Displaying items by tag: Pat Kelly
Kelly Family are Sailors of the Month for June (Regatta)
Sailing is often promoted as a family sport for all ages. But if anyone doubts that this can be happily achieved with racing success thrown in, then they only have to consider the Kelly clan of Rush SC with their J/109 Storm.
Aboard Storm, the patriarch Pat Kelly heads a multi-talented crew which includes three generations of his family, and they clearly demonstrated they’d lost none of the successful touch shown in previous years by winning overall in June’s four-day Bangor Town Regatta on Belfast Lough.
Pat Kelly from Antrim Boat Club
The late Pat Kelly from Antrim Boat Club on Lough Neagh in Northern Ireland was known far and wide in Ireland.
His passing last week at the age of 85, less than a year since he last sailed, was acknowledged with great sadness by his many club associates, and the dozens he had sailed with and taught to sail and race over his years as a boat owner.
Pat began racing GP14s and Scorpions in the late Sixties and competed over about 12 years at every level from Irish right through from European to World championship.
In the Eighties, he moved to the Puppeteer Jelly Roll and with crew, Tom Molloy raced at East Down YC on Strangford Lough where he also raced the Impala Mipaal, in which he came second in the European championships. He competed in the Scottish Series in an Impala during the 1990s. The number of boats Pat has owned and sailed is impressive.
 Papagena Pat Kelly and Alfie Mayrs in the Howth Autumn League 2002
Papagena Pat Kelly and Alfie Mayrs in the Howth Autumn League 2002
During the Nineties we can add among the list, the One Tonner Commanche Raider at Carrickfergus, the Half Tonner Trinity, with Chris Boyd in Murphy’s Law at the ¼ ton cup , Fait Accompli and Quest. In 2003 Pat won the Howth Autumn League in the Puppeteer 22 Papagena.
His last race was the Cat’s Cradle inter Lough Neagh club event in September 2021 when he got line honours and the handicap win after a 20-mile beat in Fait Accompli from Antrim south to Kinnego, thus winning the trophy for Antrim BC yet again.
Jeff Harrison who crewed for Pat for nineteen years paid tribute. “My Dad taught me to sail but Pat taught me to race; he taught me to have fun doing it and also taught me in an almost lost tradition of how to do things within the ‘spirit of sailing. No one had more passion for sailing than Pat, he had the best feel for a boat of anyone I have sailed with, almost a sixth sense and he could keep calm in any tense situation”.
Jeff also said that at the age of 71 Pat qualified as a Dinghy Instructor and had the satisfaction of knowing that, over the years he had been sailing, he had given the opportunity to over 300 people to sail and race and indeed, had a list of the names of those people.
Pat leaves his wife Ruth, sons Graeme and Neil and daughter Lisa.
ICRA Hears Appeals for Greater Participation in Sailing
#SAILING – The tenth Annual ICRA Conference took place in Dun Laoghaire for the first time on 26th November in the same year ICRA was awarded the Mitsubishi Club of the Year trophy writes ICRA Commdore Barry Rose. It was a well attended event by a very representative group of sailors and club representatives from all Coasts of Ireland.

Barry Rose Chaired the ICRA Conference in Dun Laoghaire
The format this year created an inter active discussion in the morning session on Class Bands and the promotion of participation in Cruiser Racing in general. A lively, frank discussion took place with strong views being expressed by most present highlighting the problem of attracting crews to enable boats to go racing and creating access to allow those interested to go sailing to participate in the sport.

