Displaying items by tag: Andrew Algeo
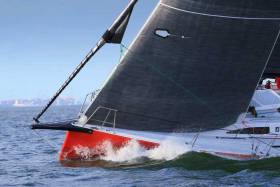
J109 National Champion Andrew Algeo of the Royal Irish Yacht Club will have his first regatta in his new J99, Juggerknot II (IRL3990) at Spi Ouest Regatta, this Friday, and it looks like the fleet of 436 boats gathering at La Trinite Sur Mer, will be the biggest in six years.
A very interesting class IRC B line up means the Irish boat will meet stiff competition from the get-go. Afloat reported on the arrival of the new J99 into Dublin in January.
A J99 sistership will be also competing in La Trinite. Called J Lance 14 she is sailed by French pro–sailor Didier Le Moal, so there's going to be plenty of pacing opportunities for the new Irish marque that has a summer of Irish-based regattas awaiting her.
Here is the full class line up at Spi-Ouest with boat types and TCCs also listed:
IRC B - Spi Ouest
| ID. | Bateau | Voile | Skipper | Club | Bateau | TCC | |
| 124 | AD HOC | FRA44058 | Jf. Cheriaux | C N LORIENT | JPK 10.10 | 1.0010 | |
| 211 | ANAVEL | FRA43914 | H. Cardon | Y C CARNAC | JPK 10.10 | 1.0050 | |
| 127 | APLYSIA 3 | 43918 | C. Faure | SUN FAST 3200 | 1.0000 | ||
| 146 | CAVOK | FRA53119 | P. Gach | Y C CROUESTY ARZON | POGO 30 | 1.0450 | |
| 149 | CLIFDEN | FRA44059 | F. Jooris | Y C TRINITE | SUN FAST 3200 | 0.9950 | |
| 199 | CRESCENDO | FRA39098 | P. Sauzieres | S N TRINITE S/MER | JPK 10.10 | 1.0000 | |
| 284 | DELNIC | FRA9210 | B. Rousselin | S N TRINITE S/MER | JPK 10.10 | 1.0040 | |
| 221 | EDM SERVICE | FRA39201 | B. Daniels | S R ROCHELAISES | SUN FAST 3200 | 0.9940 | |
| 355 | ENEDIS | FRA44737 | J. Rigalleau | SNSablais | SUN FAST 3200 | 1.0000 | |
| 332 | EXETERA | FRA21859 | A. Rougeulle | S N TRINITE S/MER | X 36S | 0.9990 | |
| 181 | FOGGY DEW | FRA37310 | N. Racine | S N P H | jpk 10.10 | 0.9990 | |
| 135 | HAKUNA MATATA | 35914 | Jf. Nouel | C N PORNIC | SUN FAST 3200 | 1.0000 | |
| 158 | HEY JUDE | FRA9624 | P. Girardin | S N TRINITE S/MER | J 120 | 1.0400 | |
| 192 | IOALLA | FRA1382 | G. Prietz/Y. Le Trequesser | S N TRINITE S/MER | X 382 | 1.0140 | |
| 394 | J LANCE 14 | FRA53145 | D. Le Moal | S R ROCHELAISES | J 99 | 2.0000 | |
| 171 | JACKPOT | 9679 | H. Mehu | S N TRINITE S/MER | J 109 | 1.0040 | |
| 136 | JIBOULIX | 25577 | Jb. Prot | S N TRINITE S/MER | X362S | 1.0060 | |
| 137 | JUGGERKNOT 2 | IRL3990 | A. Algeo | J 99 | 1.0170 | ||
| 410 | LEMANCELLO | FRA43904 | Fx. Mahon | C N FERRET | SUN FAST 3200 | 0.9930 | |
| 138 | LINGOBJECTS | FRA9804 | B. Le Marec | S R ROCHELAISES | OFCET 32 | 1.0120 | |
| 139 | MUSIX | FRA43893 | P. Baetz | S N TRINITE S/MER | J 122E | 1.0430 | |
| 183 | PEN KOENT | FRA53160 | E. Le Men | Y C VAL ANDRE | FIRST 40.7 | 1.0410 | |
| 141 | RACING BEE 2 | FRA43933 | Lm. Dussere | JPK 10.80 | 1.0420 | ||
| 314 | REALAX | FRA21706 | Jy. Le Goff | S N TRINITE S/MER | A 35 | 1.0210 | |
| 421 | TIGER 5 | 3303 | M.Menesguen | MMW33 | 1.0070 | ||
| 125 | TIP | FRA39430 | G. Pages | YC LA GRANDE MOTTE | SUN FAST 3600 | 1.0520 | |
| 151 | VALORIS&BENEFITS | FRA43673 | J. Bouic | S R ROCHELAISES | A 35 |
Didier's previous very successful boat was another J Lance, a J112e which won both the IRC Europeans and IRC Worlds last year.
