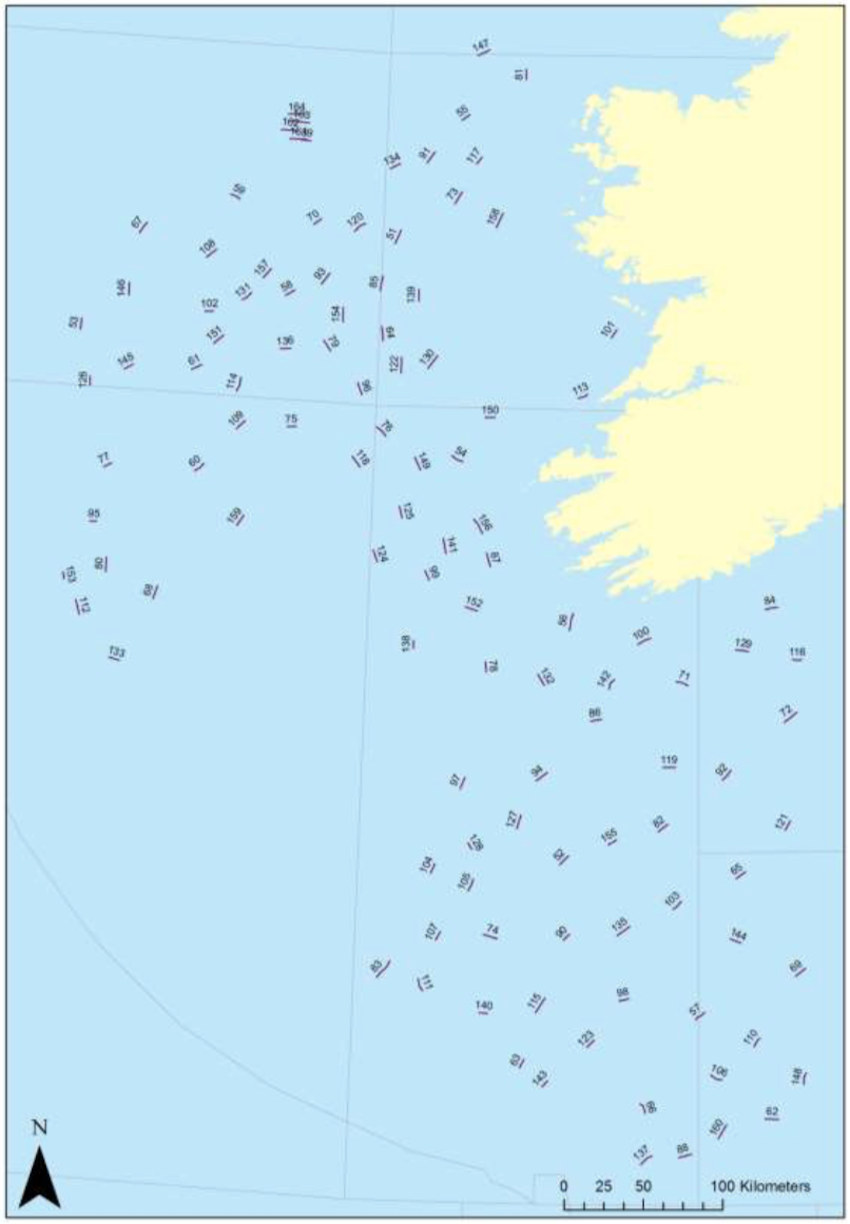
As with previous years, IAMS 2020 — which will run from Sunday 23 February to Wednesday 18 March — is a demersal trawl survey consisting of approximately 110 otter trawls (60 minutes) in ICES areas 7b, 7c, 7g, 7h, 7j and 7k.
The survey will be conducted by the RV Celtic Explorer (Callsign: EIGB) which will be towing a Jackson demersal trawl during fishing operations and will display appropriate lights and signals.
Commercial fishing and other marine operators are requested to keep a three-nautical-mile radius area around the tow points (indicated below) clear of any gear or apparatus during the survey period outlined above.
Further details of the survey, including co-ordinates of the survey stations, are included in Marine Notice No 07 of 2020, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
Open Call For 22 Marine Research Vessel Bursaries In 2020
The Marine Institute in collaboration with the Strategic Marine Alliance for Research and Training (SMART) is offering 22 bursaries on dedicated FEAS surveys throughout 2020 on the RV Celtic Explorer and RV Celtic Voyager.
