Displaying items by tag: survey
Marine Notice: Extended Cable Route Survey Off West Coast
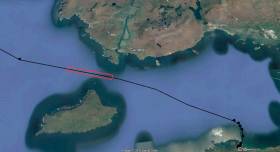
#MarineNotice - Fugro will be carrying out further marine operations on behalf of TE Subsea Communications LLC for the HAVFRUE Subsea Cable System Project south of Achill Island from this week.
The operations are an extension of the project outlined in Marine Notice No 22 of 2018 and are scheduled to be carried out between Saturday 13 July and Saturday 17 August, to last for approximately one day weather permitting.
Works will be undertaken by the RHIB Diversity (Callsign: EI-SV-7), which will be towing equipment such as a magnetometer and a side scan sonar to be used during the shallow water phase, from 50m of water depth and shallower.
Survey operations will be conducted on a 24-hour basis. The vessel will display shapes and lights prescribed in the International Rules for the Prevention of Collisions at Sea (COLREGS) Rule 27, to indicate that the survey vessel is restricted in its ability to manoeuvre. A listening watch will be maintained on VHF Channel 16.
Details of the location of the project are outlined in Marine Notice No 29 of 2018, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
2018 Anglerfish & Megrim Survey Begins Today
#MarineNotice - The Marine Institute’s annual Irish Anglerfish and Megrim Survey (IAMS) for 2018 is scheduled to resume today, Tuesday 10 April.
After January's survey off the West and South Coasts, this month's survey will be carried out till Saturday 21 April off the North and North West Coasts of Ireland in fulfilment of Ireland’s Common Fisheries Policy obligations.
The IAMS is a demersal trawl survey consisting of approximately 50 otter trawls of 60 minutes duration in ICES area 6a. Fishing will take place within a three nautical mile radius of the positions indicated in Marine Notice No 15 of 2018, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
Survey operations will be conducted by the RV Celtic Explorer (Callsign EIGB), which will display all appropriate lights and signals during the survey and will also be listening on VHF Channel 16.
The vessel will be towing a Jackson demersal trawl during fishing operations. The Marine Institute requests that commercial fishing and other marine operators keep a three nautical mile area around the tow points clear of any gear or apparatus during the survey period outlined above.
Specifics of any fishing gear or other obstructions that are known and cannot be kept clear of these survey haul locations can be notified using the contact details provided in the Marine Notice.
Marine Notice: Cable Route Survey In Irish Territorial Waters
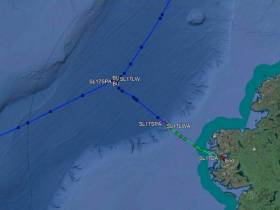
#MarineNotice - Fugro is currently carrying out marine operations for the HAVFRUE Subsea Cable System Project, further to its work carried out in January.
The current survey within Irish territorial waters off the North West Coast began on Wednesday 14 March and is expected to run till midweek next week.
The MV Fugro Discovery (Callsign 3EKE6) is surveying on Segment 2 within Irish EEZ waters towards the 1,500m contour line at the shelf, followed by operations at the BU1 position and Segment 3 as indicated on the charts included with Marine Notice No 10 of 2018, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
Marine Notice: Irish Anglerfish and Megrim Survey 2018 Off West, Southwest and South Coasts
#IAMS2018 - The annual Irish Anglerfish and Megrim Survey for 2018 (IAMS 2018) will be carried out between Monday 19 February and Monday 19 March off the West, Southwest and South Coasts of Ireland, in fulfilment of Ireland’s Common Fisheries Policy (CFP) obligations.
The IAMS is a demersal trawl and beam trawl survey consisting of approximately 85 otter trawls (60 minutes) and 25 beam trawls (30 minutes) in International Council for Exploration of the Sea (ICES) area 7b, 7c, 7g, 7h, 7j and 7k. Fishing in 2018 will take place within a 3 nautical mile (nmi) radius of these indicative positions.
The survey will be conducted by the RV Celtic Explorer (Callsign EIGB), which will display all appropriate lights and signals and will also be listening on VHF Channel 16 for CE18004. The vessel will be towing a Jackson demersal trawl or two four metre wide beam trawls during operations.
The Marine Institute requests that commercial fishing and other marine operators to keep a 3nmi area around the tow points clear of any gear or apparatus during the survey period.
While there is no statutory provision for the loss of gear at sea, the Marine Institute will make every effort to avoid gear adequately marked, according to legislation, that may be encountered in the notified areas.
In the event that an operator has static gear or other obstructions within 3nmi of the listed points, it is the responsibility of the owner to notify the survey managers or vessel directly.
This should be communicated by identifying specifically which ‘station’ is of concern using the appendix and contact details provided in Marine Notice No 03 of 2018, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
Marine Notice: Cable Route Survey Off North-West Coast
#MarineNotice - Fugro will be carrying out marine operations on behalf of TE Subsea Communications LLC for the HAVFRUE Subsea Cable System Project from this weekend.
The survey project is scheduled to begin on Saturday 20 January and last for around 14 days, weather permitting, as conducted by the MV Fugro Discovery (Callsign 3EKE6).
Survey operations will be conducted on a 24-hour basis. Throughout, the vessel will be displaying the shapes and lights prescribed in the International Rules for the Prevention of Collisions at Sea (COLREGS) Rule 27, to indicate that the survey vessel is restricted in its ability to manoeuvre.
A listening watch will be maintained on VHF Channel 16, and the vessel will actively transmit an AIS signal.
