Displaying items by tag: irish sea
ISORA Adds Double–Handed Class to 2016 Offshore Series
The Irish Sea Offshore Racing Association (ISORA) has introduced short handed sailing to the Irish Sea offshore game this season, a recognition for the Irish boats acheiving success in the discipline on the international stage over the last few seasons.
Although ISORA has always encouraged short-handed racing (it accommodates single handed racing in its day races) the 2016 initative from Commodore Peter Ryan goes a step further with the new double handed class open to any boat sailed double handed for any of the ISORA races.
Reflecting the drive of the individual for the love of offshore sailing and noting Irish short–handed wins in the 2015 Middle Sea Race and the Round Britain and Ireland Race two years ago, it will be ineresting to see the take up for the new class on either side of the Irish Sea.
The Double Handed Overall Class winner will be determined by the best four Double Handed results for that boat. Race prizes for Double Handed will be allocated depending on the number of boats taking part in the race. Double Handed boats will also qualify for the normal Overall and Class prizes.
The first race in the Avery Crest ISORA Offshore Series 2016 takes place on the 23rd April with the day race from Dun Laoghaire to Wicklow.
As the first race of the season it is anticipated that the selected course will allow boats and crew to ease into the 2016 season while having enough time after the race to sample the hospitality of Wicklow Sailing Club while waiting for the north going tide.
The second race of the Offshore Series 2016 is the Pwllheli Bay Day Race also on 23rd April. This race will take the fleet along the scenic Welsh Coastline and out into the spectacular and World renowned sailing waters of Cardigan Bay. After racing the crews will retire to the new Sailing Club in the iconic Academy where there will be opportunities to discuss the 2016 offshore campaigns and the challenge to retain the ISORA Team Trophy again this year.
This sailing season’s highlight is the Volvo Round Ireland Race and it is hoped that this will encourage those boats taking part to gain the required experience and practice in offshore racing by taking part in ISORA.
As Afloat previously reported, this season sees some new boats entering: Kuba Szymanski’s First 40.7. Grant Kinsman’s Sigma 400 and Robert Floate’s Sydney 36 should make some competitive racing for the Class 1. George Sisk’s, ICRA 2015 Boat of the Year and overall winner of the Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta, “WOW” is back racing in ISORA. There are persistent rumours of a JPK 10.8 appearing and a J105 from Wales?
Marine Notice: Hydrographic & Geophysical Survey Off Mayo Coast, Celtic Sea & Irish Sea
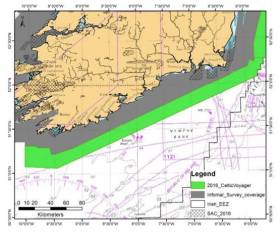
#MarineNotice - The latest Marine Notice from the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport (DTTAS) has been advised that a hydrographic and geophysical survey operation will be undertaken by INFOMAR for the Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland (SEAI) off the Mayo coast, in the Celtic Sea and also in the Irish Sea between 21 March and 30 October 2016.
The RV Celtic Voyager (Callsign EIQN), the RV Celtic Explorer (Callsign EIGB), the RV Keary (Callsign EIGO9), the RV Geo (Callsign EIDK6) and the RV Tonn (Callsign: EIPT7) are expected to carry out survey operations and will be listening on VHF Channel 16 throughout the project.
Details of co-ordinates for the survey operations are included in Marine Notice No 11 of 2016, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
Mystery Of Dead Otter Found On Manx Beach
#MarineWildlife - Wildlife experts on the Isle of Man have been stumped by the carcass of an otter – a species not native to the island – found on Port Erin beach last Friday (15 January).
As BBC News reports, while the once severely threatened British otter population has recovered to the extent that the marine mammals can now be found in every county in England, they have never knowingly been a presence on Man – until now.
And with no microchip present on the animal to determine the deceased otter's origin, or indicate how it got to the island in the middle of the Irish Sea, the local wildlife trust has something of a mystery on its hands.
BBC News has more on the story HERE.
Europe's Killer Whales Threatened By Toxic Chemicals In The Ocean
#MarineWildlife - Toxic chemicals banned in Europe nearly 30 years ago are still polluting the seas off the continent.
And marine scientists fear their continued presence could spell the end for the killer whale and other species in European waters, as the Irish Examiner reports.
The warning comes from newly published research on concentrations of polychlorinated biphenyls, or PCBs, in marine wildlife – specifically orcas and other dolphins – in Irish, British and Mediterranean waters.
Co-authored by Dr Simon Berrow of GMIT and the Irish Whale and Dolphin Group, the paper in the latest issue of journal Scientific Reports claims that despite the outright ban on the use of PCBs since 1987, they persist in "dangerously high levels in European cetaceans".