Des McWilliam spoke passionately about Irish sailing - Photo: Bob Bateman
Sailmaker Des McWilliam made a strong appeal that the future of the sport was threatened by difficulty in accessing getting afloat and sailing by the Club structures that were becoming more of a closed shop approach. Maurice O'Connell also spoke passionately on the same subject and examples were given of difficulties encountered both In Cork and Dublin in gaining access to participating in sailing and racing while boats were remaining tied up for lack of crews.
An understanding of the dilemma for the Clubs was also expressed by Flag Officers present in maintaining their facilities for those paying membership while encouraging new sailors to gain access at reasonable cost for a period.
It was agreed that all present would make every effort on a personal basis to encourage opportunities for those interested to go sailing to gain opportunities on boats and access to Club introductory offers.
ICRA will also explore creating an on line vehicle for available crews to register so boat owners gain opportunity to make contact.
There was also suggestions aired that bottom end of Class 1 should be included in Class 2 where all would have better racing.
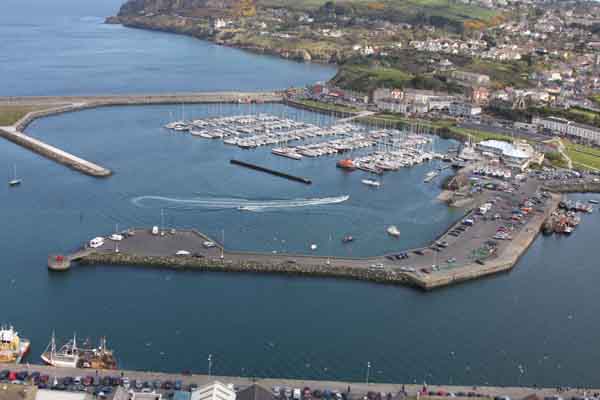

Howth, the venue for the 2012 ICRA Champs
The Royal Cork Yacht Club was complimented for running a top Class ICRA National Championships in June. Howth Yacht Club gave an update that arrangements are well progressed for an exciting ICRA National Championships in Howth 25th to 27th May 2012. The previous weekend will host the Corby Cup which will encourage those travelling to participate in Nationals and ISORA will run a feeder Race from Wales. It is hoped to announce a Sponsor shortly. Howth plan the first Race for 1600 hrs on Friday to avoid necessity for those travelling to stay over on Thursday.
The main feature of the afternoon session was a similar open forum with Race Officers Jack Roy, Henry Leonard and Harry Gallagher joining the top table for an open discussion on course types that sailors wanted and communications sailors would like with Race Officers. This was also a lively session with frank constructive exchanges which was of benefit to sailors and Race Officers alike.
The feeling of the meeting was that in addition to windward /Leeward courses sailors wanted a good variety of course types both at National Championship level but also at Regional events. Also those present strongly requested that boats over the line at starts be informed whenever possible but on strict understanding in Sailing Instructions that there be no redress in any circumstances relating to same against Race Officers.
Both these forums provided an excellent opportunity for those attending to air their views on all matters relating to Cruiser Racing and to offer ideas and this will be developed further for future conferences.

Commodore's Cup Captain Anthony O'Leary. Photo: Bob Bateman
The Commodore reported on efforts to form a team to defend the Commodore's Cup in 2012 and Anthony O'Leary brought the meeting up to date in changes to the event format and expressed confidence that there would be a positive response to ICRA 's request for declarations of interest to form a credible team to defend the Cup as is Ireland's responsibility.
Denis Noonan of Wicklow Sailing Club expressed the Clubs upset and disappointment that an Irish Club would arrange a competing event The Round Rockall Race from Galway starting on the same day as their Iconic Round Ireland Race. They outlined their plans for the 2012 Round Ireland Race and received support for their efforts from those attending. The RORC has increased their points scoring for the Round Ireland Race as further recognition of its standing in World offshore racing. Both ICRA and the ISA confirmed their support for the Round Ireland Race.

