Displaying items by tag: Raging Bull
#SAILING ON SATURDAY – The Volvo Ocean Racers were at last feeling the benefit of the northeast trade winds on Thursday on the final 1600 miles to Miami from Brazil as the three leaders recorded speeds above 20 knots, but as they were so close together when reaching the breeze, nobody had got significantly ahead. American Ken Read's Puma was 5 miles ahead of NZ's Chris Nicholson's Camper, with overall leader Telefonica (Iker Martinez, Spain) 18 miles astern again, but with breezy offwind sailing in prospect and three boat neck and neck for the remainder of Leg 6, gaps like that can disappear in hours.
Puma has led narrowly all the way from Itajai, but only by dint of finding some new and often untried sail combination or trim. The new Volvo rule that they couldn't do any pre-race training matched with another boat meant that these have been the first prolonged and intensive boat-for-boat sessions they've experienced. They're expected in Miami tomorrow.
The newly-launched defending 2011 Irish Sea Champion Raging Bull, Matt Davis of Skerries Sigma 400 Raging Bull, will miss the early races of the ISORA programme as she broke her moorings off Skerries in the recent severe northeasterly gales. Sounds unfortunate, yett the Bull was lucky. Other Skerries boats were smashed to smithereens. But the Davis winner came in on the only patch of sand in an otherwise totally rocky bit of foreshore, and can be repaired. Some day, some time, we'll see a proper harbour at Skerries.
W M Nixon's sailing column is in the Irish Independent on Saturdays
See also Round the World Cruiser Stephen Hyde is April's Sailor of the Month
Onboard Raging Bull, Photos and Vid
Raging Bull crew man (and photographer) Brian Carlin has added onboard images from last weekend's Dun Laoghaire to Dingle race. Photos from the Sigma 400, the 2010 ISORA champion, are on the Afloat gallery here.
Onboard vid below too:
Poll Shows Raging Bull as Favourite for ICRA's Boat of the Year
With just 24 hours to go to the announcement of sailing's boat of the year award at tomorrow's Cork harbour ICRA conference the consistent poll topper from Afloat's online survey shows ISORA offshore champion Raging Bull as a clear favourite with 1175 votes. Second is Marinerscove on 873 and Errislannan third on 256 votes. Polling began just over a month ago and 2,600 votes have been cast. See the poll on the left hand column of the home page. There's still time to cast your vote to try and influence ICRA judges!
'Raging Bull' Overtakes 'Errislannan' in 'Boat of the Year' Poll
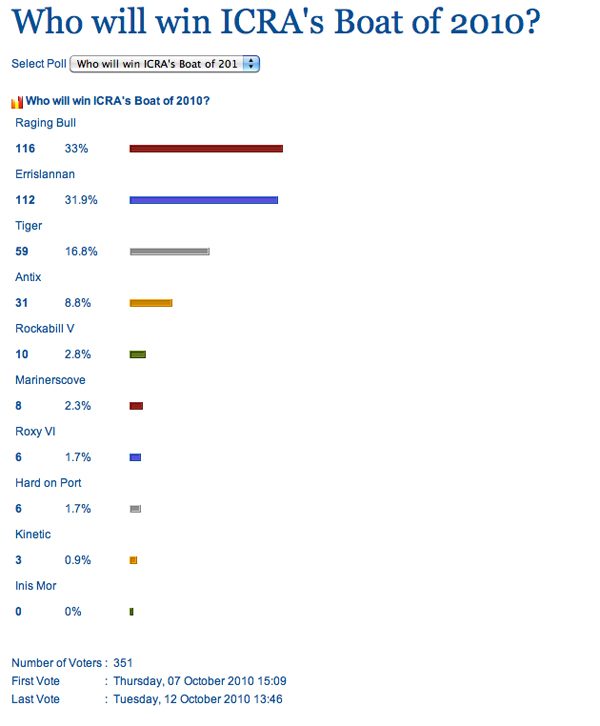
Raging Bull overtook Errislannan in Afloat readers opinion poll at lunch time on who will win the Irish Cruiser Racing Association (ICRA) Boat of the Year Award, in just over a month's time. Over 350 voters have given their opinion so far on the ten boat shortlist produced by Afloat. Errislannan proved an early poll topper since voting began last Thursday but as late as lunchtime today votes for Raging Bull saw a dramatic lift, bringing the Irish Sea offshore champion ahead of the Top Cork week Sigma 38. At 2pm a third of the votes cast were for Raging Bull. Errislannan was on 31%. Tiger had 16% and was in third place ahead of Antix with 31 votes. The poll is located on the left hand column of the home page. Cast your vote now!