High exposure to PCBs, once used in the manufacture of paints and electrical equipment, weakens the immune systems of cetaceans and has a severe effect on their breeding rates.
Pilot Named As Search Continues For Missing Light Aircraft In Irish Sea
#Missing - The family of a man whose light aircraft is believed ditched in the Irish Sea have said they are "hoping against hope he may be found alive".
BBC News reports that the missing man has been named as Ian Stirling of Douglas on the Isle of Man.
The 73-year-old sparked a major search and rescue operation yesterday morning (Thursday 3 December) when the Rockwell Commander he was piloting disappeared from radar three miles offshore on approach to Blackpool Airport.
Debris and fuel spillage were found off the Lancashire coast before the search was suspended due to failing light, as previously reported on Afloat.ie.
Local council beach patrols have joined HM Coastguard in the search as it resumed earlier today. BBC News has more on the story HERE.
World War I Shipwrecks Revealed In Irish Sea
#HistoricBoats - A team of scientists aboard the Marine Institute's research vessel Celtic Voyager has revealed detailed images of World War I shipwrecks in the Irish Sea.
The team, led by Dr Ruth Plets of the School of Environmental Sciences at Ulster University, set out to capture the highest resolution acoustic data possible of WWI shipwrecks lost in the Irish Sea, using a new multi-beam system (EM2040) on board the RV Celtic Voyager to get the best data ever acquired over these wrecks.
"We were able to capture the most detailed images of the entirety of the wrecks ever," said Dr Plets. "Some of the wrecks, which are too deep to be dived on, have not been seen in 100 years. So this is the first time we can examine what has happened to them, during sinking and in the intervening 100 years, and try to predict their future preservation state."
Among the shipwrecks surveyed were the SS Chirripo, which sank in 1917 off Black Head in Co Antrim after she struck a mine; the SS Polwell, which was torpedoed in 1918 northeast of Lambay Island; and the RMS Leinster, which sank in 1918 after being torpedoed off Howth Head, killing over over 500 people - the single greatest loss of live in the Irish Sea.
Marine Institute chief executive Dr Peter Heffernan welcomed the achievements of the survey, supported by the competitive ship-time programme, saying: "The multidisciplinary team is making an important contribution to understanding and protecting our maritime heritage and to our ability to manage our marine resource wisely."
Explaining how the survey was carried out, Dr Plets added: "We moved away from traditional survey strategies by slowing the vessel right down to allow us to get many more data points over the wreck, with millions of sounding per wreck."
"The detail is amazing as we can see things such as handrails, masts, the hawse pipe – where the anchor was stored – and hatches. Some of the vessels have split into sections, and we can even see details of the internal structure. With the visibility conditions in the Irish Sea, no diver or underwater camera could ever get such a great overview of these wrecks."
As well as acoustic imaging, the team collected samples from around the wreck to see what its potential impact is on the seabed ecology. Sediment samples were also taken for chemical analysis to determine if these wrecks cause a concern for pollution.
The project is carried out to coincide with WWI centenary commemorations, noted Dr Plets. "We often forget the battles that were fought in our seas; more emphasis is put on the battles that went on in the trenches. However, at least 2,000 Irishmen lost their lives at sea, but unlike on land, there is no tangible monument or place to commemorate because of the location on the bottom of the sea.
"In the Republic of Ireland there is a blanket protection of all wrecks older than 100 years, so all these will become protected over the next few years. To manage and protect these sites for future generations, we need to know their current preservation state and understand the processes that are affecting the sites."
The next step for the team is to use the data collected to create 3D models which can be used for archaeological research, heritage management and dissemination of these otherwise inaccessible sites to the wider public.
"There is so much data, it will take us many months if not years, to work it all up," said Dr Plets. "Some of the wrecks are in a very dynamic environment and we are planning to survey these vessels again next year to see if there is a change, especially after the winter storms. That will give the heritage managers a better idea if any intervention measures need to be taken to protect them.
"These data could well signal a new era in the field of maritime archaeology. We hope it will inspire a new generation of marine scientists, archaeologists and historians to become involved. Above all, we want to make the general public, young and old, aware of the presence of such wrecks, often located only miles off their local beach."
The research survey was supported by the Marine Institute, through its Ship-Time Programme, funded under the Marine Research Sub-Programme by the Government.
The diverse team included maritime archaeologists Rory McNeary from the Northern Ireland Department of the Environment and Kieran Westley from the University of Southampton; geologists Rory Quinn and Ruth Plets, both Ulster University; biologists Annika Clements from Agri-Food and Biosciences Institute and Chris McGonigle from Ulster University; Ulster University marine science student Mekayla Dale; and hydrographer Fabio Sacchetti from the Marine Institute who works on Ireland's national seabed mapping programme INFOMAR, run jointly with the Geological Survey of Ireland.