Other interesting boats in the class will be a J112e, Musik, a very well sailed Beneteau 40.7 Pen Koent, a number of A35s, a number of JPK 10.10s, Jpk 10.80s and Jeanneau sunfast 3200s. These three last designs will perform well if the conditions turn out strong, but will not be great if conditions are light and the long range forecast looks light.
Algeo previewed his new J99 for Afloat in January here and he gave one of the reasons for downsizing to the newer but smaller J model as local crew availability.
On board for Algeo's maiden sail in France as part of the Irish crew is North Sails Ireland's, Nigel Young.
The J99 type has been sailed recently under IRC at the Warsash Spring series and so far the IRC optimised J109s are still holding sway. Unfortunately, there won’t be many tricked up J109s at Spi Ouest to see how they go. Unlike the Warsash J99, both J99s that will be sailing in La Trinite will be using Symmetric Configurations (with spinnaker poles) as against the sprit asymmetric configuration of the Warsash J99.
From a Dublin Bay and also a national perspective, it will be interesting to see how she goes.
Symmetric v Asymmetric Spinnakers
Another J109 in Ireland, the new Outrageous of Richard Colwell and John Murphy launches this week complete with a symmetric configuration, with the ability to change to asymmetric, if she wishes. Pat Kelly's J109 Celtic Cup champion Storm changed over to symmetric in 2017 too with well-documented success in the Scottish Series. The all-conquering J112e, J Lance, mentioned above, is also a symmetric setup.
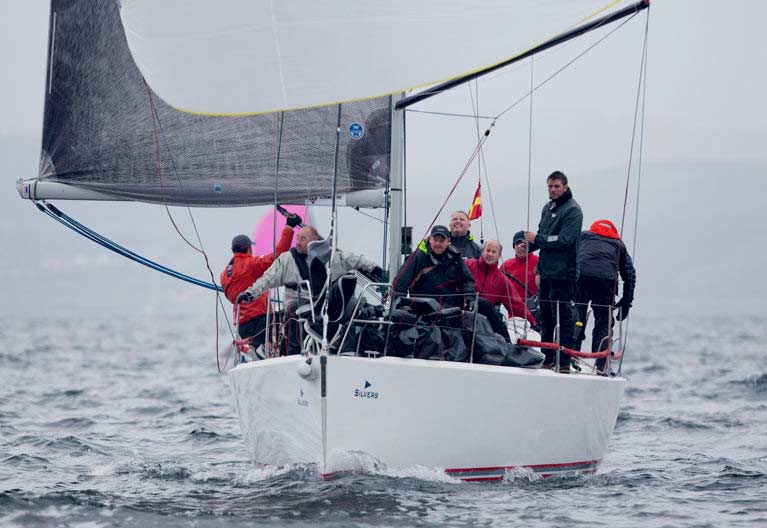 (Above) Howth J109 Storm sailing to success in the 2017 Scottish Series with an 'experimental' symmetric kite Photo: Mark Turner and (below) Storm using an asymmetric at last year's Irish Nationals on home waters Photo: Afloat.ie
(Above) Howth J109 Storm sailing to success in the 2017 Scottish Series with an 'experimental' symmetric kite Photo: Mark Turner and (below) Storm using an asymmetric at last year's Irish Nationals on home waters Photo: Afloat.ie

Generally, it is thought that windward leeward events, especially in medium to strong winds suit boats with poles, whereas offshore likely would suit sprit boats.
