Displaying items by tag: fish quotas
EU Commission Moves to Quell Fears Over Talks with Norway on Fish Quotas off Irish Coast
The European Commission has said it hopes to represent “the best interests” of EU member states in talks with Norway on blue whiting.
A Commission official was responding to fears voiced earlier this month by Irish fishing organisations that Norway would be granted greater access to annual quotas in Irish waters, while offering no reciprocal arrangement.
In a joint statement, industry organisations had appealed to Minister for the Marine Charlie McConalogue to ensure that the EU “blocks Norway, a non-EU member, from gaining unilateral access to our blue whiting grounds”.
 Minister for the Marine Charlie McConalogue
Minister for the Marine Charlie McConalogue
“The EU already threw Ireland under the bus when it came to quota cuts after Brexit,” Irish Fish Producers Organisation (IFPO) chief executive Aodh O’Donnell said.
“We took the hardest hits. A staggering 40 % of the total value of quotas transferred to the UK under Brexit came from Ireland,” he said, questioning whether the EU was “now considering that we take the hit again for a non-EU member?”
"The EU already threw Ireland under the bus"
“ It’s time to ask serious questions about the EU’s attitude to Ireland and our fishing industry,” O’Donnell had said, pointing out that “the fact that Norway is making their request to the EU and NOT directly to Ireland, speaks volumes”.
 Irish Fish Producers Organisation (IFPO) chief executive Aodh O’Donnell
Irish Fish Producers Organisation (IFPO) chief executive Aodh O’Donnell
Norway seemed “optimistic that the EU would unilaterally surrender access to Irish fishing grounds to a non-EU member – based on the track record of EU treatment of the Irish fishing industry”, he noted.
Brendan Byrne of the Irish Fish Processors and Exporters Association (IFPEA) said that Norway was pushing the EU to increase a transfer of quota by a staggering 158% to 80,000 tonnes, in addition to access.
“Most of this will be caught in our waters. Essentially, the Norwegians have enormous quotas but want additional access to Irish waters to catch this valuable stock. Their total catch of this species will have a value in excess €100 million in the coming year,” Byrne had said.
Irish South and West Fish Producers’ Organisation chief executive Patrick Murphy said that Norway’s quotas were nine times those of Ireland, and there was “no justice in allocating them more rights to fish in the Irish Box.”
The Irish organisations said it was a “red line” issue, and stressed that any agreement by the EU with Norway must be balanced by a reciprocal arrangement.
A Commission official said that “when representing the EU in international negotiations, the European Commission operates on the basis of positions coordinated with the member states”.
“The Commission notes that the current fisheries arrangements between the EU and Norway include reciprocal access to waters to fish for blue whiting and that the exchanges of fishing opportunities for 2023 are still to be discussed between the parties,” the official said.
“The Commission welcomes the contribution of industry organisations and representatives to these consultations and looks forward to achieving progress in the best interest of the EU and its Member States,”the official said.
EU Fish Deal for 2020 hailed by Creed & Condemned by Environmental NGOs
