Displaying items by tag: James Carroll
Ireland's James Carroll on 'Black Pearl' Leads on the Water in RORC Transatlantic IRC Zero
At 0800 UTC on the eighth day of the RORC Transatlantic Race, 17 boats are still racing in the Atlantic, with the first finishers in the monohull fleet expected on the 17th and 18th of January. The battle for the overall win under IRC and the RORC Transatlantic Race Trophy is beginning to sizzle. There is a clear leader on the water, vying for the IMA Transatlantic Trophy; Volvo 70 I Love Poland (POL), skippered by Grzegorz Baranowski.
IRC Super Zero
I Love Poland leads the big boat class on the water and corrected time, but the all-Polish team have sailed 400 miles from the rhumb line with their bow pointing at Guyana in South America. IMOCA Canada Ocean Racing (CAN) raced Two-Handed by Scott Shawyer and Alan Roberts is 144 miles behind I Love Poland. The Swan 115 Jasi (SWE), skippered by Toby Clark is to the north of the rhumb line to Grenada. Johannes Schwarz’s Volvo 70 Green Dragon (skippered by Galway's Cathal Mahon) has just over 1000 miles to finish the race.
IRC Zero
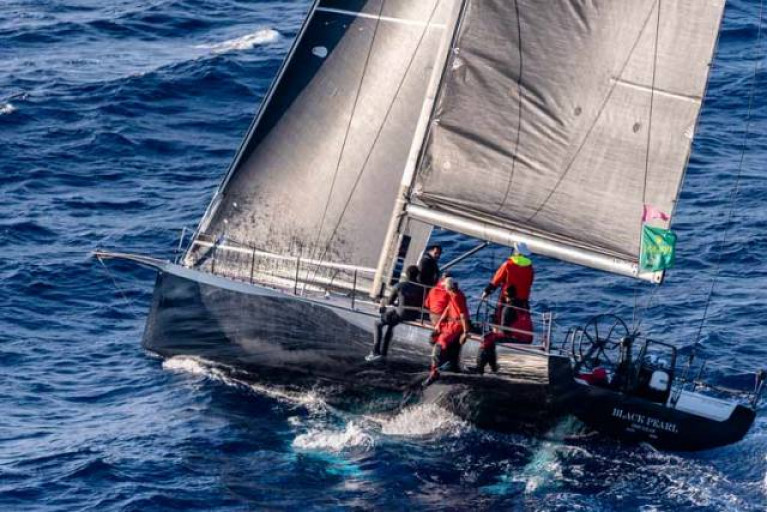
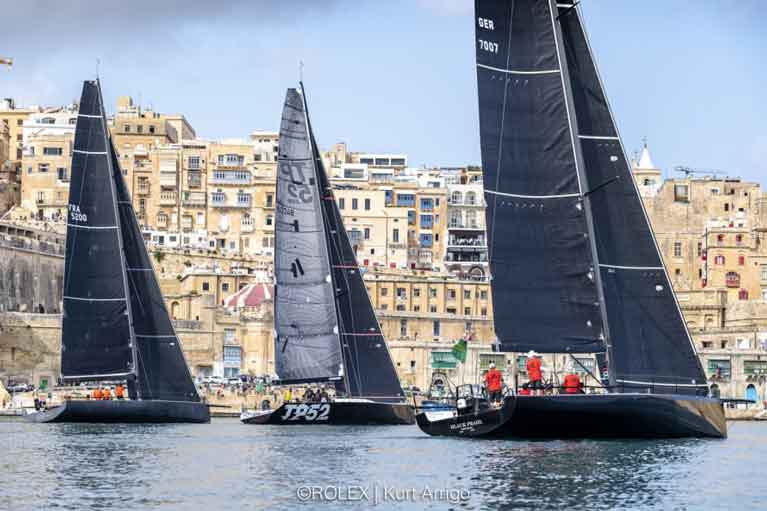
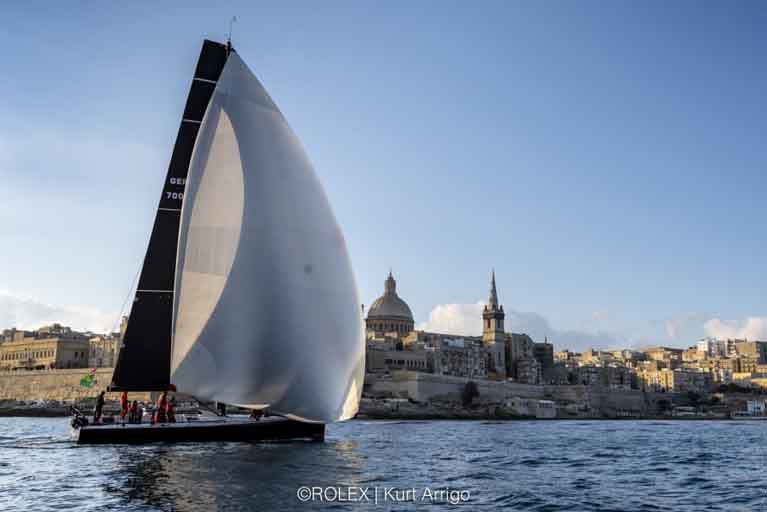
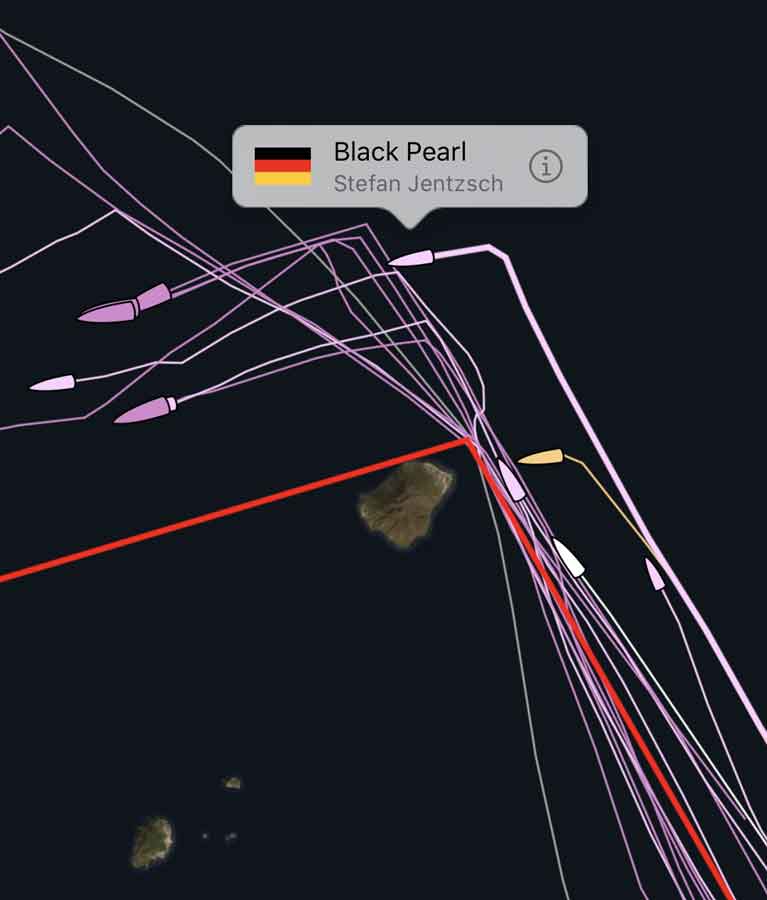
