Displaying items by tag: Festival des Bateaux
French OPV ‘Guard-ship’ to Follow Figaro Fleet From Dun Laoghaire
The 447 tonnes OPV provides communication liaison and assistance should the forty six sailors require during the arduous race including SAR. As such the vessel can deploy a rapid response high speed RIB-craft from an internal dock-well located at the stern.
Otherwise the RIB is used to board fishing vessels as part of fishery monitoring duties and patrolling France's Exclusive Economic Zone out to 200 nautical miles (370 km). She is a Flamant class OPV and was built in 1997 by the Cherbourg based shipyard Constructions Mécaniques de Normandie. The 54m/177-ft craft is equipped with two 12.7mm machine guns.
As Dun Laoghaire is the only international port of call during the four-leg stages of the 1,695 nautical miles (3,390kms) the hosting of the Irish harbour is a welcomed boost to the sailing community and the local economy. Leading off the Carlisle Pier are pontoons where the one-design boats are moored and opposite is the East Pier jetty berth where the PSP Cormoran is docked.
Also at the East Pier is a festival market which is part of the Festival des Bateaux. The three-day festival ends tomorrow and was organised by the race-hosts the National Yacht Club, the Dun Laoghaire Harbour Company and Dun Laoghaire Rathdown County Council. For further festival details click HERE.
The presence of a foreign naval visitor to the harbour was more commonplace particularly during festivals held in the 1980's. In addition to the French, navies from Belgium, The Netherlands were regular festival participants.
- National Yacht Club
- Solitaire du Figaro
- Dun Laoghaire Harbour Company
- Dun Laoghaire Rathdown County Council
- Dun Laoghaire Harbour
- French Navy
- Festival des Bateaux
- Dun Laoghaire Harbour News
- Naval Visits
- PSP Cormoran
- Dun Laoghaire East Pier
- Dun Laoghaire pierheads
- Guardship
- Dun LaoghaireSables d'Lonne
- Vedee
- Dun Laoghaire Festivals
French Naval Vessel Escorts 'Figaro' Fleet to Dun Laoghaire
To celebrate the stopover of the four-stage 1,695 nautical mile (3,390 km) race, Dun Laoghaire Rathdown County Council, Dun Laoghaire Harbour Company and the National Yacht Club have joined forces to create the Festival des Bateaux (12-14 Aug).
A festival highlight will be a fireworks display which be held on Friday night at 10pm on the East Pier. In addition during the three-day festival programme includes live bands, street entertainment and a market on the Carlisle Pier. For more details and times of the free event go to www.dlrevents.ie
Visitors to the East Pier can take a closer view of the PSP Cormoran from the quayside where the 23 knot offshore patrol vessel (OPV) will be berthed. The Flamant class (OPV) entered service in 1997 after completion by Constructions Mécaniques de Normandie, Cherbourg, where the 477 tonnes vessel is based.
The 54m/177-ft vessel has two 12.7mm machine guns and is used for fishery monitoring, SAR and patrolling France's Exclusive Economic Zone out to 200 nautical miles / 370 km. In addition she is equipped with a high speed RIB-craft that can be deployed from an internal dock-well at the stern.
Dublin Bay it set to burst alive with 'joie de vivre' during the only foreign stopover in the world-famous Solitaire du Figaro yacht race.
Dun Laoghaire will be the only international stop in the race, considered the unofficial world offshore solo championship, between 11 and 14 August.
To celebrate the visit of the iconic 3,390km race, Dun Laoghaire Rathdown County Council (dlrcoco), the Dun Laoghaire Harbour Company and the National Yacht Club have joined forces to create the Festival des Bateaux.
The harbour will be a magnificent tapestry of colour as the boats arrive for this international event. Dun Laoghaire will be resplendent with fireworks, music and the sights, sounds, foods and ‘joie de vivre’ of France.
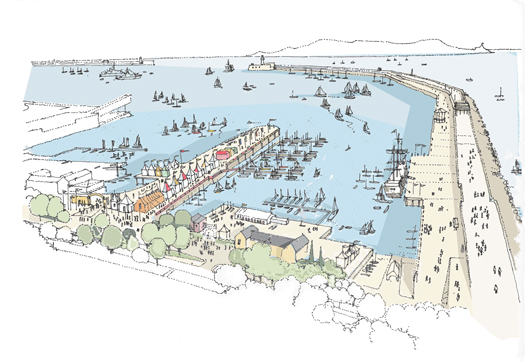
How Dun Laoghaire will look in August
Fireworks will light up the sky at 10pm on Friday 12 August. There will also be a festival village with public access to visiting boats, a colourful and authentic French market and exhibition, a festival stage at Harbour Plaza and activities throughout Dun Laoghaire, not to mention a spectacular farewell as the boats depart early on Sunday 14 August.
Meanwhile, plans to berth the 45 or so competitors expected are well underway, according to the National Yacht Club.
Funding was secured between dlrcoco and Fáilte Ireland, and the tender for the supply and delivery of 18x11.5m pontoons and associated service bollards was won by McNiven Marine, Irish agents for Ronautica Marine.
The gangway contract was secured by Tynes Gangway, and the last contract for the installation and de-commissioning of the infrastructure is currently underway.


























































