Displaying items by tag: inland waters
Waterways Ireland Launches 2020 Event Programme
Applications are open until Wednesday 15 January for the 2020 Waterways Ireland Event Programme, which aims to support events on or along Ireland’s inland waterways throughout the year.
Taking place annually for the past 13 years, the programme has supported competitions, learning experiences and community, historical and educational events for people with and without disabilities across thousands of communities nationwide.
Involving angling, canoeing, rowing, sailing and power sports, arts, history, drama and learning new skills, Waterways Ireland these events have most importantly been about having fun.
Sharon Lavin of Waterways Ireland said: “The new vision for the Event Programme will activate event organisers to consider how they can build in ongoing activity and sustained use of the waterways corridors into their event.
“Tourism and participation in recreation has a social and economic impact in waterfront communities, and events are a great way to engage communities with previously under-utilised waterways.”
The application form (with guidance notes) can now be viewed and completed online. Terms and conditions apply. The closing date the receipt of completed applications is Wednesday 15 January.
The chief executives of Fáilte Ireland and Waterways Ireland met last week to discuss their new Strategic Partnership Programme to develop tourism along the latter’s network of inland waterways.
The agreement is focused on delivering “a programme of works to improve the quality of the visitor and user experience along Waterways Ireland’s waterways”, the cross-border body said in a statement.
These include the Barrow Navigation, Royal and Grand canals, Shannon-Erne Waterway and Shannon Navigation.
It’s aimed to link these projects with Fáilte Ireland’s regional brands the Wild Atlantic Way, Ireland’s Ancient East, Ireland’s Hidden Heartlands and Dublin.
And the partnership also involved cross-promotion and marketing efforts, such as Waterways Ireland’s Shannon Masterplan to develop sustainable tourism in the Shannon corridor, and future plans to encourage visitors’ engagement with the canals in Dublin city.
“The waterways are a key part of the tourism offering in rural Ireland and the Dublin region,” said Fáilte Ireland chief executive Paul Kelly.
“Unlocking the incredible tourism potential of waterways such as the Shannon River which flows through so many rural communities will mean generating a huge number of opportunities and growth in local economies.”
Waterways Ireland acting CEO John McDonagh added that the Shannon Masterplan in particular “is an excellent first step in our programme and we look forward to a fruitful partnership which benefits the communities and economies across our waterways”.
Despite the growing demand for houseboat living in Ireland, there are only 28 residential moorings across the whole of the country, as RTÉ Radio 1’s Morning Ireland reports today (Wednesday 3 July).
Grand Canal Dock alone has a waiting list of some 215 hopefuls for its 20 places, and the programme hears from some of those fortunate enough to have made their home on Ireland’s inland waterways.
Waterways Ireland says it received as many as 10 queries a week from prospective houseboat residents — who will likely be waiting some time as only Grand Canal Dock and Shannon Harbour, with eight moorings, have provision for live-aboard homes.
Others make do with part-time waterways living, using the current 90-day permits to move around the country’s canals and rivers.
But with demand on the increase, it’s a situation that Waterways Ireland acknowledges has to change. RTÉ Radio 1 has more on the report HERE.
Waterways Ireland has issued Marine Notices related to a number of events taking place on Ireland’s inland waterways this weekend.
On the Royal Canal, a Junior Canoe Polo Competition will take place at Kilcock Harbour from 10am to 6pm tomorrow, Saturday 22 June.
Passage will be possible between 1pm and 2pm. Masters of other craft are requested to proceed at slow speed and with minimum wash and note any directions issued by the stewards.
On the Shannon-Erne Waterway, masters and owners of vessels are advised that they may experience short-term delays between Lock 1 at Corraquill and Ballyconnell Marina between 1pm and 6.30pm tomorrow due to the waterway’s 25th anniversary event.
Masters are requested to proceed at slow speed and heed any instructions issued by the event marshals.
Elsewhere on the River Shannon, the swimming element of a triathlon event will take place in Tarmonbarry on Sunday 23 June between 9.30am and noon.
Tarmonbarry lock will be closed to traffic during this time, and the N5 Shannon lifting bridge will also be closed, requiring large airdraft vessels to berth north of the bridge for the period.
A children’s swimming event will take place at 6pm on Saturday in Tarmonbarry, but this will not affect vessels in the navigation.
Masters are requested to proceed at slow speed and with minimum wash when approaching this section of the river and heed any instructions issued by the event marshals.
Meanwhile, on Upper Lough Erne, masters and owners of vessels are advised that dredging works are due to commence at Kilmore Quay on Monday 1 July and last for approximately nine weeks.
The map below shows the area to be dredged and the route the vessels will be taking in order to bottom-dump the material.
