Displaying items by tag: Galway Docks
Galway Docks Hosts Artist John Gerrard For Arts Festival
Galway Docks transforms to an outdoor gallery over the next fortnight with a simulation by leading Irish artist John Gerrard.
“Flare [Oceania] 2022” is the title of Gerrard’s work, which is part of the visual arts programme for the Galway International Arts Festival.
The simulated gas flare, which hovers between a flare and a national flag, is being streamed live on a seven-metre by seven-metre LED wall at the docks.
It is set within a seascape, based on photographs taken by Tongan artist and activist Uili Louisi depicting his heating ancestral ocean near the archipelago of Tonga in the Pacific.
Gerrard’s work is said to represent “an ecology in hyper distress and a world faced with the existential threat of rising seas”.
Gerrard is best known for his large-scale and site-specific work which has been exhibited in Ireland and abroad, including “Mirror Pavilion” which was Galway arts festival’s commission for the Galway 2020 European capital of culture.
The event takes place as cruise ship traffic returns to the Port of Galway. The port is also taking delivery of 80 metre turbine blades for the Ardderroo wind farm, a 101MW onshore wind power project due to be commissioned this year.
"Flare [Oceania] 2022" runs for 24 hours, and continues at Galway Docks until July 24th.
Limerick Ketch Ilen Makes Temporary Migration To Galway
They do things differently in Limerick and along the west coast. Where other migrating birds of passage head south as winter approaches, the restored 56ft trading ketch Ilen of 1926-vintage is departing her usual base in the Shannon Estuary today (Friday), and is heading north to spend part of the winter in Galway, where she has been allocated a snug berth in the docks at the heart of a city where she’ll find plenty of traditional sailing craft with which to share the long nights.
It now seems a long time since she made a free-spirited voyage to western Greenland in 2019, but even with her wings clipped by pandemic regulations, when possible she has made shorter passages along the Irish coast, a programme which revealed that the spirit of the Ilen Marine School can be carried to many ports.
Galway in particular provided a hospitable showcase, and Ilen is expected into port around 2.30 pm tomorrow (Saturday).
 The cleansing sea - crewmen Brian and Jim rinsing Ilen’s decks as she heads down the Shannon Estuary at 1300hrs today (Saturday). Photo: Gary Mac Mahon
The cleansing sea - crewmen Brian and Jim rinsing Ilen’s decks as she heads down the Shannon Estuary at 1300hrs today (Saturday). Photo: Gary Mac Mahon
 IIen’s allocated betty in Galway Docks
IIen’s allocated betty in Galway Docks
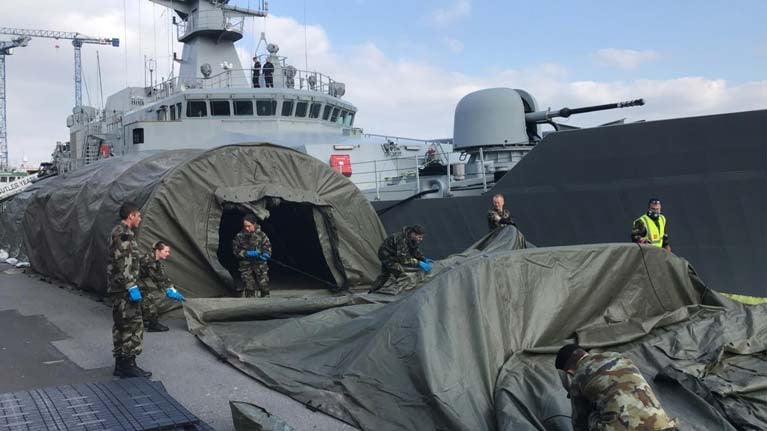
The Naval Service patrol ship LÉ James Joyce prepared to depart Galway port at the weekend, as COVID-19 virus test centres in the west were scaled down.
The LE James Joyce berthed in Galway on April 8th, replacing the LÉ William Butler Yeats which set up the first field hospital in Galway for the Health Service Executive last month (march).
It is understood the test facilities at Galway’s dockside were used minimally over the ten days, and the LÉ James Joyce was informed at the weekend that its services were no longer required.
Two other patrol ships are still providing assistance to the HSE – the LÉ Niamh on Sir John Rogerson’s Quay in Dublin, and the LÉ Eithne on Albert Quay in Cork.
Testing is not taking place at the LÉ Eithne, but the ship’s crew has been assisting with storage of personal protection equipment and decanting hand sanitisers.
.Galway had 273 confirmed cases of the COVID-19 virus as of yesterday, an increase of seven over a 24-hour report period.
Both Galway and Mayo are said to be at the lower end of the scale of confirmed cases of the virus.