The top three teams for the overall win after IRC are all in IRC Zero. Eric de Turckheim’s NMYD Teasing Machine (FRA) is 845nm from the finish and leading after corrected time. Botin 56 Black Pearl (GER), sailed by Stefan Jentzsch leads on the water, 806nm from the finish. Black Pearl is way south and Teasing Machine are covering from astern. As IRC is a fixed time correction rule, Teasing Machine know that if they can keep up with Black Pearl overall victory is a strong possibility. However, 47 miles away on Teasing Machine’s starboard quarter is Henri de Bokay’s Elliott 52 Rafale (GER). Rafale is very much in the hunt for Class and Overall Honours with 892 miles to the finish.
The top three teams for the overall win after IRC are all in IRC Zero. Eric de Turckheim’s NMYD Teasing Machine (FRA) is 845nm from the finish and leading after corrected time. Botin 56 Black Pearl (GER), sailed by Stefan Jentzsch and with Ireland's James Carroll on board leads on the water, 806nm from the finish. Black Pearl is way south and Teasing Machine are covering from astern. As IRC is a fixed time correction rule, Teasing Machine know that if they can keep up with Black Pearl overall victory is a strong possibility. However, 47 miles away on Teasing Machine’s starboard quarter is Henri de Bokay’s Elliott 52 Rafale (GER). Rafale is very much in the hunt for Class and Overall Honours with 892 miles to the finish.