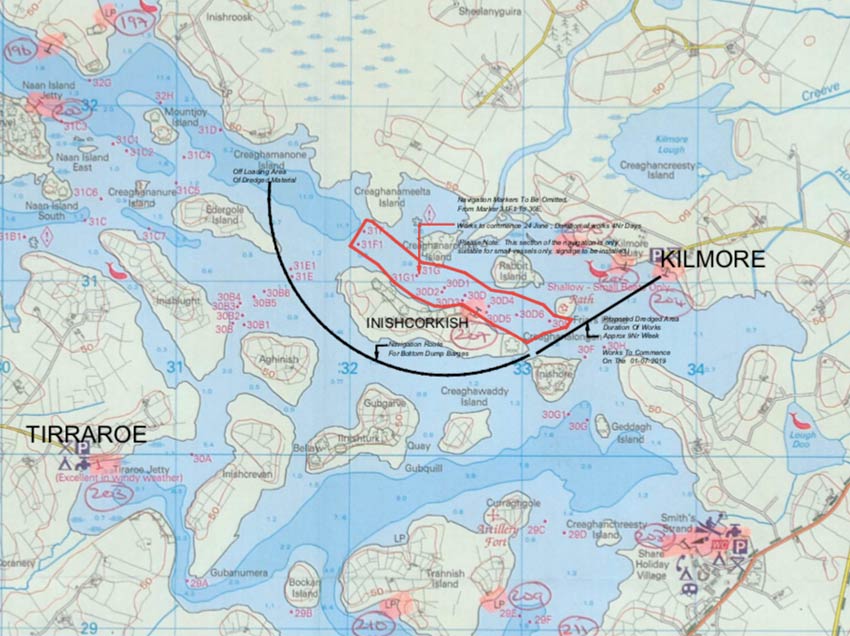
Masters of vessel are requested to proceed with additional caution in the vicinity of the dredging operations and dredging vessels.
Waterways Ireland thanks its customers for their co-operation in this and all other matters.
Barrow Locals Say What River Needs Is Promotion, Not Blueway
Proposals for a new blueway along the River Barrow have been blocked by planners who objected to the scheme for a hard surface along the 115km of towpath.
But as The Irish Times reports, many locals and users of the waterway believe what the Barrow and the communities along its reach really need are better promotion.
Earlier this month, An Bord Pleanála rejected plans long in the offing for the Barrow Blueway, a new cycling and walking path between Lowtown in Co Kildare and St Mullins in Co Carlow.
Hundreds of Barrow locals had their say at public meetings, with campaigners against the path plans — among them broadcaster Olivia O’Leary — citing the existing grassy surface as more than suitable for walkers.
Others saw the blueway as “a fantastic opportunity” to save business such as pubs which have been closing at a rapid rate in rural areas, and raised the question of boggy or overgrown stretches that are a deterrent to visitors.
But others still argue that with proper maintenance and a weight of a promotional campaign behind it, the existing path would prove a major tourism attraction both domestically and abroad.
“I have people coming from the States, Canada, Australia, Europe, UK and they are just flabbergasted at how incredibly gorgeous it is, and they can’t believe there is nobody on it,” said local canoe tour operator Charlie Horan.
Those sentiments are shared by environmental journalist Lenny Antonelli, who tweeted that the Barrow is “already walkable, paddle-able and often cycle-able too.
It's already walkable, paddle-able and often cycle-able too. The #Barrow doesn't need a greenway, but it does need better marketing & promotion, particularly within Ireland, and better facilitates for visitors. Imagine if all its derelict lock cottages became bothies for example?
— lenny antonelli (@lennyantonelli) April 29, 2019
“The Barrow doesn't need a greenway, but it does need better marketing and promotion, particularly within Ireland, and better facilitates for visitors. Imagine if all its derelict lock cottages became bothies for example?”
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
Network Of Inland Waterways Of Europe Launches New Website
The Network of Inland Waterways of Europe (NIWE) has launched its new website to celebrate and promote the many and varied benefits of Europe’s canals, lakes and rivers.
The NIWE, of which Waterways Ireland is a member, has been involved in numerous transnational projects boosting waterways organisations, local communities and businesses, and users alike.
The network’s shared objectives are to:
- Celebrate and promote the economic, social and environmental benefits of Europe’s inland waterways;
- Monitor and disseminate information on EU policy development and programmes;
- Support members’ participation in European initiatives and funding programmes;
- Promote the exchange of experience and knowledge transfer across the NIWE and among other relevant organisations and potential members;
- Create stronger engagement with the EU institutions to ensure the potential of European inland waterways is understood and reflected in EU policy and future programme development; and
- Collaborate with national and international organisations to achieve these stated objectives.
The new website at WaterwaysNetwork.eu is being touted as key tool in realising these objectives, serving as the NIWE’s marketing, project knowledge transfer and promotional platform for the future.
It it hoped it will also assist the network in developing future collaborative opportunities both with both European partners and local, regional and national partners.
Waterways Ireland Encourages Locals In Kildare, Carlow & Laois To Get ‘Walking On Water’ This Spring
Waterways Ireland has announced the launch of a walking programme along canal and river routes across Kildare, Carlow and Laois.
