Displaying items by tag: Green Dragon
Jamie Boag Honoured At Atlantic Youth Trust Gala
#JamieBoag - Volvo Ocean Race team commercial boss Jamie Boag was honoured for his contributions to sailing at the Atlantic Youth Trust's conference and dinner in Galway last weekend, as the Galway Independent reports.
The commercial director of Abu Dhabi Ocean Racing – winners of the most recent Volvo Ocean Race – received the trust's Lifetime Achievement Award for his work with its Irish-flavoured predecessor Green Dragon Racing, as well as his hand in bringing the world's most gruelling ocean yacht race to Galway.
Also on the evening last Saturday (12 March), the Galway Independent contributed €5,000 towards a seed fund to develop a bursary for youth sail trainees in the West of Ireland, along the lines of those already established in Drogheda and West Cork.
The day's conference also saw discussions and workshops on the trust's plans to build a new tall ship for Ireland, as previously reported on Afloat.ie.
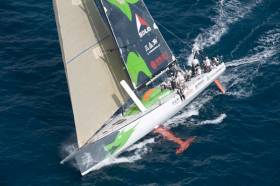
Green Dragon Available For Charter at Antigua Week
Regular Afloat readers will recall Green Dragon's departure from Dingle in County Kerry crewed by sea scouts last year but now after debuting in new colours at last October's Middle Sea Race, the 2008/9 Irish Volvo Ocean Race veteran is sailing around the Caribbean and is available to charter.
Miramar Sailing based in Antigua has places available on Green Dragon at the forthcoming 49th edition of Antigua Sailing Week.
From Russia to Australia, yachts and crew from over 20 nations will be competing in the regattta.
Green Dragon was specifically built as the Irish entry in the 2008-2009 Volvo Ocean Race, in which she finished fifth of seven. In 2012 she took line honours in the Round Ireland Race.
Miramar sailing took delivery of the Irish yacht last September
The Volvo Ocean 70 (also known as the Volvo Open 70) is the former class of racing yachts designed for the Volvo Ocean Race. It was first used in the 2005–06 race (replacing the Volvo Ocean 60 yachts which were first used in 1993) and use a Canting keel which is capable of canting transversely up to an angle of 40 degrees.
VOR Roundup: Abu Dhabi Returns, Puma Quits Sailing
#VOR - Abu Dhabi will return to the Volvo Ocean Race in 2014-15 both with a sailing team and a stopover in the UAE capital, it was announced earlier this week.
Once again skippered by Ian Walker, the team is the third confirmed entrant in the 12th edition of the round-the-world yacht race, after the all-woman Team SCA and a team representing the Brazilian state of Pernambuco.
The Abu Dhabi team joined the last edition of the race under the auspices of former commercial director David Hassett, who was previously instrumental in bringing the race to Galway for the first time in 2009, and was one of the team behind Ireland's underdog entry the Green Dragon, which surprised the yachting world by clinching three podium finishes.
Meanwhile, the stopover will be the end point of Leg 2 from Recife in Brazil, making for "one of the longest and most challenging in the 40-year history of this race" according to Volvo Ocean Race CEO Knut Frostad.
"Heading into the Southern Ocean is never easy and this route will test the sailors to the limit," he added. "The finish line in Abu Dhabi will be one of the most eagerly awaited in the race.”
The news comes two weeks after Newport in Rhode Island was announced at the sixth host port of the race - and an understanding that no Irish ports will feature in the final route, according to The Irish Times.
Elsewhere, the VOR website visits the Persico factory in Italy in where the hulls are being completed for the new design VOR 65 in its latest video update - and also takes a look at the construction of the rigs for the new boat at Southern Spars in New Zealand.
In other news, it's emerged that Puma is pulling out of the sailing market, cutting its support for the Oracle team in the America's Cup and permanently dry-docking its Volvo Ocean Race team.
Reuters reports that the decision was made in the face of dwindling profits at the German sportswear brand.
Puma came third in the last edition of the VOR, which has its successful climax in Galway last summer.
#VOLVO OCEAN RACE - Former Paralympic sailor and Irish National Helmsman’s Champion Feargal Kinsella will realise the dream of a lifetime when he sails on a round-the-world racing yacht in Galway as part of the Volvo Ocean Race festivities tomorrow Saturday 7 July.
The story of Feargal’s triumph over physical disability has touched the hearts of millions in recent radio and television interviews, and tomorrow morning he will finally get to fulfill one of the ten things he most wants to do in life.
"I just want to get my hands on the helm of one of the fastest and most powerful sailing boats in the world and I am absolutely thrilled that I may be able to do that on Saturday when I will join the crew of the Green Dragon on Galway Bay.”