Minister for Agriculture, Food and Marine Michael Creed has hailed EU agreement on next year’s fish quotas, while the deal has been condemned by environmental NGOs Birdwatch Ireland and Our Fish writes Lorna Siggins
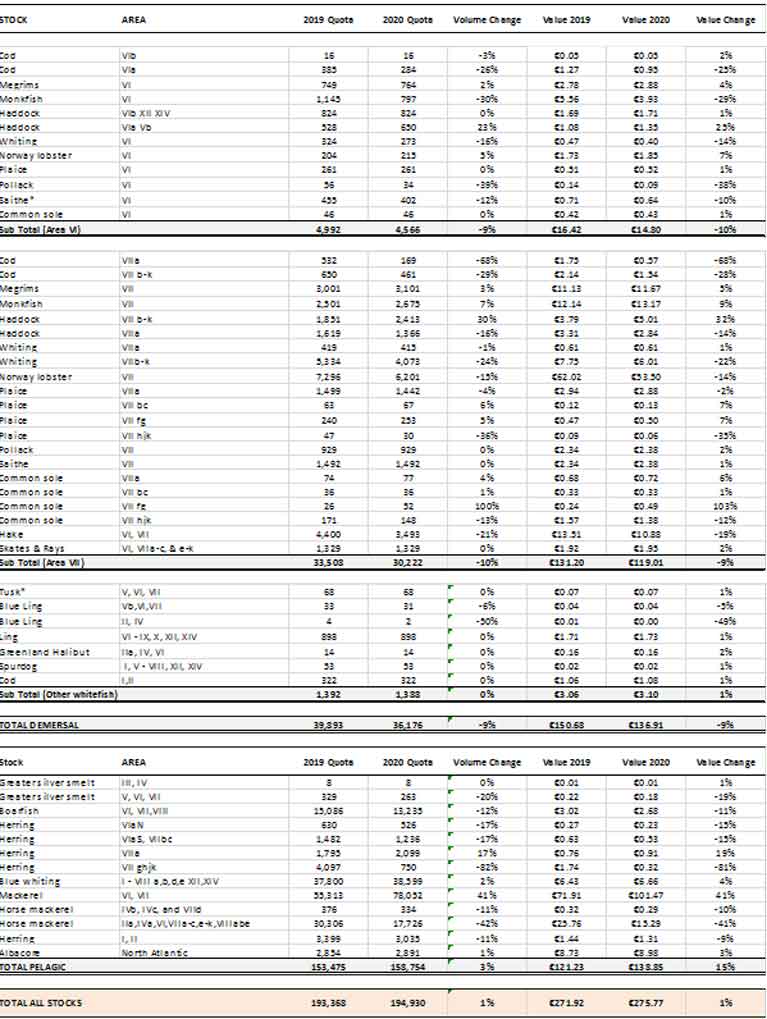
Mr Creed said that securing agreement on rebuilding measures in the Celtic Sea was “one of the most difficult aspects” of the negotiations, and said the total package agreed is 195,000 tonnes – worth 275 million euro for the Irish industry next year.
Increases in key stocks include mackerel (41% increase), haddock (+30%), monkfish (+7%) and megrims (+3%) in the Celtic Sea.
Mr Creed said Ireland’s second most important fishery, prawns, has been reduced by 15% in accordance with the scientific advice “due to the decline in stock density in some important prawn beds”.
“Some stocks such as cod and whiting in the Celtic Sea remain in very poor shape and at this Council, agreement was reached on the introduction of significant additional safeguards designed to rebuild these stocks,” he said.
Measures to protect cod and whiting “were trialled by our experts in BIM and the Marine Institute, working closely with our fishing fleet”, he said.
“ By taking these necessary steps now, we can rebuild the stocks in our Celtic Sea fisheries and avoid the need for closures,” he said.
He said that for 32 of 47 target stocks of interest to Ireland, the quotas for 2020 were set at or below the scientific advice where available, meeting maximum sustainable yield criteria. Restrictive quotas were set for four vulnerable stocks of interest to Ireland, while very small quotas for three depleted herring stocks were set to allow for the collection of scientific data.
However, EU fisheries ministers have been criticised by NGOs, including Birdwatch Ireland and umbrella group Our Fish.
Our Fish accused ministers of continuing to prioritise economically important species over vulnerable non-profitable species and was critical of the failure to introduce monitoring at sea to ensure the ending of discards.
Our Fish said a preliminary assessment of available information suggested that a number of all total allowable catches (TACs) have been set above scientific advice, including several vulnerable cod stocks such as west of Scotland and North Sea and southern hake.
Birdwatch Ireland said that EU ministers, including Mr Creed, had “failed abysmally to meet the EU’s legal deadline to end overfishing” by 2020.
“Both the Irish Government and the European Parliament have declared a climate and environmental emergency. This is just another example that EU leaders neither comprehend the scale of the existential crisis we face or have any intention of doing anything about it,” it said.
“While Minister Creed will say that meeting the 2020 deadline was too great a challenge due to the poor state of many stocks, the reality is that he has played a significant role in creating the situation. Ireland has one of the worst records in the EU at driving overfishing,” it said.
“The Celtic Sea Herring fishery had to close this year due to the state of the stock and there are no signs it will open next year. While the minister has argued that he has been fighting for the interests of the fishing industry, the facts are that overfishing is costing jobs,” it said.
EU fish deal table
#Fishing - The State’s promise to protect economic links between fishing quotas and local coastal communities is “not happening on the ground”, according to a Rossaveal seafood plant that faces an uncertain future.