Bursaries include groundfish, acoustic and underwater TV surveys (UWTV) on 13 survey legs between February and December of this year on the shelf waters of the Irish EEZ.
Successful applicants will receive a Student at Sea Bursary at a fixed rate of €95 per survey night.
Participants will receive hands-on training in data collection and sampling techniques, be fully integrated into the survey work programme and make an important contribution to achieving the survey goals for marine science.
In so doing they will gain valuable sea going experience and assist the Marine Institute in building the necessary capacity for offshore research and monitoring.
Applicants should be marine-oriented graduates, postgraduates, researchers or practitioners in marine-oriented enterprises. They must hold current ENG11 medical and Personal Survival Techniques (PST STCW95) certificates, and should have some prior sea-going experience.
Further information on the available bursaries can be found on the SMART website, which also has details of the online application process.
New Online Resources Bring ‘Ireland’s Deep Atlantic’ Into The Classroom
TV documentary Ireland’s Deep Atlantic will feature in new online classroom resources for Junior Cert students, it has been announced.
Ireland’s Deep Atlantic — produced by Sea Fever Productions and supported by the Marine Institute, BAI and the Environmental Protection Agency — sees filmmaker Ken O'Sullivan embark on a series of voyages in the North Atlantic in search of blue whales, sharks and deep-water coral reefs.
O’Sullivan filmed part of the series on board the Marine Institute’s research vessel the RV Celtic Explorer and documented coral reefs at a depth of 3,000 metres using the ROV Holland 1.
The series joins two other Irish-produced and publicly funded TV programmes used to create the new online classroom resources.
Business Studies students will use the series, including video clips of the RV Celtic Explorer and scientists, to learn about consumer behaviour and sustainable development, and the impact of economic growth on society and the environment.
Geography students, meanwhile, will learn about the ‘Real Map of Ireland’ and the importance of Ireland's ocean territory. The students will also learn about the exploitation of water, fish stocks, forestry, and soil and the relationships between the physical world, tourism and transport.
Ken O’Sullivan welcomed the new resources, saying: “It’s just wonderful now to realise that every teenager in Ireland will see our beautiful, fertile oceans and learn not just about the rich life within them, but the impact of human behaviour on our oceans with things like consumer spending habits, marine plastics and also the value of eco-tourism to coastal communities.
“Ireland’s Deep Atlantic is the first documentary to be used in this way and the platform has now been built for RTÉ to host many more publicly funded documentaries in this way for the secondary school education curriculum.”
Teachers and students can access the educational material and the programme clips referenced from the RTÉ Learn website.
Annual Irish Groundfish Survey Commences End Of This Month
The annual Irish Groundfish Survey (IGFS 2019) will take place off the North, West and South Coasts for six weeks from 31 October.
Carried out by the Marine Institute, the IGFS is a demersal trawl survey consisting of around 170 fishing hauls, each of of 30 minutes’ duration, in ICES areas VIa, VIIb, VIIg and VIIj.
As part of the requirements for the 2019 survey, fishing will take place within a 2-nautical-mile radius of indicated positions.
The survey will be conducted by the RV Celtic Explorer (callsign EIGB) which will display appropriate lights and signals.
The vessel will be towing a high headline GOV 36/47 demersal trawl during fishing operations.