The Green Dragon was the Chinese-Irish entry in the last Volvo Ocean Race and as part of the festival organised around the arrival of the VOR fleet in Galway, Feargal has been invited to sail it on the bay - fresh off its challenge in this year's Round Ireland Race.
A keen sailor who had sailed in many international sailing events including Fastnet and the Round Ireland Races, Feargal broke his neck in 1996. Looking back at that time. Fergal was convinced he would never sail again.
“After my first spinal injury, in 1996, my life and that of my family were thrown into turmoil. After nine months in hospital, I left in a wheelchair, paralysed from the chest down and convinced I would never sail again,” he said.
However, the Portmarnock man did take up sailing again, competing in the National Disabled Sailing Championship, the ISA Champion of Champions and representing Ireland in the 2004 Paralympics in Athens. He also won the Irish National Helmsman’s Championship in 2001 against able-bodied sailors.
A second spinal injury this Christmas saw Fergal break the fourth, fifth and sixth cervical vertebrae in his spine. Following an operation on Christmas Day, Feargal has spent the last few months at the National Rehabilitation Hospital in Dun Laoighaire recovering.
One of the many things Feargal learned from recovering from his last injury is the importance of having goals.
“They're not all achievable,” he said, “but a person should have something to strive for. In my case, I now have a short list, to which I'm adding as I go, of things that I should most definitely do now that I have been given something of a second chance.”
High on Feargal’s list is sailing on a fast yacht. As he said himself: “The idea of actually having a sail on one of those magnificent sailing machines is just so exciting."
Feargal’s dream will finally come true tomorrow when he takes to the water with the crew of the Green Dragon.
Round Ireland (Thurs 3pm). Can Inis Mor do it?
#roundireland – While the official tracker has Inis Mor as the overall leader in the 2012 Round Ireland Race, it's going to be a nail biting few hours for the French boat.
As of 3pm, Inis Mor has 30.6 miles to go. To beat Tonnerre she needs to cover that distance in five hours and 34 minutes. Simple math says she needs to average 5.49 knots and as she is making 5.7 knots just south of Lambay Island, it should work for her.
But, the 5.7 knots is not quite in the right direction – because the wind has headed her, she can only make 221° instead of the 190° she needs to reach Wicklow on one tack. So while 5.7 knots looks good, her actual progress towards the finish or VMG, is currently 5.4 knots – just outside the 5.49 knots needed.
To make matters worse, she is entering an area of stronger tides that will be directly against her for the last few hours into Wicklow. She can mitigate some of this by hugging the coast, but at what cost windwise?
Fascinating stuff, www.afloat.ie's money's on Tonnerre, at least in this battle. Keep an eye on Cavatina though – she still has a day left to win!
#roundireland – Inistrahull, or more accurately, Tor Rocks, a sea mile or so to the north, is the most northerly point on the Round Ireland Race Course rhumb line. Green Dragon, saddled with the burden of being the biggest boat in the race, was once again struggling to get deeper as the wind backed into the southwest as she rounded at 1930 this evening. Not only was the direction unfavourable but she now faces lighter breezes entering the tidally challenging North Channel.
DOWNLOAD CURRENT 9pm Tuesday LEADERBOARD BELOW
Behind her, the battle for overall leader continues with Tonnerre De Breskens briefly taking over from Inis Mor, which has lead almost from the start. However, the initial gains may well be all for nought, as the bulk of the fleet, off the Connemara coast, are enjoying stronger breezes, and catching the bigger boats rapidly. It is one of the delights of this great race that it can start and restart several times along the coast and the Rathlin/North Channel tidal gate could well determine the overall honours.
While it means little to publish the current leaderboard, the table below shows that the leading group have stretched out a bit, while there is considerable bunching with only two hours separating 9th and 22nd. No doubt many of the yachts will suffer from a hole or two over the next 24 hours or so and we may well see some anchoring during the same period.
So, while the Irish Open Golf competitors can look forward to low scores as the fleet heads past the Portrush course, the Round Ireland sailors will not be setting any records this time
#roundireland – Round Ireland race organisers have confimed Ireland's former entry in the Volvo Ocean Race, 'the Green Dragon', will sail in Sunday's Round Ireland yacht race from Wicklow Sailing Club as one of the biggest entries in the race.
Wicklow SC say the 70-foot sloop will be raced by an 'amateur crew' but any other details of arrangements for the race are yet to be made public. Afloat.ie understands Green Dragon's crew are made up of a consortium of Dun Laoghaire yachtsmen.
