Displaying items by tag: Irish Coast Guard
Airstrip is the Answer for Homeless Cleggan Coast Guard, Says TD
Cleggan Coast Guard in Connemara is long overdue a permanent base — and a local TD insists the village’s airstrip is the answer.
As the Connacht Tribune reports, Éamon Ó Cuív says it is unacceptable that the coastguard service for north Connemara has been seeking a fixed abode for so long.
A number of sites are being considered by the OPW — but Deputy Ó Cuív says none would be more suitable than the State-owned Cleggan Airstrip.
The Connacht Tribune has more on the story HERE.
Two Rescued From Cliff Face Near Howth’s Baily Lighthouse
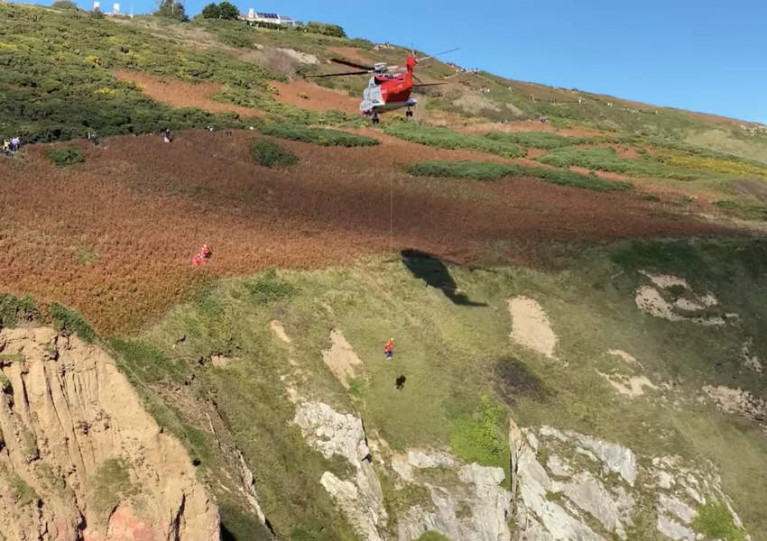
Two people — one with an injured ankle — were rescued by the Irish Coast Guard after getting stuck on a cliff near the Baily Lighthouse on Howth Head yesterday afternoon (Sunday 11 October).
Howth Coast Guard’s cliff team reached the scene just as the Dublin-based helicopter Rescue 116 arrived, and it was decided the helicopter crew would recover the casualties to the cliff top.
The winchman was lowered with a double hoist lift both casualties, which TheJournal.ie reports were an adult and a teenager, to the top and into the care of the cliff team.
The younger of the pair had sustained an ankle injury that was not thought to be serious, but as a precaution they were stretched to the nearest road to meet an ambulance crew fro transfer to hospital.
“This was a lucky escape for the two casualties,” said a coastguard spokesperson.
“Due to the quick response by the public in calling 999 and giving an accurate location of the incident, rescue teams were able to quickly deploy.”
Irish Coast Guard Issues Reminder On Planned Changes To VHF Channels
The Irish Coast Guard is reminding mariners of its planned changes to the VHF working channels currently used for communications with the public.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, upgrades of radio equipment at a number of remote locations around the coast will be made over a 10-week period scheduled to begin tomorrow, Tuesday 6 October.
Notwithstanding the changes, which are also outlined in the previous report, Channel 16 will remain available at each site for distress, safety and calling.
Channel 67 is also available when required but may not be actively monitored at all times.
Updates as the work progresses will be made on the coastguard’s social media accounts in Twitter, Facebook and Instagram as well as on the gov.ie and Safety on the Water websites.
Irish Coast Guard Saved Nearly 380 Lives In 2019, Says First Report On New National SAR Plan
The Irish Coast Guard saved 379 lives and assisted more than 3,500 people during the course of 2019.
The figures are included in the first annual report on Ireland’s National Search and Rescue Plan, which was published yesterday (Monday 21 September).