Matt Davis and Raging Bull are 2010 ISORA Champions
Race 10 – Pwllheli to Howth – James Eadie Sailing Race 11th September 2010. From an entry list of 31 boats, 13 boats came to the line in Pwllheli for the last race in the 2010 ISORA Offshore series writes Peter Ryan. It was the James Eadie Trophy race. While in the past this race was one of the most popular, the bad weather on Thursday night and Friday put off many boats from delivering to Pwllheli. Those boats that braved the weather were reward with another great race. The race was started by Richard Tudor of Pwllheli sailing Club.
Due to the extraordinary strong spring tides it was decided to omit Bardsey Sound from the course and to take Bardsey Island to starboard. From there the course was direct to Howth – 75 miles. The start was at 09.00.
The forecast for the race was for south-west winds 10-15 knots to veer west then continue and increase north west. The forecast was correct at the start with a beat to Bardsey and the wind increasing to 20 knots. The strong tides produced some spectacular overfalls at Bardsey Island. First around Bardsey was "Tsunami", Vincent Farrell followed closely by "Raging Bull", Matt Davis and "Team Windmill", Andrew Sarratt. The overfalls appeared to take toll on the fleet with the remainder of the fleet having difficulty in rounding Bardsey. This caused a split in the fleet with the first three boats taking advantage of the last of the north going tide.
The course to Howth first seemed like a simple reach but this changed regularly and often with the wind oscillating and fluctuating continuously. The front-runners appeared to escape the holes that formed and held the bulk of the fleet back. What started as a reach ended in a beat into Howth into a 20 knot north westerly.
The first into Howth was "Tsunami", crossing the line at 23:19 followed closely by "Raging Bull" at 23:27 and "Team Windmill" at 23:54. "Lula Belle", Liam Coyne and "Dinah" Barry Hurley were separated by only 2 seconds on the line at 00:51. Four boats crossed the finish around 01:40 while the last boat "Sarnia", Michael Creeedon, crossed the line at 08.35. John Doran of Howth Yacht Club stood the long watch and recorded the boats finishing.
"Raging Bull" took 1st in Class 1 and Overall while "Tsunami" took 2nd in Class 1 and Overall and "Team Windmill" took 3rd Class 1 and Overall. "Just Enough" took 1st Class 2 with "Dinah" taking 2nd Class 2 and "Lula Belle" taking 3rd Class 2.
The Overall ISORA Champion of 2010 is Matt Davis and "Raging Bull" from Skerries Sailing Club. "Just Enough", Stephen Tudor from Pwllheli Sailing Club took 2nd place while "Tsunami", Vincent Farrell from the National Yacht Club took 3rd. The prize giving dinner will be in the National Yacht Club on the 6th November.
Big ISORA Fleet Gathers for M2 Buoy Race
- Dinah
- Dublin Bay
- Just Enough
- Lula Belle
- ISORA
- National YC
- irish sea
- English Mick
- Quite Correct
- Galileo
- African Challenge
- Lancastrian
- Tsunami
- Rebellion
- Orna
- Madam Wen
- Rollercoaster
- Raging Bull
- Miss Scarlett
- Team Windmill
- First of September
- Finnigans Wake
- Windshift
- Mojito
- Adelie
- Gwawr
- Yahtzee
- Legally Blonde
- Katanca
- Oystercatcher
- Obsession
- Sarnia






























