Black Pearl’s navigator, Marc Lagesse contacted the RORC Media Team as they approached the halfway mark. “Black Pearl has raced 1,540 miles in 100 hours - 15.4 knots average; that tells you it’s been a fast trip with the speedo frequently in the 20 knot+ range. We are expecting things to cool down in the coming days, but not by much. We are having a few technical gremlins; while not effecting our performance, they are certainly annoying. Life onboard otherwise is good. We are suitable impressed by the performance of the other boats in our class. Despite best efforts, we can’t get away from them - Nice work guys!!”
Recalling Dublin Sailor's Offshore Success in October's Middle Sea Race
Professional sailor James Carroll overcame the disappointment of a dismasting in 2018 to win class two of October's Middle Sea Offshore Race on Stefan Jentzsch's Black Pearl, a German Carkeek 47. Here the Dublin Pitman, Sail Trimmer and Driver recounts the race and reveals plans for a new and bigger Black Pearl for 2020.
With the addition of a brand new bulb and an owner and crew hungry for victory, Black Pearl occupied pole position as we reached the home stretch in the 2018 Middle Sea Race. Following a very windy downwind leg with the A4 spinnaker, there were the customary squalls, thunder and lightning to contend with, which we have come to expect with the Middle sea race. We rounded the island of Lampedusa and were leading the race overall on IRC. We came up to a reaching angle with the J3 on a reaching strut, genoa staysail and full main. It was 4 am and pitch dark with the wind blowing at 25-30kts. We were getting ready to reef when we got hit by a gust and then heard a huge crack from the mast. It had snapped in the middle and fell directly to leeward.
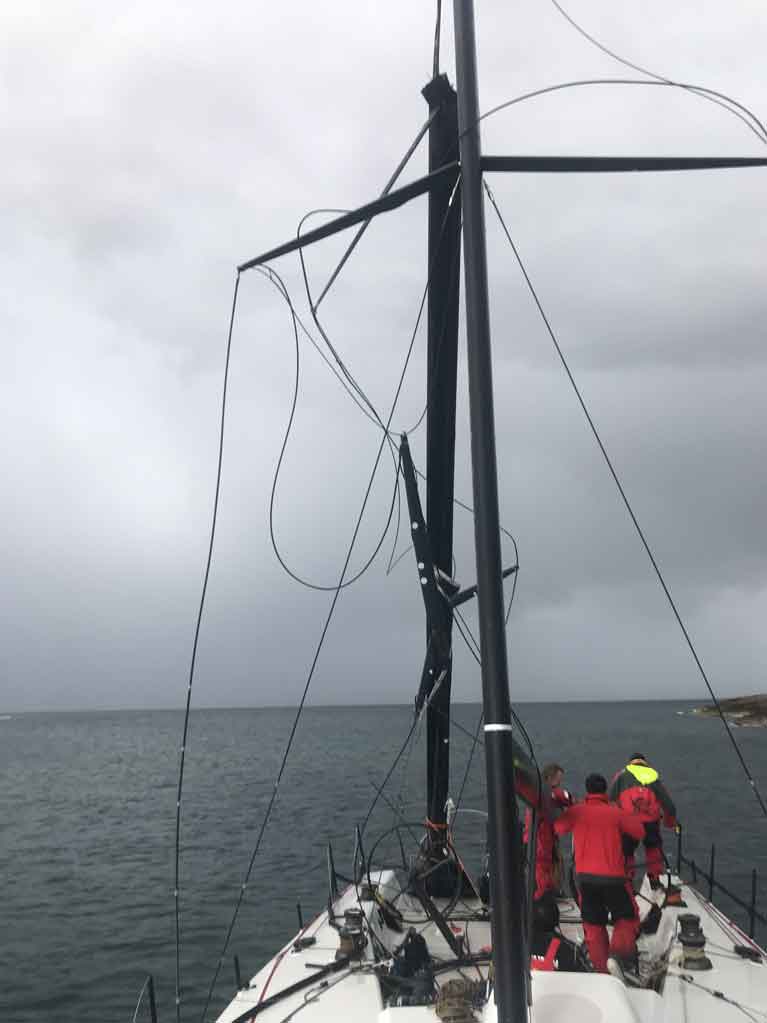 Dismasting and (below) jury rigged
Dismasting and (below) jury rigged

Thankfully nobody was injured, but we needed to get the situation safe and ensure the mast did not puncture a hole in the side of the boat. After over an hour of cutting and securing the broken pieces, we limped back to Lampedusa to effect repairs and come up with a plan. Due to bad weather conditions, it was three days before we could depart. Eventually, we motored back to Malta under jury rig. It was a devastating outcome for the owner and crew given that we were so close to winning.