Also noted in the report, and is available to download below, the coastguard’s three rescue co-ordination centres managed a total of 2,500 incidents in 2019, broadly similar to figures for the previous two years.
And its fleet of Sikorsky S-92 rescue helicopters flew nearly 800 missions last year — the majority of these from its Sligo and Shannon bases on the West Coast.
“Given the additional challenges imposed this year by Covid-19, the report is a strong endorsement of the commitment and dedication of all those involved in search and rescue in Ireland,” said Minister of State Hildegarde Naughton, who published the report yesterday.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, the new plan provided for a National SAR Committee which for the first time brings together all key stakeholders in maritime, land and aeronautical SAR under an independent chair.
Among the key lessons from its first year is that Ireland “already had a very well established SAR system in being” when the review began in 2018 “and the fundamental integrity of this system must be protected even while seeking improvements in effectiveness, oversight and safety”.
Its work for the coming year is, among other things, to identify and monitor the system’s key performance indicators.
“The new plan represents a step change in how we do and oversee search and rescue in Ireland,” Minister Naughton said.
“One year on, I am very pleased with the progress including continued strong working relations between the Irish Coast Guard, the Irish Aviation Authority and An Garda Síochána who provide these vital services.”
More Details Emerge Over Emergency Beacon Incident Off West Cork Last Month
The Irish Coast Guard has revealed further details over an incident involving the activation of an emergency positioning beacon off West Cork last month.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, Baltimore RNLI was called out to search or the EPIRB which activated two nautical miles west of the Calf Islands on the afternoon of Wednesday 19 August.
Despite an extensive operation which also involved Schull Coast Guard, a coastguard helicopter and the Naval Service vessel LÉ Samuel Beckett, nothing was found and the search was stood down by early evening.
‘…it is highly unusual to have detections of the type that was encountered on 19 August’
In response to further enquiries from Afloat.ie, the Irish Coast Guard said the EPIRB in question, which was last detected at Coosnagulling on the southwest of Long Island, “did not appear to be fully functional and the homing signal was not active.
“It was not registered in Ireland and registration details were not available. It was not of Irish origin.”
Confirming that the search was terminated with “no further action being deemed necessary”, the IRCG added: “Accidental activations of EPIRBs are not unusual but it is highly unusual to have detections of the type that was encountered on 19 August.
“Every effort was made to locate the device both inland and on the coast but as outlined above, the search proved to be unsuccessful given the operational gaps in the information that was available.”
Changes Proposed For Irish Coast Guard VHF Channels
The Irish Coast Guard has proposed a series of changes to its VHF working channels later this year.
The move follows amendments to transmitting frequencies in order to harmonise the VHF maritime mobile band internationally, which also require the coastguard to upgrade its radio equipment at a number of sites.
These upgrades are expected to take place between Monday 5 October and mid December, with dates for the channel changeovers yet to be confirmed. The affected remote sites are listed below:
|
Site |
Radio Call Sign |
Current Channel |
New Channel |
|
Howth Hts |
Dublin Coast Guard |
CH 83 |
CH 03 |
|
Rosslare Hts |
Rosslare Coast Guard |
CH 23 |
CH 05 |
|
Mine Hd Hts |
Mine Head Coast Guard |
CH 83 |
CH 03 |
|
Cork Hts |
Cork Coast Guard |
CH 26 |
CH 02 |
|
Bantry Hts |
Bantry Coast Guard |
CH 23 |
CH 05 |
|
Valentia Hts |
Valentia Coast Guard |
CH 24 |
CH 62 |
|
Shannon Hts |
Shannon Coast Guard |
CH 28 |
CH 64 |
|
Belmullet Hts |
Belmullet Coast Guard |
CH 83 |
CH 63 |
|
Clifden Hts |
Clifden Coast Guard |
CH 26 |
CH 03 |
|
Malin Hd Hts |
Malin Head Coast Guard |
CH 23 |
CH 05 |
|
Scalp Mountain |
Malin Head Coast Guard |
CH 85 |
CH 01 |
|
Glen Hd Hts |
Glen Head Coast Guard |
CH 24 |
CH 03 |
The remaining sites of Carlingford, Wicklow, Mizen Head, Galway, Clew Bay, Donegal Bay, Galley Head, Lough Ree and Lough Derg will retain their currently assigned channel.