The aim of the Waterways For Health programme — in conjunction with Get Ireland Walking, and Local Sports Partnerships from Kildare, Carlow and Laois — is to immerse participants into natural waterway environments with guided support from county walking facilitators from Local Sports Partnerships.
“Waterways Ireland has seen a huge increase in the number of recreational and tourist users on and along all our waterways in recent years,” said Sharon Lavin of Waterways Ireland>
“With the provision of our Blueway and Greenway trails, we have now created even more opportunities for people to try new recreational activities. This also offers greater health and well-being and social opportunities for locals”.
For more information on the new Waterways For Health programme, its partners and their services, see GetIrelandWalking.ie and www.SportIreland.ie (to find your Local Sports Partnership).
#InlandWaters - Seán Kyne, Minister of State at the Department of Culture, Heritage and the Gaeltacht, has announced a €3.2 million investment by Waterways Ireland infrastructure on the Shannon Navigation at Meelick Weir.
The funds will be used for the restoration and replacement of the Meelick Weir walkway, the installation of tilting weir boards and remedial works to the weir structure.
The minister was joined on site yesterday (Friday 1 March) by Éanna Rowe, regional manager with Waterways Ireland and by Ministers of State Seán Canney Ciarán Cannon, along with Anne Rabbitte TD and local community representatives.
Meelick Weir was originally built in the 1790s as part of the Shannon Navigation. The weir, which is over 300 metres in length with a 12-sluice barrage, maintains and regulates the navigation level for that section of waterway between Athlone (Lough Ree) and Meelick (Lough Derg).
The weir and its walkway link the historic village of Meelick in Co Galway to Lusmagh in Offaly, and also link into the Hymany Way walking trail. The weir was damaged during storms in 2009 and the walkway was closed following further storms in 2015 and 2016.
Speaking yesterday, Minister Kyne said: “I am fully aware of the importance of this restoration to the counties of Galway and Offaly and in particular to the local communities of Lusmagh and Meelick who have been without the walkway for a number of years now.”
He added: “Meelick Weir is not just a walkway but a hidden gem on the River Shannon and its restoration shows the Government’s commitment to supporting all aspects of rural Ireland`s economic development.”
Éanna Rowe of Waterways Ireland said: “The development and re-instatement is critical to the management of the navigation and regulation of water levels.
“Reopening the connectivity between the communities of Lusmagh and Meelick and the re-instatement of the link to the Hymanny is a hugely positive and significant development for both communities.”
Waterways Ireland initiated design work on the project in 2012, completed the statutory environmental assessment and submitted planning for the project to Galway and Offaly county councils, which was given in 2017.
The works will involve the restoration of the weir, its walkway and the tilting weir boards along with the other critical infrastructure requirements (replacement of lock gates, jetty replacement, embankment works and bridge strengthening).
The new tilting weir system is being touted as a significant improvement in health and safety for employees managing water levels on site.
Following an open tendering procedure, a contractor will be shortly appointed and the project will be completed mid-2020.
Waterways Ireland Floats ‘Village Market’ Among Ideas For Grand Canal Dock Development
A floating food market is one of a number of ideas being mooted for in Grand Canal Dock by Waterways Ireland, the Dublin InQuirer reports.
Such a scheme would include a waterfront dining area and a co-working space along with the “curated, carefully selected floating village market on canal barges”, as suggested in a feasibility study conducted late last year.
Local councillors also recently heard of plans to develop the triangle of land Waterways Ireland owns at South Dock Road and Grand Canal Street Upper, where the canal basin and the River Dodder meet the Liffey.
The lands currently house two Georgian era graving docks, one of which is where the former Aran Islands ferry Naomh Éanna is being restored as a luxury hotel.
However, concerns remain that Waterways Ireland’s plans could be detached from the wants and needs from the local community in Ringsend.
The Dublin InQuirer has much more on the story HERE.
Waterways Ireland To Hold Sale Of Craft Removed From Grand Canal
Waterways Ireland intends to dispose, by public tender, of a number of vessels removed from the Grand Canal at Shannon Harbour, Tullamore, Barrow Navigation, Killaloe Canal and Shannon Bridge.
Twelve vessels are presently stored on the South Bank of the Grand Canal adjacent to the Transit Shed in Shannon Harbour. One vessel is stored in Fenniscourt on the Barrow Navigation and other vessels are stored in Ballyleague and Munster Harbour, Portumna.
All vessels may be inspected (externally only) by local arrangement. Tender and relevant documentation is available from the Assistant Inspector of Navigation at +353 87 286 5726 or [email protected]. Alternatively you can download the tender documentation from the Waterways Ireland website.
Sealed tenders should reach the Assistant Inspector of Navigation at the above address not later than noon on Monday 18 March.
A condition of sale is that vessels be removed from the canal property once purchased. Removal details will be notified to successful purchasers once transactions are finalised.





































