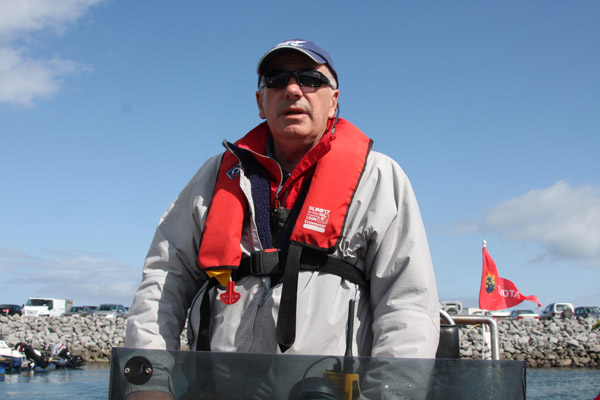
Pat Kelly's Storm is ICRA's Boat of the Year. Photo: Bob Bateman
The Conference finished with the presentation of the magnificent crystal ICRA Boat Of The Year trophy for 2011 to Pat Kelly's J 109 Storm who won the ICRA Nationals in Cork in June, The Cruiser Challenge in Dublin in August, The Howth Autumn Series and also travelled to the Scottish Series and Sovereigns Week. It was felt she embodied the spirit of a well campaigned ICRA cruiser racer. A week later Kelly became Afloat's Sailor of the month for November.
Sailors Plan Month Long Journey from Shannon to Liffey and Back
Nenagh resident and inland waterways enthusiast, Nick Theato, single-handed aboard 'Bo-Bo, a five metre Pedro trailer/sailer and Pat Kelly, Killadangan, with his son Andrew in 'Shu-Ra-Nu', a 6 metre Etap 20 trailer/sailer, plan to raise funds for Lifeboats Ireland by undertaking the IWAI Green & Silver Challenge in June, 2011. Their fundraising target is €5,000.00.
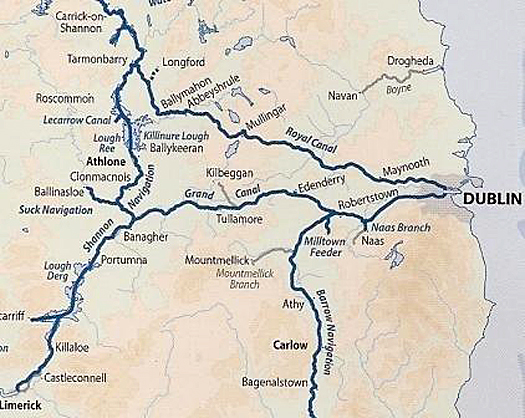
On the 25th June, 1946, Tom and Angela Rolt left Athlone aboard 'Le Coq', a 28ft.x8ft. converted ship's lifeboat on a voyage that would inspire contemporary and successive generations of inland waterways enthusiasts.
Tom Rolt wonderfully documented the voyage in his book 'Green & Silver', published in 1949, which has since become a classic. This work was instrumental in inspiring the small group who founded the Inland Waterways Association of Ireland in 1954, whose objective was to save the Shannon navigation from strangulation by low bridges. Indeed, the colour scheme of the IWAI's logo and burgee derive from the cover design of Rolt's book.
With the re-opening of the Royal Canal in October 2010, it is now possible to retrace Rolt's journey in full and complete the circular route formed by the Royal Canal, River Liffey, Grand Canal, River Shannon and Camlin River.
To celebrate this event, the IWAI has initiated the 'Green & Silver Challenge' in an effort to encourage people to make the circular journey. Nenagh resident, Nick Theato single-handed aboard 'Bo-Bo, a 16 foot Pedro trailer/sailer and Pat Kelly, Killadangan, with his son Andrew aboard 'Shu-Ra-Nu', a 20 foot Etap trailer/sailer, plan to raise funds for Lifeboats Ireland by travelling the full Green & Silver Route throughout June 2011.
Departing on June 1st, they will travel from Dromineer through Lough Derg and Lough Ree and enter the Royal Canal at Richmond Harbour. They plan to cross the Liffey in Dublin 17 days later, where they will take a welcome day off before commencing the return journey via the Grand Canal to Shannon Harbour. The journey will take approximately 28 days, will cover a minimum of 333 km. and navigate through 92 locks (some double), 91 of which are manual. Their fundraising target is €5,000
Nick Theato is Treasurer of the Lough Derg RNLI Fundraising Branch and Lough Derg Lifeboat Station at Dromineer.
Pat Kelly is Secretary of the Lough Derg RNLI Fundraising Branch.
Nick and Pat welcome all sponsorship, however modest. Contributions can be pledged online at http://www.mycharity.ie/event/green_silver_event/. Nick may be contacted on 086 1738014 ([email protected]). Pat is at 087 6908099 ([email protected]).
For further details / interviews / photos: Contact Pat Kelly at 087 6908099 ([email protected]). Support photography: Gerardine Wisdom 087 6522582 ([email protected]).

























