Iasc Mara Teoranta managing director Cathal Groonell tells The Irish Times that if the company is unable to find a buyer for its fish processing facilities, it would be forced to close with the loss of 25 jobs.
Groonell’s company claims a significant fall in mackerel and herring landings in Rossaveal is related to the loss of fishing vessels once based out of the Connemara harbour to larger operators in Killybegs, Co Donegal.
Such moves appear to reflect the Department of Marine’s own statement that “concentration of rights into the hands of large companies would seriously risk fishing vessels losing an economic link with Ireland’s coastal communities.”
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
Marine Minister Welcomes Mackerel Deal
#Fishing - Marine Minister Simon Coveney has welcomed the positive outcome of the international fisheries negotiations that concluded today (Tuesday 27 October) at the National Seafood Centre in Clonakilty, Co Cork.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, the negotiations between Norway, the Faroe Islands and the European Union concerned the management of mackerel in the North East Atlantic.
The mackerel quota for Irish fishermen for 2016 will be just over 75,000 tonnes. This reflects a precautionary approach in accordance with the latest scientific advice and the long-term management strategy also agreed between the parties today.
“I welcome the outcome of the international mackerel negotiations today, which Ireland not only hosted but was also a central participant as the second largest EU quota holder," said the minister.
"Irish fishermen will now have a quota of 75,000 tonnes, worth over €63m directly to our catching sector, for 2016 and the new long term management strategy will provide stability to our fishermen in this vital fishery for Ireland by avoiding large variations in the quota from year to year.”
Mackerel is Ireland’s single most valuable fishery and today’s agreement provides a high quota, stability and a framework to help ensure the long term sustainability of the stock.
The latest agreement builds on the five-year sharing agreement reached in March 2014 between those parties. Further discussions on that agreement are expected in the coming months.
Minister Coveney added that “while the quota achieved by Ireland is less than that of the last two years, those quotas were unusually high by historical standards.
"The quota of 75,000 tonnes achieved today is considerably higher than our historical average quota of approximately 54,000 tonnes, apart from the last two years. Crucially, for the sustainability and stability of this vital fishery for Ireland, we now also have a long-term management strategy in place for mackerel.
"As always, industry representatives, in particular, Sean O’Donoghue of the Killybegs Fishermens Organisation were extremely helpful to the Irish negotiating team.”
Ireland Opposes Transfer of Fish Quotas to Norway
Under the EU/Norway Fisheries Agreement each year Norway and the Community swap fishing opportunities in each others waters. However, this has resulted in the EU giving fish stocks off the west coast of Ireland to Norway in exchange for Norwegian cod. Minister Connick advised his fellow Ministers of the Commissions commitment from last November "to ensure that the costs and benefits for individual Member States of the annual arrangements with Norway should be as balanced as possible".
Minister Connick said "Ireland has continually opposed what has to date been an unfair and inequitable process which results in a Member State, like Ireland which does not benefit, paying for the fishing opportunities of other Member States".
The Minister added "I want to make it crystal clear that Ireland will totally oppose any moves to include the stocks that the Irish fleet fish in the waters off the west coast such as horse mackerel and mackerel in the balance".
The Minister then re-iterated Irelands long held request for a radical re-look at the way the swaps are achieved. He said "It is very clear that there will be a major problem balancing any EU/Norway agreement this year and Ireland calls on the Commission to bring forward a new framework whereby, Member States who want to avail of the Cod on offer can contribute to a communal EU pool for exchange with Norway. In this way those Member States who want the Cod can avail of it but not to the detriment of Member States who do not benefit".
On a side topic the Minister referred to the ongoing negotiations between the EU, Norway, the Faroe Islands and Iceland on arrangements for the management of the mackerel stock which is so important economically to Ireland. The Minister restated Ireland's support of the Commissions efforts to bring about an agreement but not at any cost. The Minister said " It is in all our interests that the level of fishing on the mackerel stock is reduced and that Iceland and the Faroe islands enter into a four party coastal state arrangement for it's management" He went on to say that "Any final share out of the mackerel resource must be fair and proportionate".































