We decided to ship the boat to Valencia to assess the damage, make repairs and commission a new mast. The new mast would be built by Hallspars Holland and was to be shorter. Jib area would stay the same. Spinnaker area reduced slightly and the mainsail area would remain the same, with a shorter P. The goal was to improve upwind performance and reduce slightly the downwind performance. With the lower sail plan and bigger bulb, it resulted in a lower CG and improved upwind performance particularly in waves and we were also faster reaching. Most importantly our rating also fell 3 points.
Unfinished business
Our first outing with the new mast was the Giraglia Race in June, which ended in disappointment as we were forced to retire. All the pressure was now on the Middle Sea Race where we felt we had some unfinished business.
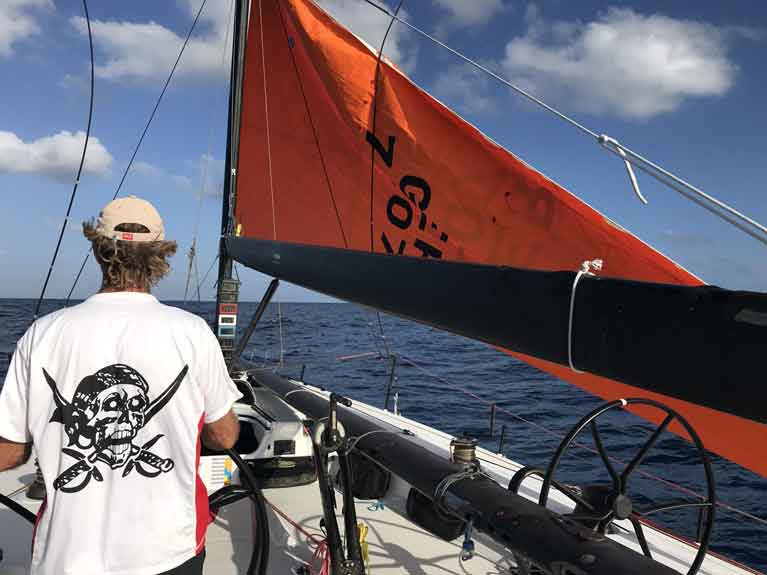
We had a longer than usual pre-race prep of 4 days in Malta and felt in good shape for the race. After a 30-minute start delay due to wind, we started in 5-7 knots Southeasterly. We found ourselves ghosting over the start line at the pin end and had a perfect start. A beat out of Grand Harbour to the offset mark. We then rounded to an A1 spinnaker and a run down the coast. Passing slower boats was very tricky and there were big gains and losses. After clearing the spectator mark we were fetching at a TWA of 50-60* towards Sicily’s southeastern tip. We set-up to be the most easterly boat in the fleet.
 Light airs at the start of the '19 race
Light airs at the start of the '19 race
Our pre-race weather advice showed that the wind would go very light approaching the Sicilian coast and recommended to be east of the fleet. Unfortunately, that proved incorrect and we woke on the morning of Day 2 with a 18-mile deficit to the leading 50 footer. Instead of dwelling on the loss we focused on our approach to Messina and the strategy for getting through. By midday, we were VMG running in 6-10 knots and worked to the mainland shore. Committing to mainland shore reduced the time spent in foul current and there was also better pressure on the shore.

Once clearing Messina, we realised that we had closed the gap on the group of 50fters and could see their lights as the sunset. Two gybes early to stay clear of an area of light winds and we laid through to Stromboli. A favourable left shirt and we set-up for a wide approach of the island, as the wind shadow had caught us out four years earlier in the same race. VMG running in light winds, we gybed five miles stood off Stromboli. We were treated to a few hours of fireworks from the erupting volcano and were now right in touch with our competition and the wind was getting even lighter.
