Displaying items by tag: Crosshaven
#RNLI - A major search was mounted on the south coast between Crosshaven and Kinsale on Friday (15 July) after a lone yachtsman broadcast a Mayday call that he was on the rocks at the Little Sovereign Rock.
Lifeboat pagers were activated at 12.07pm and both Crosshaven and Kinsale RNLI headed to the location, joined by Crosshaven Coast Guard and the Waterford-based Irish Coast Guard helicopter Rescue 117.
Conditions were poor on scene, with a fog reducing visibility to just 200m. Kinsale RNLI found no trace of the yacht at the Sovereigns, while Crosshaven RNLI searched the shore from Roberts Head west. Crosshaven Coast Guard stood offshore as a radio relay to Valentia Coast Guard.
The Crosshaven lifeboat crew eventually located the vessel aground in Rocky Bay. One crewmember swam to the yacht with a towline and retrieved the its anchor and line. The yacht was then refloated and towed into deeper water.
After handing off the tow to Kinsale RNLI, the vessel and its yachtsman were returned to Oysterhaven none the worse for wear.
Crosshaven Lifeboat Helm Appointed To RNLI Council
#RNLI - Crosshaven RNLI has announced that Ian Venner, a helm with the crew, has been appointed to the RNLI Council for Ireland as one of its 15 members.
Venner has been a member of the lifeboat crew and a helm since the station was re-established in 2000.
An accountant by profession and a keen powerboater, Venner replaces on the council well-known Cork businessman and sailor Peter Crowley, who after 10 years on the council becomes an RNLI vice president.
The RNLI Council acts in the interest of the RNLI in the Republic and Northern Ireland and makes recommendations and gives advice to the RNLI Board, the Council and the Executive Team concerning lifeboat matters.
RNLI Crosshaven Take Yacht off Beach in Cork Harbour
Crosshaven RNLI lifeboat launched at 10.53pm last night to a small yacht aground at White Bay on the East side of Cork Harbour.
At the scene, the crew found one person in the water attempting to hold the yacht off the beach in the swell and another person on the beach.
One RNLI crewman swam ashore to assess the situation and attach a towline to the yacht. As the casualties were cold and wet, they were handed into the care of Guileen Coast Guard unit for transportation, while the lifeboat brought the vessel to Crosshaven.
#RNLI - Crosshaven RNLI launched to reports of a man overboard from a visiting US Coast Guard cutter off Cork Harbour yesterday morning (Tuesday 24 May).
According to the station's Facebook page, the Crosshaven lifeboat was tasked alongside the local Irish Coast Guard unit and the Waterford-based coastguard helicopter Rescue 117 after the crewman fell overboard from the vessel conformed by gCaptain as the sail training barque Eagle.
However the operation was stood down shortly after launch as the tall ship mounted its own successful rescue of the casualty.
Eagle, which previously visited Irish waters in 2011, is expected in Dublin later this week before sailing to Britain and Portugal next month.
Cork Trawler Owner & Skipper Fined Over Safety Breaches
#Fishing - Out-of-date safety equipment has seen a Cork trawler skipper and owner landed with €4,000 in fines, as RTÉ News reports.
Pat O'Mahony of Kinsale and the Crosshaven-based Labardie Fisher Ltd pled guilty at district court in a case taken on behalf of the Minister for Transport, Tourism and Sport.
The former was convicted of having expired distress signals and hydrostatic life raft releases on his fishing trawler on 5 October last year.
Meanwhile, the trawler owner was fined on a charge of arriving in port with expired distress signals, and for failing to send the port superintendent a signed crew manifest as of 28 May last year.
The court heard that both skipper and owner, who lost 12 days of fishing during the investigation, co-operated fully during the process.
RTÉ News has more on the story HERE.
New RNLI Lifeboat for Crosshaven In Cork Harbour
The RNLI have announced the replacement of the Crosshaven Atlantic 75 class lifeboat “Miss Betty” with the newer and improved Atlantic 85 Class of lifeboat.