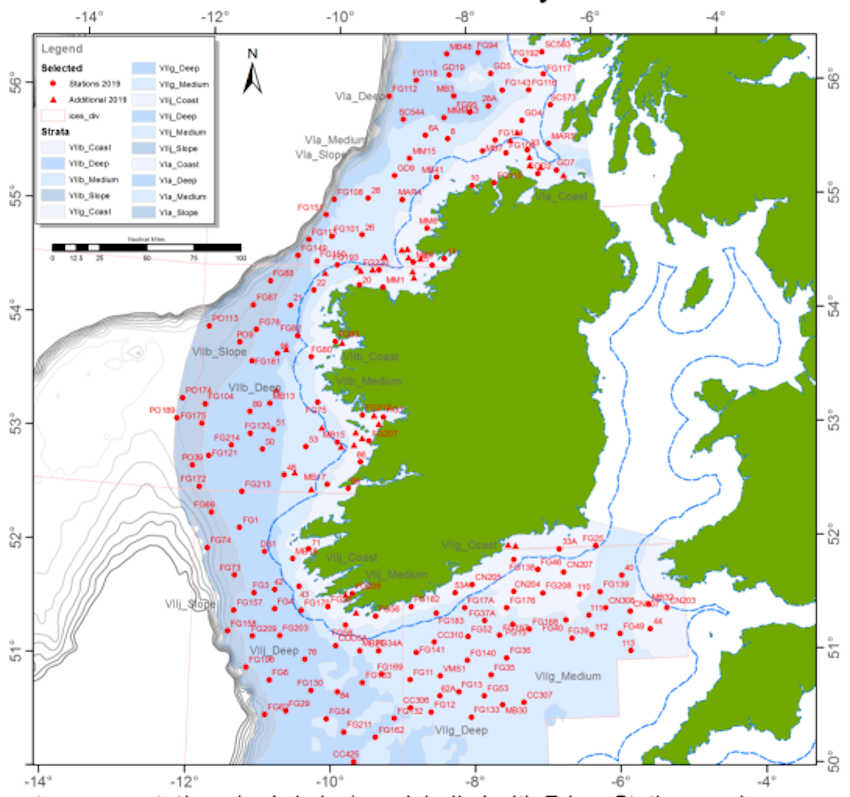
Co-ordinates and approximate locations of these hauls are included in Marine Notice No 47 of 2019, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
The Marine Institute requests that commercial fishing and other marine operators keep a 2nm area around the tow mid-points clear of any gear or apparatus during the survey period between Thursday 31 October and Friday 14 December.
This survey follows the annual Irish Anglerfish and Megrim Survey which was conducted off the West South West and South Coasts in March.
Marine scientists from University College Cork have discovered plastic at the bottom of a deep submarine canyon while investigating cold-water coral habitats.
UCC’s Marine Geology Research Group has been investigating cold-water coral habitats in the Porcupine Bank Canyon, some 320km due west of Dingle, on a research expedition led by UCC’s Dr Aaron Lim on board the Marine Institute’s RV Celtic Explorer.
The team had recovered eight novel monitoring stations, called ‘landers’, worth €450,000 and deployed between 700m and 2500m water depth by the Marine Institute’s Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) Holland 1 earlier this summer.
The monitoring stations record the speed, temperatures and direction of the currents around these habitats as well as trapping samples of the food, sediments and microplastic being deposited around the corals, to understand conditions and how the corals are coping with changing oceans.
The researchers found plastic in the bottom of one canyon at 2,125m water depth — as deep as ten Eiffel Towers stacked on top of one another.
The reach of human plastic waste is now confirmed as this deep, even 320km offshore.
“It’s always sad to see plastic rubbish in these otherwise pristine habitats. It’s quite incredible that our plastic waste can get this far out and so deep in the oceans,” said Professor Andy Wheeler of UCC, who has pioneered research on cold-water coral mounds offshore of Ireland over the past 20 years.
“I don’t think people think about this when that dump their rubbish. We’re also trying to see if microplastics are being fed to the corals from above. We’ve just got the samples; let’s hope we're wrong.”
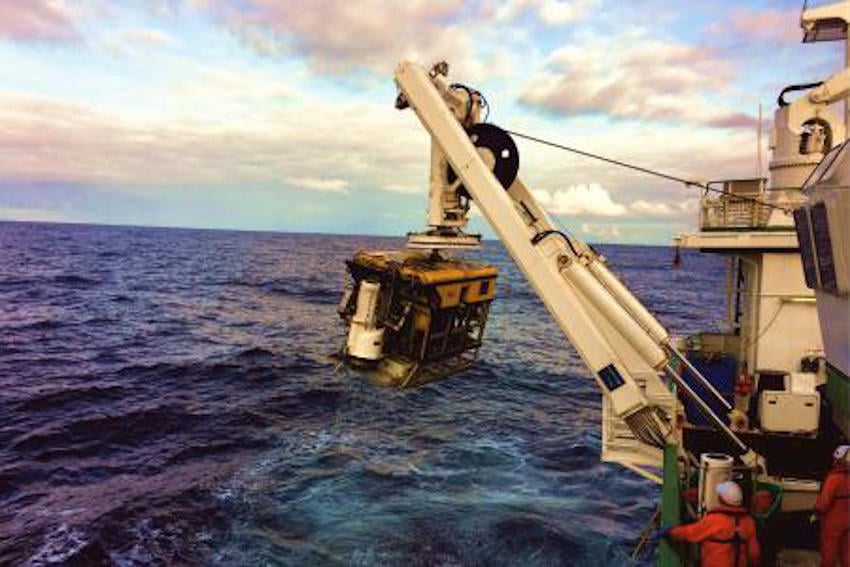 ROV Holland 1 recovering one of the monitoring stations | Photo: UCC
ROV Holland 1 recovering one of the monitoring stations | Photo: UCC
The Porcupine Bank Canyon is teeming with a whole range of cold-water coral habitats, just on Ireland’s doorstep, says Dr Lim.