On the morning of Day 3, we were set-up for a long day of VMG downwind chess, trying to stay out of areas of light winds while keeping the boat moving. We were changing between the wind seeker (our Spinstay tacked off the end of the bowsprit on the fractional halyard) and our A1 spinnaker. When the A1 would fly, then that was the sail and when it started to collapse, we would change bareheaded to the Windseeker. With the Windseeker we could keep the boat moving albeit at 1-2 knots of boat-speed, just about keeping steerage. There was a leftover westerly swell and that made it very hard to make progress west on a port gybe, so we needed 4 knots of wind speed or more to make progress on port gybe. This light airs requires maximum concentration from all the on-watch crew and lots of patience. We remained focused and input on strategy from all crew was considered.
During the morning we had passed a number of our 50ft competitors and the front of the fleet compressed. We were now sailing with the Volvo70s and 80 footers. Rambler was the only boat that had got through the light airs and was on the leg to Lampedusa. Finally, the wind steadied at 95-105TWD and 6-7 knots and this allowed us to get onto port, bank our gains and be laying Capo San Vito (the north western tip of Sicily). On approach the breeze went forward and we were hard on the wind passing close to the islands off Trapani. We were behind the IRC 52 Arobas and her stern light two miles in front, meant we were right back in the race.
The breeze built overnight which was expected and a nice jib change from J1 to J2 just before we exited the wind shadow of one of the islands, set us up nicely for the increase in pressure. Once we cleared Trapani and got away from the shore we had a solid 18-20 knots fetching on port at the island of Pantelleria. The sea was rough and it was a bouncy ride onboard. Rambler was now finished as we rounded Pantelleria and braced ourselves for the leg up to Lampedusa. We had a nice setup with the J2 and a reef in the mainsail. When the breeze was sub 20 knots we could be at Full main and when it was above 22 knots we were at 1st reef. This made for very efficient moding, rather than trying to do a change to a smaller jib. We took a couple of tacks on shifts and made some good gains relative to the boats that did not.
We were still just in touch with Arobas as night fell on Day 4 and on approach to Lampedusa. Some tricky short tacking up the Lampedusa shore and we were now on starboard tack fast upwind angle on the leg back to Malta.
The breeze got lighter as we approached the channel between Malta and Gozo. We took 2 tacks and laid the channel. The sun was now coming up and the 50fters behind us could clearly be seen. In the channel, the breeze got very light and shifty. We changed to the Masthead cableless Code zero and were reaching at 100TWA at the northeastern end of Malta. A change on deck to have the J1 ready was a key speed decision and so when we exited the channel it was J1 upwind to the fairway mark off the finish. Rounding the fairway mark we hoisted the A2 and ran to the finish.
We knew that we had beaten the Class 2 boats behind us as they gave us time, but unfortunately we were not sure where Arobas had finished and so we needed to wait. A relief when we found out that they had finished just 52 minutes ahead of us, which was not enough time and thus Black Pearl secured the IRC Class 2 win. It was a great result considering the disappointment of the previous year.
A very worthy winner of the race was Maltese yacht Elusive 2 skippered by a good friend of mine and local man Chris Podesta. They sailed a great race and put a very good campaign together.
A new Black Pearl is now in production and will be an offshore focused carbon 56 being built by King Marine in Spain. The Carkeek 47 is up for sale and looking for a new home. The program for 2020-21 will be to race the new 56 in the offshore classics and build on the successes of the 47.
 James Carroll
James Carroll
James Carroll is a professional sailor with experience of competing at the highest level for over 18 years. He has competed in the Volvo Ocean Race, TP52s, Maxi World Championships and the Sydney to Hobart races. Both inshore and offshore racing he specialises as a Pitman, Sail Trimmer and Driver and has filled that role for multiple high profile international teams. With a background in boatbuilding and rigging it has complemented his sailing experience. James has been Project Managed numerous successful racing boat builds and overseen many complex refit projects in Europe, USA, China, Dubai and UK.
Carroll Lifts Antigua's Bluff Cove Trophy
Antigua Sailing Week has been running for 45 years and the Bluff Cove "Bell" is probably the most famous regatta trophy awarded so there was great celebrations at the weekend when an Irish sailor got his hands on it writes Louay Habib.
The Bluff Cove Trophy has some very famous yacht names on it; Marionette, Highland Fling, Morning Glory, Titan and more recently Ran.
Dubliner James Carroll (pictured below) lifted the bell at the weekend for his role racing one of the most powerful yachts in the world.
'Jimbo' was the Pitman on Hugo Stenbeck's canting keel Dubois 90 Genuine Risk for Antigua Race Week, winning Class One.