The new lifeboat is 8.5 metres long with extra load carrying space for stretchers and the ability to take an extra fourth crewman. The new boat will also carry RADAR, direction finding equipment , a full crew communication system and uprated Navigation equipment.
The new lifeboat will be named ”JOHN AND JANET “ and will carry the service number B892. The lifeboat is expected to arrive in May and the crew will go into extensive training to familiarise themselves with the new boat.
The funding of the JOHN AND JANET came from an anonymous legacy which stipulated that the funds were to be used
for a lifeboat and that it be named JOHN AND JANET.
Commenting on the new arrival, Patsy Fegan, Lifeboat Operations Manager said, “ Miss Betty has given Crosshaven and the harbour area 14 years of sterling service and not once has she let us down. Miss Betty will retire into the relief fleet and continue to save lives around the coast of Ireland and the UK. We would like to thank the Clayton Love family once again for funding Crosshaven’s first lifeboat in 2002. Whilst we will miss “Miss Betty”, we also look forward to the increased capabilities that the Atlantic 85 will give us in the saving of lives at sea”.
A naming and dedication service for the “JANET AND JOHN “will take place at the lifeboat station on Sunday September 11th next.
1720 Sportsboat Europeans Photos From Royal Cork (Day Three)
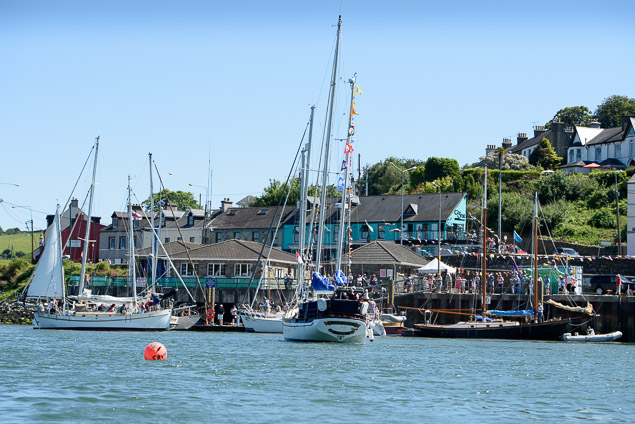
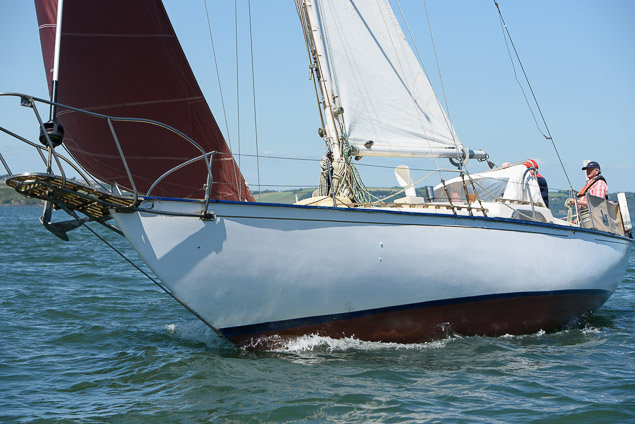
































#classicboats – A buoyant 65 entries graced Crosshaven's 20th anniversary Classic boats festival in Cork Harbour at the weekend. Boats ranging in size from Graham Bailey's 65–ft Sailing Luger 'Peel Castle', to Conor English's locally built 8 ft Rankin marked its significant birthday with a weekend programme of events on land and sea.
Brian Martin's recently restored gaff rigged cutter 1968 'Gillymoth' and Pat Dorgans Cork Harbour One design 'Elise' enjoyed the champagne sailing conditions on both days with a warm westerly breeze. Race officer Hugh Cassidy took full advantage of setting an inner Cork harbour course.
A number of boats came from outside the harbour including Cormac Levis's Saoirse Muireann from Ballydehob and Joanna Mary from Rosslare.
Ashore the pubs and restaurants in the village had sailing themes, costumes and food.