The team blogged about the seven-day survey at Scientists@Sea.
Liam Shanahan’s 'Ruth' Retains ISORA Offshore Championship Crown
The last race of the ISORA Avery Crest Offshore series that was sponsored by LC Tyres, took place on Saturday 12th September with the race from Pwllheli to Dun Laoghaire (74 miles) writes ISORA's Peter Ryan. The boats compete for the famous “James Eadie” trophy. As like the same race last season, the weather forecast for the race and particularly the delivery to Pwllheli was not favourable all week. This put off many of taking part in what is normally a well supported end of season race.
The race was of more interest than usual due to the fact that the Overall Championship was still be be raced for with Liam Shanahan’s J109, “Ruth” and Andrew Hall’s J125, “Jackknife” only a 5 point apart and Peter Dunlop and Vicky Cox’s J109 “Mojito” close behind. While either “Ruth” or “Jackknife” could have taken the Series with a good result in the race, “Mojito” needed a well attended race to secure sufficient points in the high points scoring used by ISORA.
Of the 26 entries received for the race, 19 had confirmed taking part on the Monday prior to the race but only 9 came to the start on Saturday morning. Several boats had left Dun Laoghaire the previous morning but turned back when they were met with strong south easterly winds on the nose and a big sloppy sea. Those that persevered were rewarded with nearly “champagne” sailing for the race. Bryan Mullarkey’s Collins 40, “Harriet Marwood” was taking part in an ISORA race for the first time. Richard Mossop’s Oceanis 411, “Yachtzee” and David Simpson’s Swan 371 “Albeiro” were battling for the Overall Class 2.

Liam Shanahan's Ruth from the National Yacht Club has successfully defended her 2015 ISORA offshore crown
Due to the uncertain forecast due to the presence of two depressions, north and south of the race area, the decision was taken to set the course from the start direct in Pwllheli to the finish between the pier heads in Dun Laoghaire.
Despite the poor forecast, the lashing winds during the night and the strong winds, conditions were relative pleasant for the start. The wind was 10-12 knots from the south west giving a beat to the first corner at St Tudwal’s Sound. Stephen Tudor’s J109, “Sgrech” was first off the line and lead the fleet until the faster “Jackknife” too to the front. From the start “Ruth” and Mojito” were always in close contact leaving.
As the fleet approached St Tudwal’s Sound the wind had increased to 20knots and the expected overfalls at the end of the sound awaited the fleet. The next leg was the beat to Bardsay Sound. The wind appeared to veer westerly and maintained the 20-22 knots leaving the fleet to beat through the rough seas towards Bardsey Sound. Fortunately, the tide was right for a fast shoot through Bardsey Sound. Unfortunately, the overfalls in the sound were significant but had settled soon after exiting it.

By that stage the battle was on. “Jackknife” cracked sails and took the direct line to Dun Laoghaire in the last of the north going tide. The remainder of the fleet retained their height and the three J109’s with Conor Fogarty’s 2-handed Jenneau 3600, “Bam”, bunched together for the leg to Dun Laoghaire. Shortly after leaving Bardsey the wind backed allowing the boats to ease sails and speed up. Of the bunch of four, “Bam” lead the group with “Ruth” and “Mojito” close behind and “Sgrech” snapping at their heels. Paul Sutton’s “Pipedreamer VI” was just behind this pack.
As the fleet approached the Irish coast the winds abated to 12 knots and backed further to the south allowing those with Code Zeros to accelerate. The positions within the fleet did not change for the long leg despite continuous trimming and hard driving being done on all the boats. It was not until approaching Dublin Bay that “things started to happen”. The winds became fickle and dropped further in Killiney bay. While “Jackknife” avoided much of the light wind to keep powering towards the line, the three J109’s and “Bam” got into a tactical battle with rapid sail changes taking place to deal with the oscillating winds. As the fleet approached Dublin Bay the wind veered to the west and decreased again giving the boats a short final beat to the finish line. Despite the work on each boat the positions generally remained the same.
“Jackknife” took line honours but could only manage 5th Overall allowing “Ruth”, who won the Overall race and Class1 to regain the ISORA Avery Crest Offshore Championship title. Class 2 was won by “Yahtzee” who also won Silver Class.
The crew of Liam Shanahan’s “Ruth” include his four sons. There is a great tradition of offshore racing in the Shanahan family with Liam Shanahan Snr playing a huge part in ISORA racing in the early days.
The race sponsor, LC Tyres, provided day prizes for the race. These were presented at the après sail party that took place in the NYC. The prizes were presented by Caroline Coyne aided by her son, Billy and daughter, Isobel.
