Displaying items by tag: IOM Steam Packet
New Ferry Terminal Deal for Isle fo Man Agreed for in Port of Liverpool
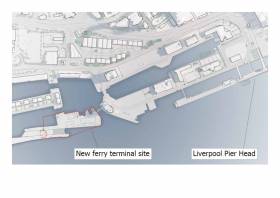
#FerryNews - A new ferry terminal for Isle of Man services, BBC News reports could cost up to £30m and open in Liverpool in 2021, the Manx government said.
It will be built half a mile (800m) from the current Pier Head facility at Princes Half-Tide Dock.
Subject to Tynwald approval, the Manx government will sign a long-term leasehold agreement with Peel Land and Property Limited for the site.
Liverpool Mayor Joe Anderson said: "It will cement our strong links with the Isle of Man. I'm delighted."
The existing Pier Head facility is set for a major redevelopment as a cruise liner berth as part of the £5bn Liverpool's Waterfront scheme.
More on the story click here.
Public Input Sought on Future of Manx Sea Services
#FerryNews - Views of the Manx public and businesses are being sought by the Department of Infrastructure, as it looks at potential changes to the Island's sea services.
A new document reports Manx Radio, to replace the existing 'User Agreement' is going to be drawn up, following the government's purchase of the Isle of Man Steam Packet earlier this year.
On the radio station, Infrastructure Minister Ray Harmer (click for audio) said similar gauging of people's opinions has been done before.
Isle of Man Steam Packet Will be Ready for Fuel Laws
#FerryNews - Isle of Man Steam Packet has confirmed it will be ready for new laws designed to clean up shipping.
Under new laws, writes IOMToday, fuel will have to be cleaner and more efficient under a global directive to reduce sulphur emissions.
A report on the new laws state: ’The current global limit for sulphur content of ships’ fuel oil is 3.50% m/m (mass by mass). The new global limit will be 0.50% m/m will apply on and after January 1, 2020.’
For more on the story click here.
Details of Isle of Man New Ferry Berth in Liverpool Docks
#FerryNews - Manx Radio reports that tenders are now in, to build the road that would take passengers to and from the new vessel berth in Liverpool's Princes Half Tide Dock.
An Infrastructure Department is considering specifying the use of liquified natural gas and/or low sulphur diesel, in any replacement Isle of Man Steam Packet vessels.
These details are given in a series of Tynwald written answers (see related coverage).
There is the indication in these answers of the Manx Government's arms length approach to running the ferry company which means there are some areas where the Infrastructure Department doesnt know specific details.
For example the detailed contractual agreement between the Steam Packet and the Mersey Docks and Harbour Company.
Click here for more on this ferry berth development.
Liverpool Link for Isle of Man Steam Packet Under Threat?
#FerryNews - There have been concerns raised that the new Liverpool landing stage for the Isle of Man ferry will not be ready in time.
As IOMToday reports passenger watchdog TravelWatch has released a statement in which it states its ’concern’ at the tight timescale available to ensure the new Princes Half-Tide Dock is operational when the current landing stage deal expires at the end of next year.
The watchdog’s concerns stem from a lack of information regarding contingencies for any delays to the planning application process and what could happen if there are objections to the plans, given the need for the new terminal to be completed by spring 2020.
For more on this ferry development, click here.
Manx Treasury Chief Completes Steam Packet Deal
#FerryNews- The Manx Treasury chief has put pen to paper to seal multi-million pound takeover.
IOM Today reports that the Government has completed a deal to purchase the Steam Packet Company.
Tynwald members overwhelmingly supported the £124m of what Chief Minister Howard Quayle described as a 'once-in-a-lifetime opportunity'.
Treasury Minister Alfred Cannan has now signed the formal agreement which will see control of the Island's sea services shifted to Government.
Mr Cannan says the move is aimed at providing long-term stability to the ownership of the Island's lifeline ferry operations.
#FerryNews - The Manx public should have the chance to share in the fortunes of the Isle of Man Steam Packet Company in the years to come.
That's the view of Ramsey Member of the House of Keys (MHK) Lawrie Hooper, following Tynwald's approval of government's proposal to purchase the ferry operator last Tuesday (15 May).
Mr Hooper speaking on Manx Radio said the public should be given the chance to invest in the company.
To listen to the MHK click here to the radio's audio link.
#FerryNews - Tynwald, the Manx Parliament made history as it voted to take the Isle of Man Steam Packet into public ownership.
According to IOM Today, following a three hour debate, Tynwald voted by 23 votes to one in the Keys and unanimously in LegCo to acquire the ferry company for £124.3m.
The only member to vote against was LibVan leader Kate Beecroft.
Under the deal, negotiated between Treasury and the Packet’s bank and hedge fund owners, government will acquire a 100% shareholding of parent company MIOM Ltd using £124.3m of cash reserves.
Some £76m will appear in the accounts as a loan.
Government will look at options to restructure that loan.
For further reading on the decision to acquire the ferry operator, click here.
#FerryNews - A state-owned Isle of Man Steam Packet would be better for passengers as well as the economy, the Manx Chief Minister believes.
Howard Quayle speaking on Manx Radio has advocated a government takeover of the company since he first stood for the House of Keys in 2011.
Tynwald will be asked on Tuesday to approve the use of reserves to purchase the Steam Packet at a cost of £124 million.
Mr Quayle says the deal will safeguard the Island's 'strategic sea services'.
To hear the Manx minister's comments on the topic, click here for the audio link.
Manx Steam-Packet Rival Plans Takeover Bid
#FerryNews - A shipping line that was set up by a businessman as a planned rival to the Isle of Man Steam Packet has poured scorn over the Manx government’s takeover plan.
As IOM Today reports, Kurt Buchholz founded the Ellan Vannin Line in 2013 in an attempt to launch a roll-on, roll-off daily cargo service between Douglas and Heysham.
But without government support, and no ship, it never got off the ground. He stood as a House of Keys candidate in Douglas Central in the 2016 general election.
Reacting to the announcement of the government's planned £124m deal to buy the Steam Packet, he said: ’The Steam Packet ships are close to scrap value with their age, about £15m.
For more on the story, click here.