The gala fireworks on Saturday night were a huge success for the 20th celebrations.
Minister for the Marine Simon Coveney presented prizes on Sunday evening.





Crosshaven Lifeboat Rescues Teens From Homemade Raft
#RNLI - Six teenagers have been rescued by Crosshaven RNLI this morning (Tuesday 16 June) after a member of the public spotted them in the water and raised the alarm.
The volunteer lifeboat crew was requested to launch their inshore lifeboat at 6.10am following a report from the Irish Coast Guard that six teenagers, three male and three female, were on a homemade raft half a mile east of Crosshaven.
Weather conditions at the time were described as good but the tide was changing and going out rapidly.
The lifeboat, helmed by Gary Heslin and with crew members Vincent Fleming and Aoife Dinan onboard, was launched at 6.15am and was on scene three minutes later. The crew observed five teenagers on the raft while another was in the water trying to pull the raft ashore using a rope.
The crew proceeded to take the six – one of whom was cold – onboard the lifeboat and transport them safely back to Crosshaven Harbour where they were made comfortable in the lifeboat station.
"Time was of the essence this morning and we have to thank the vigilant member of the public who spotted the group and raised the alarm," said Heslin after the callout.
"While weather conditions were good the tide was starting to turn pretty fast and was pushing the group out to sea. Thankfully, all are now returned to shore and are safe and well.
"We would encourage anyone taking to the water this summer to always be mindful of tides and weather conditions and always carry a means of communications in case you find yourself in any difficulty."
Laser Ace Séafra Guilfoyle wins Royal Cork PY 500
#py500 – Séafra Guilfoyle has won the Royal Cork Yacht Club's PY 500 dinghy prize this afternoon. Only 8 seconds separated 3 dinghy classes at the finish writes Claire Bateman.
Saturday March 14 was the due date for the second annual PY 500 race at the Royal Cork Yacht Club. Well, what a story. The morning dawned with a beautiful blue sky and wonderful reflections in the clear water but alas and alack not a hint of a breeze could be felt and Race Officer Nathan Kirwan had no option but to postpone racing. As the race was to be held in the river, it was hoped to have a start an hour before high water but it was not to be. 'Experts' scanned the skies and ascertained that what clouds were there were moving slightly from the east. And so, when the light fickle breeze did fill in at 11.45am a windward/leeward course was set starting from the club marina with instructions for all boats to sail three rounds.
With a prize fund of €500 for the lucky winner and the ebb tide starting to flow more strongly the competitors were somewhat over eager and a general recall was necessary for the first start but all boats got away cleanly on the second attempt. The race had attracted an excellent entry of 38 but with the light wind morning this was whittled down to 32, still an excellent number. There was a great variety of craft on the water heading for the first mark ranging from National 18's, RS 400's, Lasers full rig, Laser Radials and Lasers 4.7, Toppers, an International 14, a 29er, a Pico, a Laser Stratos, a Finn and a brave Mirror and they all rounded the first mark without any incidents. They completed three rounds of the course and great concentration was needed in the light wind sailing but it proved to be a very enjoyable event resulting in only minor shouting between the competitors
When the results were calculated using the Portsmouth Yardstick only eight seconds separated the first three boats and indeed only three seconds separated the first two boats. Séafre Guilfoyle in a Laser full rig was the popular winner followed by a National 18 sailed by Nicholas O'Leary crewed by Michael O'Brien and Alex O'Connell, in second place and David Kenefick crewed by Grattan Roberts in an RS400 third .
Given the tightness of the results, one wonders what would have been the final placings if the two leading National 18's hadn't decide to concentrate between themselves on having a luffing match approaching the leeward mark in round 2, and who can tell whether or not this was where the vital three seconds between first and second place was lost. Neither they nor we will ever know for sure!















































