"Obviously delighted to be on Genuine Risk and over the moon to win", Carroll told afloat.ie

Afloat's March/April Issue Out Next Week!
Is there no end to the achievements of Irish boaters against seemingly impossible odds?
The winter may have been a time of hibernation for some of us but as the stories in Afloat's March/April issue will bear out Irish sailors have been battling the elements all winter long.
James Carroll competed in January's Sydney-Hobart offshore race and, much closer to home, Paul A. Kay journeyed through snow and ice in December from Dun Laoghaire to a new marina on Valentia Island.
As if to prove a point that we're down but not out, a winter of results on foreign waters includes a win in the Mirror World Championships in Australia and a top Olympic result in Florida, USA.
They are gutsy performances from youth teams that shows, if nothing else, the next generation of Irish sailors is really up for a fight. All this plus lots, lots more on news-stands next week!
Selected contents from Ireland's only boating magazine include:
News
Surveyors Issue Boat Launch Warning, Buoyant Dinghies Buck the Market, Ice Diving in Ireland, German U-Boat Rediscovered in Cork Harbour, an Historic Trophy for South Pacific Dream Cruise, MGM open in Cork, Hugh Mockler joins Crosshaven Boatyard plus lots, lots more.
News Focus
A new masterplan for Dun Laoghaire harbour is badly needed but it needs buy in from all those that use it
Going Offshore
The tenth Dun Laoghaire to Dingle offshore race was launched in style
Marine Conference
Combating the downturn was the focus of a unique marine gathering on both sides of the Irish sea.

Gear Review
New dinghy gear, a new Crosshaven boot from Dubarry, a new raincoat for girls and an upgrade for Musto's MPX.

This Island Nation
The decision to shut down the fog signals was based on a detailed risk assessment. Tom MacSweeney on the loss of fog horns
Sailor of the Year
Anthony O'Leary of Cork is the Afloat.ie/Irish Independent "Sailor of the Year" in celebration of his outstanding achievements afloat nationally and internationally.
Tall Ships
W M Nixon looks at the realities of national sail training in the 21st Century.
Tall Ship Conference
Ireland could yet have a tall ship to replace the Asgard II and the Lord Rank, if a new group formed to press for a replacement is successful
Racing update
Ulstermen's World Title, Topper worlds for Dun Laoghaire, Two Irish campaigns line up for Figaro Race, SB3 Sailors Cry Foul at Dun Laoghaire Parking Fees and an Irish entry in the Moth worlds in Australia, Irish Mini 6.50 Campaign in Prospect.

Youth Worlds preview
Results achieved abroad this Winter are the backbone for further Irish youth
success

Figaro Preview
Two fledgling Irish La Solitaire du Figaro campaigns edged closer to the start line last month
Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta
Volvo Dun Laoghaire regatta has taken in 22 entries six months ahead of the first race of the biggest regatta in Irish sailing.

Fireball Worlds preview
Dun Laoghaire's Noel Butler intends to continue his winning run in the Fireball class this season but the year ahead doesn't look so easy as the World Championships come to Sligo
Sovereigns cup preview
Up to 30 Quarter tonners will be at the Sovereigns Cup this year including one from New Zealand.
Shiver to deliver
A journey through snow and ice from Dun Laoghaire to Valentia Island
Sydney-Hobart Race
Outside of the Volvo Ocean Race, the Sydney Hobart is one of the world's most challenging offshore races. James Carroll Raced it in January.
Inland
As the cuts begin to bite, it may be time to look at the British direction for our waterways, writes Brian J Goggin
Dubarry Nautical Crossword
Soundings
A Google aerial photo proves useful navigating for Baldoyle Estuary
- Anthony O'Leary
- Dun Laoghaire
- Tom MacSweeney
- Harbour
- MGM Boats
- Asgard II
- World Championships
- Dinghies
- Olympic
- Cork Harbour
- Valentia
- Mirror
- Dingle
- youth
- Lord Rank
- Island Nation
- Hugh Mockler
- Dubarry
- Tall ship
- brokerage
- sydneyhobart
- fog horn
- moth
- Mini 6.50
- Uboat
- Fireball worlds
- Sovereigns
- James Carroll
- Paul A. Kay
- Crosshaven Boatyard
- Baldoyle
- MPX
- W M Nixon

































