In a post on its race website Wicklow officials say the Volvo 70 had arrived in Dun Laoghaire marina from Alicante in Spain to finalise preparations for her Round Ireland competition against an international fleet of 36 yachts, many from the UK.
The Reichel Pugh designed canting keel yacht was built in 2008 and competed in the 2008/09 Volvo Ocean Race under British skipper Ian Walker where she finished fifth out of seven starters.
Wicklow Sailing Club Commodore John Harte said: 'It will be great to have such an iconic yacht such as the Green Dragon in the Round Ireland Yacht Race. She will be a very impressive spectacle on the start line'.
The yacht has been stored in Galway since the end of the last VOR race before being moved to the continent for a number of promotional engagements including the VOR Legends Regatta.
Green Dragon is set to be involved in a number of initiatives as a youth academy boat.
New 'Green Dragon' Sailing Academy Targets Youth Sailors
In what is being termed 'a major initiative' for young Irish sailors the Green Dragon Academy has been launched to use a second generation Volvo Open 70 and Ireland's entry in the 2009 Volvo Ocean Race as a platform to discover the next generation of Irish offshore sailors.
'Our mission focuses on the 18–30yr old Irish sailors who are looking to forge a career in this niche sector within sailing' says project director Cillian McGovern. 'The Green Dragon is an ideal platform from which to gain invaluable exposure to the level of seamanship required to sail at the highest level' he adds.
With only eight of this class in operation, six of which are currently competing in the Volvo Ocean Race, the opportunity presented, cannot be understated', says McGovern.
At present, the boat has been hauled out of the water in Alicante and is being serviced in advance of the upcoming sailing season.
Late in 2011, the Green Dragon left Galway, where it had been safely stored for two years, and was sailed to Rotterdam. From there, it was loaded onto 3 trucks and travelled 270+ miles through Germany to Frankfurt where it was Volvo's showpiece at the Frankfurt Motor Show. After the motor-show, it was sailed to Alicante via Southampton, Cascais and Cadiz.
The highlight of which was a 24-hr between Cowes and Finisterre at an average speed of 19knots, with a crew of 8 sailors, all of whom were under 30.
The Green Dragon was present in Alicante for the Legends Regatta, enjoying a healthy duel with Telefonica Black before the Spanish boat, crewed by Olympic sailors pulled away.
The Legends Regatta was of great benefit to the young Irish sailors on board who gained great knowledge from the Whitbread/Volvo Legends on board, notably: Joe English, Bouwe Bekking and Jerry Kirby, not to mention, leading Open 60 designer, Merf Owen from Owen Clarke Design.
The forthcoming sailing season will see the Green Dragon Academy sail to Lisbon for the Volvo Ocean Race stopover, sail to Dublin and train out of the Royal Saint George Yacht Club before sailing to Galway for the Grand Finale of the Volvo Ocean Race.
Green Dragon Crew Say 'Ola' from Alicante!
#VOLVO OCEAN RACE – Ireland's Ocean Race Green Dragon is basking in Spanish sunshine and settling into her new role as a 'legend' as our photo from Alicante shows below. The photo was taken before she left the dock for the first race in the Legends Regatta. Can you spot some famous Irish sailing faces? (Answers below!) Her core sailing crew is all Irish and under 30, her skipper is a 28–year old Kiwi, bearing out the youth development possibilities of this Irish owned Volvo 70 design.

The 'Legends' or past Ocean Race sailors on the Dragon are:
1. Joe English.
2. Harry Cudmore.
3. Kilian Bushe.
4. Bouwe Bekking.
5. Jerry Kirby.
6. Chris McLaughlin - arriving tonight.
7. Merfyn Owen - Owen Clarke design.
Could Green Dragon be Ireland's Next Youth Boat?
Support is needed, say Galway organisers to put the 70-footer into a youth development role. Her real value is in doing this, says Galway's Enda O'Coineen and such use is of 'much greater than her market value'.
The boat, under British skipper Ian Walker, failed to meet expectations in the 2008-9 race when it was discovered that the boat's keel bulb was too light. It did however get a rapturous welcome into Galway for the port stopover in May 2009.
In the longer term Galway owners are still trying to figure out what to do with the vessel but some youth development role is touted as a favourable option.
Just how this might come about or how inexperienced hands could master such a high tech vessel has yet to be revealed, however.
The Chinese built boat came out of storage this summer and VOR organisers have been putting it to good promotional purposes on the Continent.
Green Dragon is now in Spain and will represent Galway in this month's VOR 'Legends Regatta' in Alicante. It is sailing with a young Irish crew.
The regatta is another marketing opportunity for the boat that might yet throw up a buyer.