Say Hello to J/99 'Juggerknot 2' - The Boat to Suit the Crew
Royal Irish Yacht Club skipper Andrew Algeo on why he has sold his national championship-winning J109 Juggerknot and replaced it with a brand new J99, Juggerknot 2.
Juggerknot has been the means to get a bunch of old friends out on the water together and it has worked a treat, most of the time.
Paul Nolan, Gary Haughton, Richard Knatchbull, Ben Cooke and I have sailed with or against each other in one combo or another in boats as varied as RS400s, SB20s, J/24s, Flying Fifteens, 1720s, Lasers and Enterprises going back to the 80s and since. But the activity levels had fallen somewhat in recent years and it was time to kick start our sailing - hence the J/109 in 2016.
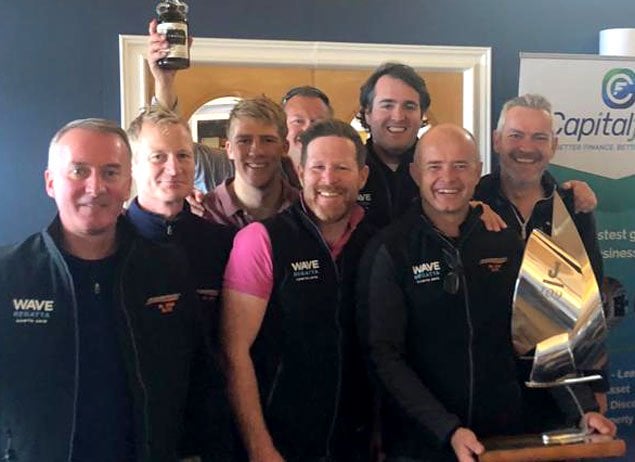 Juggerknot champions - the winning J109 crew at the 2018 national championship prizegiving at Howth were Richard Knatchbull, Shane Conneely, Gary Haughton, Paul Nolan, Ben Cooke, Joe Hughes, Rob O’Leary and Andrew Algeo (with trophy)
Juggerknot champions - the winning J109 crew at the 2018 national championship prizegiving at Howth were Richard Knatchbull, Shane Conneely, Gary Haughton, Paul Nolan, Ben Cooke, Joe Hughes, Rob O’Leary and Andrew Algeo (with trophy)
Juggerknot got us competing again together on the race track, learning a new discipline of sailing, socialising in the RIYC bar and most enjoyably allowed us to rope many others in so that we’re a much a bigger bunch of friends now in team Juggerknot. Add to that that the J/109 is probably the most competitive boat under IRC in these parts, as well as having its own one design scene, and really what could be better?
"There was not enough of us to get the boat to the start at the weekends"
The only fly in the ointment, albeit a sizeable one, is that we haven’t been able to sail as often as we’d like to. We have found that while the spring and early summer is great, there was not enough of us available to get the boat to the start line from mid-July to the end of Sept at the weekends. That’s 10 or more weekends out of a short season.