The HSE has said it is up to date on COVID-19 test referrals, with waiting time for an appointment at under 24 hours.
Paying tribute to all staff involved, it said that community test centres could be stepped up again if required.
Newest Ship in the Irish Navy Open to Tours in Galway Docks
#NavalService - LÉ George Bernard Shaw, the latest ship to join the ranks of the Irish Navy, will be open for the public to look around next week in Galway Docks.
As the Galway Daily writes, LÉ George Bernard Shaw was brought into Naval Service this year and will have a formal naming ceremony in 2019.
The Offshore Patrol Vessel is the latest of four modern ships delivered to update the Irish Naval Service since 2014.
Free guided tours of the ship will be offered to the public by her crew on Monday, December 31 and Tuesday, January 1 from 2pm to 5pm.
The four ships built for the navy since 2014 are often referred to as the ‘Playwright’ sisters, for more read here.
Appeal Halts Galway Docks Student Housing Plans
#Property - Four different parties have lodged an appeal against plans for student housing on the former Topaz oil site in Galway Docks, according to Galway Bay FM.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, Galway County Council granted planning permission for the construction of two blocks by Bonham Dock Limited, which would provide 345 bedrooms as well as space for business start-ups.
But VP Motors argues that the development encroaches on lands already occupied by its business, while the scheme also faces separate objections from An Taisce, and CIE, which owns adjacent rail yards.
Galway Bay FM has more on the story HERE.
Two Drown In Separate Galway Incidents
#Galway - BreakingNews.ie reports that two people are dead after separate drowning incidents in Galway city yesterday afternoon (Saturday 11 June).
North of the city, the body of a 19-year-old man was recovered from the River Corrib near NUI Galway around 2pm.
At the same time, the body of a woman thought to be in her 40s or 50s was discovered in Galway Docks. BreakingNews.ie has more HERE.
Galway Blocks Docks Slipway After Buncrana Tragedy
#Galway - Galway Harbour Company has blocked open access to a slipway in Galway Docks weeks after the Buncrana tragedy, as the Connacht Tribune reports.
The move was made a month after five members of the same family, including three children, died after their car slipped into Lough Swilly from the open slipway at Buncrana, Co Donegal on Sunday 20 March.
Galway's docks slipway had been used freely by recreational boaters – but as of last Thursday (21 April) local sailing clubs have been informed that the slipway can only be used with permission.
Access times have also been restricted to 9am-5pm on weekdays and by appointment on Saturdays in what the harbour company says is a move to avoid "risk to life".
But one local user has branded the locking-up of the slipway as "ridiculous" and said "there should have been a more measured response and consultation".
The Connacht Tribune has much more on the story HERE.
#Search - Galway Bay FM reports that coastal searches resumed this afternoon in Galway for a man who was spotted entering the water last night (Thursday 10 March).
The search began in Galway Docks after the man, believed to be in his 30s, was seen entering the water at Wolfe Tone Bridge over the Corrib, but no trace has been found.
A separate search for a person calling for help on the shoreline near Mutton Island has also yielded no results thus far, and it is not yet known if the two events are related.
Major Search For Woman In Galway Docks Is False Alarm
#RNLI - Galway RNLI joined a major search for a woman believed to have entered the water at Galway Docks in the early hours of yesterday morning (Friday 1 November) that turned out to be a false alarm.
The Irish Coast Guard received a report about the missing woman shortly before 2am and immediately sought the assistance of Galway RNLI volunteer crew who launched the lifeboat from the nearby station within minutes.
Galway Fire Brigade and Mill Street Gardai searched the perimeter of the docks, including the boats and marina, while the Galway lifeboat searched the rest of the Docks.
They were joined in their efforts by coastguard rescue helicopter from about 3am but nothing was found.
After some investigation, it was discovered that the person who was reported missing was in fact safe and sound at another location.
Galway RNLI lifeboat operations manager Mike Swan said the search operation was eventually stood down at about 4am.
"While this incident proved to be a false alarm, Galway RNLI is always willing and ready to respond to anyone who is thought to be in danger in the water," said Swan.
"Each time the lifeboat is called out it costs the station up to €4,000. All of our lifeboat crew and land crew are volunteers and we rely solely on fundraising and the generosity of the public to keep the station and service running."
Galway Harbour Plans 'Will Put City On Map For 800 Years'
#GalwayDocks - The planned expansion of Galway Harbour will put the City of the Tribes on the map for the next 800 years, according to Galway Harbour Company chair Paul Carey.
Galway Bay FM reports on Carey's grand statement made at a presentation to city councillors on Monday 9 September.
As reported last week on Afloat.ie, the finalised plans for the multi-million expansion and modernisation of the city's harbour and docks will be lodged with An Bord Pleanala before the end of September after the original deadline was pushed back several months.