Channel 16 will remain available at each remote site for distress, safety and calling and will not be affected by these changes. Channel 67is also available when required but may not be actively monitored at all times.
As the upgrade work progresses, the Irish Coast Guard will inform the public that a channel has changed by the following means:
- By broadcasting on the channel that will be changing in the days leading up to the switchover
- The Irish Coast Guard’s social media accounts on Twitter, Facebook and Instagram.
- Updated information on the gov.ie website and the Safety on the Water website.
Further queries are directed to the coastguard at [email protected]
On Saturday morning (29 August) the Irish Coast Guard was called on short notice to carry out the high-priority transport of a child to the UK for urgent medical treatment.
The Waterford-based coastguard helicopter Rescue 117 was scrambled for the important mission, with the crew flying the little boy to RAF Northolt in north-west London.
From there the young patient was transferred to the city’s King’s College Hospital for a lifesaving organ transplant.
“This multi-agency operation saw many people and agencies involved,” the Irish Coast Guard said. “Well done to all those involved.”
Rescue 118 In Long-Range Medevac From Container Ship
Sligo’s Irish Coast Guard helicopter Rescue 118 was tasked yesterday (Friday 28 August) for a medevac from a container ship west of Tory Island.
The Sikorsky S-92 completed the 190-nautical mile round trip to retrieve the sick crewman from the MSC Sao Paulo for treatment on land.
Woman Rescued After Fall From Cliff At Mullaghmore Head
A woman rescued after falling from a cliff at Mullaghmore Head yesterday afternoon (Thursday 13 August) was “very lucky that she was spotted”.
The casualty was found unconscious at the bottom of the cliff on the Co Sligo headland by concerned passers-by who alerted the Irish Coast Guard.
Bundoran’s RNLI lifeboat volunteers and the Sligo-based coastguard helicopter Rescue 118 were both called out to the scene.
And the woman was treated by helicopter and ambulance crew before being airlifted to Sligo University Hospital.
Bundoran lifeboat crew member Rory O’Connor commented: “The casualty was very lucky that she was spotted and that the alert was raised so quickly.
“We would remind anyone that if they see anyone in trouble on the coast to ring 999 or 112 and ask for the coastguard.”
In the absence of this year’s Bray Air Display due to the coronavirus pandemic, the Irish Coast Guard’s Dublin-based helicopter Rescue 116 conducted a special fly-past to pay tribute to Ireland’s frontline healthcare workers.
The Sikorsky S92 helicopter took to the skies over the Co Wicklow town at 3pm yesterday, Saturday 25 July, on the same afternoon it flew to the rescue of a family of four stranded by the tide at Sandymount.
Rob Tatten, general operations manager of CHC Ireland, which operates the coastguard’s SAR helicopter service, was in attendance to make small presentation to Mr Paul Reid, chief executive of the HSE, and spoke before the event.
He said: “CHC, who operates the helicopter search and rescue contract on behalf of the Irish Coast Guard, has been taking part in the Bray Air Display every year. However due to the pandemic that wasn’t possible this year.
“But with the organisers of the show we said could we do something to recognise the phenomenal work of our fellow frontline healthcare workers, who like us continue to work 24/7, 365 days a year.
“So today, Rescue 116, while out training, will do a fly-past to thank those workers while we also make a short presentation to Paul Reid and other frontline workers to say thank you on behalf of CHC, the Irish Coast Guard, the aviation community and Bray Air Display.”