Juggerknot 2 is launched
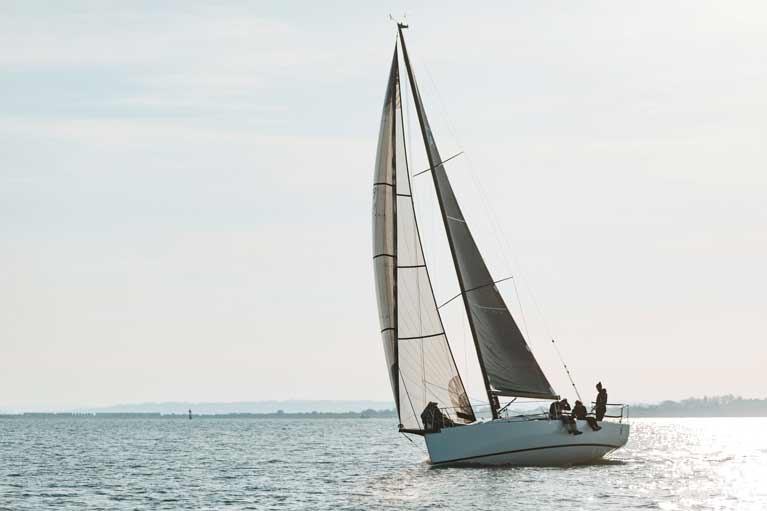

Juggerknot 2 will be a J/99 which will suit us better. With an optimum crew number of 7 or 8 we’ll still get the large team out for regattas and every other time we can. Yet the J/99 is a few feet shorter, has smaller sails and is a good deal lighter than the J/109 so we’ll be able to give racing a shot when only 3 or 4 of us are available because the degree of physicality necessary to sail her is less.
"Our first sail will be for Spi-Ouest, La Trinité Sur Mer at Easter"
So we hope to sail more often in 2019, build the team further and race again in IRC1 which we enjoy so much. Our first sail will be near the J-Composites factory for Spi-Ouest, La Trinité Sur Mer at Easter. In at the deep end for sure, but bucket list stuff too...
Sharkbait earns home win in SB3 Easterns
The Howth crew of Ben Duncan, Brian Moran and Rick Morris on ‘Sharkbait’ are this year’s SB3 Eastern Champions after the six-race series ended on home waters with the local boat tying on points with Cork visitor ‘Sibelius’ (Kieran Dorgan) but taking the title on countback, having two bullets to the rival’s one. Overall results table here.
Brian Carlin SB3 photos from the event on the Afloat Gallery
Consistency was the name of the game, with ‘Sharkbait’ never out of the top four and ‘Sibelius’ notching three third places, a second and a 5th. Both crews are heading to Torbay in mid-May for the SB3 Worlds so this was a useful work-out, especially in difficult conditions. The north-easterly winds were fresher but steadier than on the first day but the swell was significantly greater, making life tougher on crews and equipment.
That only five points after discards separated the top five boats overall speaks volumes for the intensity of the competition at the head of the 30-boat fleet. These five dominated proceedings to such an extent that the difference in points after discards between fifth and sixth overall was a massive 26 points.
After leading overnight by a slender margin, ‘Sharkbait’ got off to a dream start to the second day with a bullet ahead of’Flutter’ (Andrew Algeo) and Dorgan in the fourth race of the series. Fourth-placed Peter Kennedy of RNIYC in ‘Ridgefence.com’ was making amends for his OCS on the Saturday by following up that result with a win in the penultimate race, with ‘Flutter’ again second. Sean Craig’s ‘Yeti’ was third while Duncan and Dorgan filled 4th and 5th respectively.
Dorgan left his best to last, winning the final race from Kennedy, Craig and Duncan in that order, a result that set up the tie after discards. In the race for the rest of the fleet, three northern boats filled the sixth to eighth places overall while Shane Murphy’s ‘Dinghy Supplies’ in 9th was the next best placed Howth entry.
SB3 Eastern Championships – overall results
- Sharkbait (Duncan/Moran/Morris) HYC 12 points
- Sibelius (K.Dorgan) CSC 12 points
- Flutter (A.Algeo) RStGYC 14 points
- Ridgefence.com (P.Kennedy) RNIYC – 15 points
- Yeti (S.Craig) RStGYC) – 17 points