“The environment is much more dynamic than we thought, with two of the monitoring stations knocked over by the currents; food supply for the coral is variable but the corals are doing okay.
“Some of these habitats have existed for millions of years and have grown so large they resemble hills made of coral, called coral mounds.
“This is the first time eight of these monitoring stations have been deployed and collected using the ROV Holland 1. It will provide scientists with an insight into the processes affecting these cold-water coral habitats, food sources and the impact of microplastics.”
Dr Lim said Ireland’s cold-water coral reefs are found in the cold, dark ocean at water depths of 600m to 1,000m along our continental margin.
“Not only is this expedition vital for understanding these habitats and our impact upon them, it also acts as a baseline to start monitoring how our deep-water habitats here are changing,” he added.
The team has a research agenda which will see them return to the canyon and other habitats alike for a number of years, to monitor the changes in the environment around these habitats. The monitoring stations will be brought back to UCC for detailed analyses.
This research survey is carried out with the support of the Marine Institute, funded under the Marine Research Programme 2014-2020 by the Government to support and promote the Atlantic Ocean Research Alliance, which facilitates common research and knowledge exchange for us to provide healthy, resilient oceans for our future generations.
The survey has also received funding from Science Foundation Ireland, Geological Survey Ireland and UCC.
New Shark Species Spotted In Irish Waters
A shark species previously unrecorded in Irish waters has been sighted in the Celtic Sea.
A smooth hammerhead shark was reported on the edge of the continental shelf, south-west of Ireland, during a recent fisheries survey on the Marine Institute’s RV Celtic Explorer.
The sighting was made by experienced marine mammal observer John Power and bird observer Paul Connaughton during the Marine Institute’s Western European Shelf Pelagic Acoustic Survey (WESPAS).
“While scanning the ocean surface, we sighted a dorsal fin unlike anything we had encountered before,” said Power.
“It was quite different to the fins seen on basking sharks and blue sharks. After consulting available ID keys, we agreed that the shark must be a smooth hammerhead.”
The large, tall and slender dorsal fin of the smooth hammerhead shark distinguishes it from other shark species. The smooth hammerhead also has a single-notch in the centre of its rounded head and is up to four metres in length.
The species gives birth to live young and the pups are usually found in the shallow sandy waters near Florida, the Caribbean and West Africa. However, the species has been recorded as far north as England and Wales.
The smooth hammerhead was sighted during the WESPAS survey, which surveys the waters from France to Scotland and the West of Ireland each year.
Marine scientists collect acoustic and biological data on herring, boarfish and horse mackerel, which is used to provide an independent measure of these fish stocks in Irish waters. Scientists also monitor plankton, sea birds and marine mammals during this survey.
This is an exciting encounter, especially since a rare deep-water shark nursery was discovered by Irish scientists last year
Dr Paul Connolly, director of fisheries and ecosystems services at the Marine Institute, said: “Our Irish waters support a range of marine life and diverse ecosystems, including 35 known species of sharks.
“This is an exciting encounter, especially since a rare deep-water shark nursery, 200 miles west of Ireland, was discovered by Irish scientists last year using the Marine Institute's Remotely Operated Vehicle [ROV Holland 1].”
He added: “This sighting of a new shark species shows the importance of our fishery surveys to monitor our marine environment, and to observe changes in our oceans and marine ecosystems.
“Observing and understanding a changing ocean, is essential for protecting and managing our marine ecosystems for the future.”
The hammerhead shark poses little risk to humans, and there have been no known fatalities from hammerhead sharks anywhere in the world to date.
The species is listed as Vulnerable on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, and is being increasingly targeted for the shark fin trade as its large fins are highly valued.
Thirty-five species of sharks have been recorded in Irish waters, including the blue shark, porbeagle shark, lesser spotted dogfish and the second-largest shark in the world, the basking shark — a regular visitor inshore during the summer months.






































