The ISORA Avery Crest Offshore Championship trophy, the Wolf’s Head, will be presented to Liam Shanahan at the ISORA dinner in the NYC on the 14th November. “Jackknife” took 2nd place Overall and “Mojito” took 3rd place.
Overall Series Calls 1 was won by “Jackknife” and Class 2 was won by “Albeiro” who also took Overall Silver Class. The team prize, known as the “Victoria Cup”, was again won by Pwllheli Sailing Club.
All the results can be found on the ISORA website. The YB tracking of the race can also be accessed on the ISORA website and on the YB app for smart phones.
Skipper Blames 'Submarine' For Irish Sea Trawler Incident
#Fishing - Was a fishing boat dragged backwards by a submarine in the Irish Sea?
That's what the crew of an Ardglass prawn trawler are saying after an incident yesterday afternoon (Wednesday 15 April).
As the Belfast Telegraph reports, skipper Paul Murphy says the 60-foot wooden-hulled trawler was some 18 miles off the coast, near the Calf of Man, when something snagged its nets.
“Without warning, were were stopped and pulled backwards very violently at around ten knots which is the top speed of the vessel. I really thought that was it," he says.
"It was fortunate that one of the steel ropes holding the net snapped or we would have been pulled under very quickly."
Murphy says the scary episode only lasted a few seconds, but still managed to cause thousands of pounds' worth of damage to his fishing gear – and alleges that the culprit was a submarine.
The Belfast Telegraph has more on the story HERE.
It wasn't the only drama in the Irish Sea yesterday, as a coastguard helicopter was scrambled to rescue three from a fishing boat that sank off Wicklow.
Marine Wildlife News: Seals Returned To Wild, Dolphin Says Adieu, Irish Sea Life Revealed
#MarineWildlife - Cute by name, cute by nature: Sherkin, Buoy and Splash were returned to the wild after being nursed back to health by the volunteers at Seal Rescue Ireland.
As the Irish Examiner reports, the three young seals – rescued after tips from the public from locations in Cork and Kerry – were rehabilitated over the past three months at the new marine wildlife refuge in Courtown.
But they were finally fit to return to the open water last weekend at Fountainstown beach in Co Cork. The Irish Examiner has much more HERE.
As three return to Irish waters, another says adieu – as Clet the lone dolphin has now been spotted off the Dorset coast, according to the Bournemouth Echo.
Last spotted between Ireland and Scotland's west coast in December, the solitary cetacean first noted in French waters in 2008 appears to have completed a full loop around the island of Ireland.
Along the way he bypassed Dingle's famous resident Fungie and spent a few days in the company of fellow 'dolphina-non-grata' Sandy, also known as Dusty.
Now he's attracting the attention of locals at Portland, south of Weymouth, across the English Channel from his original splashing grounds.
Closer to home, conservationists in the the North West of England have released a video documenting the wealth of wildlife living in the Irish Sea as a reminder to political movers and shakers of the importance of its protection.
Groups such as the North West Wildlife Trusts have criticised Westminster for 'lack of ambition' over the past year since plans for a network of well over 100 Marine Conservation Zones (MCZs) were scaled back to just 27 approvals in November 2013.
More recently a further 23 MCZs were designated proposed, only two of which are out of out of seven proposals covering the waters between Britain's west coast and Ireland (updated Tuesday 17 March).
Bad Weather Causes Widespread Ferry Cancellations on Irish Sea
#CancelledSailings – Met Eireann has issued a status 'orange' warning of gale to storm force winds tonight on all Irish coastal waters, which have led to widespread cancellation of ferry sailings across the Irish Sea.
Passengers are advised to consult for up to date information as sailings are cancelled tonight and for tomorrow (January 15). For up to date sailing information, click the ferry operator websites listed below.
Those travelling with Irish Ferries, should also take note that in addition to cancelled conventional sailings, the operators Dublin-Holyhead 'Swift' fast-ferry crossings are currently not in service as Jonathan Swift is on scheduled annual maintenance.
She headed for dry-docking in Birkenhead, where Ulysses as previously on Afloat.ie is also undergoing annual overhaul.
Isle of Man-England services are also effected to the adverse weather, with Isle of Man Steam Packet sailings on the Douglas-Heysham route cancelled today.
Further disruption and cancelled sailings (subject to which crossing) also apply to sailings tomorrow (January 15).
To recap, passengers are advised to check latest sailing information from the following website links:
Irish Ferries, Stena Line, P&O Ferries and the Isle of Man Steam Packet Co.
For additional information details are available by visiting the AA's ferrywatch service HERE
For weather forecasts visit Met Eireann's coastal reports and sea crossing's forecast visit this LINK.