The survey comprises a dynamic programme to be conducted in several stages. The survey vessel will be deployed within the working area at times and positions determined by client requirements, weather and sea conditions.
Co-ordinates of the survey area are included in Marine Notice No 02 of 2018, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE. Please note that the survey within Irish territorial waters as indicated is not part of this notice and will be undertaken at a later date under separate notification.
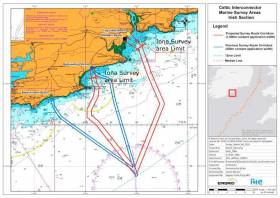
#MarineNotice - The survey vessel Kommandor Iona is conducting offshore survey operations associated with the proposed Celtic Interconnector, on behalf of EirGrid.
As with last month’s nearshore survey, the current works are in two main corridors to three landfall points off the South Coast of Ireland, namely Ballinwilling Strand, Redbarn Beach, Claycastle Beach.
The Kommandor Iona (Callsign: GAAK) was scheduled to begin operating on a 24-hour daily basis since this Tuesday (24 October) for approximately a week’s duration, collecting geophysical data utilising vessel mounted sensors and towed sonar extending up to 200m from the vessel.
The survey will be conducted under Foreshore Licence FS006722 in the deeper waters offshore from the Iona survey area limits.
Survey activities will extend no more than 35km from the shoreline within a 500m area or corridor centred on the co-ordinates listed in Marine Notice No 47 of 2017, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
Those engaged in fishing are respectfully asked not to leave any static fishing equipment within a distance of 250 metres of the proposed survey route centre lines as detailed in the route position list, and skippers are advised to withdraw and keep beyond a safe distance (1 nautical mile) from survey vessels.
Marine Notice: Nearshore Survey Operations For ‘Celtic Interconnector’ Project
#MarineNotice - RMS Submarine Ltd advises that they will be conducting nearshore survey operations associated with the proposed Celtic Interconnector on behalf of EirGrid, at three coastal locations in Co Cork — namely Ballinwilling Strand, Redbarn Beach and Claycastle Beach.
The survey vessel Severn Guardian (Callsign 2FGL5), an 18m catamaran coastal survey vessel, will operate on a 12-hour daily basis, in daylight hours only, commencing from today (Thursday 28 September) for the next two weeks, approximately. Common frequency VHF Channel 16 shall be used throughout the project.
This survey is to collect geophysical data utilising vessel mounted sensors and a towed sonar which will extend up to 100m from the vessel. The survey will be conducted under Foreshore Licence FS006722, as per the foreshore licence map included in Marine Notice No 41 of 2017.
The nearshore survey activities will extend no more than 5km from the shoreline, within a 1km area or corridor centred at each of the three coastal locations. The remaining offshore sections will be surveyed by a separate vessel in the coming months, for which a separate notice to mariners will be issued.
Full details of co-ordinates of the work areas and more are included in Marine Notice No 41 of 2017, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
Fish Stock Survey On Lough Ennell This Week
#Angling - Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI) is currently carrying out a fish stock survey on Lough Ennell, near Mullingar, to assess the current status of the fish populations in the lake.
The survey takes place from today (Tuesday 19 September) till the Friday (22 September) and will involve netting throughout the lake undertaken by IFI staff from Limerick and research staff from Citywest headquarters crewing a total of two boats.
It’s expected that the survey will provide a range of information on the fish stocks in the lake, such as size distributions of fish captured, age and growth information for all species, diet of selected species, and catch per unit effort (CPUEs) for each fish species.
Samples for genetic analyses of brown trout and pike will also be taken. The information collected will assist IFI in managing, conserving and monitoring any changes in the fish stocks of the lake.
The survey crews will be very visible on the lake and all sets of nets will be marked with distinctive buoys labelled ‘IFI Survey’. Any anglers or other lake users are asked to be vigilant if out and about on the lake to avoid snagging in the nets.
Further details on the background of this survey are available on the IFI website.
#InlandWaters - BirdWatch Ireland is appealing to users of Ireland’s inland waterways to get involved in its survey of river birds in man-made structures.
Ireland supports a rich and diverse network of rivers, canals and other waterways. Though often difficult to access, these sites are regularly visited by tourists, anglers, canoeists and other recreational users.
If you use our national waterways this summer, you can help by recording any river bird nest sites you encounter.
With support from the Heritage Council, Birdwatch Ireland is specifically looking for sightings of birds nesting in or on man-made structures – for example, dippers nesting under bridges, sand martins in quay walls, grey wagtails in holes in old mill walls or kingfishers in artificial banks.
If you are out on one of our fantastic waterways, please keep an eye out for the nesting activity described above.
If you do observe nest site, please submit a record on Birdwatch Ireland’s website. All you need are a few details (location, etc) and you can also add a photo of the site if you managed to capture one.
Marine Notice: Annual Monkfish & Megrim Survey
#MarineNotice - The latest Marine Notice from the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport (DTTAS) advises that the Marine Institute is carrying out its annual Irish anglerfish and megrim survey (IAMS 2017) in fulfilment of Ireland’s Common Fisheries Policy obligations from this Tuesday 14 February to Friday 17 March.
The IAMS is a demersal trawl and beam trawl survey consisting of around 85 otter trawls (60 minutes) and 25 beam trawls (30 minutes) in International Council for Exploration of the Sea (ICES) area 7b, 7c, 7g, 7h, 7j and 7k off the West, South West and South Coasts.
Fishing in 2017 will take place within a three-nautical-mile radius of the positions indicated in Marine Notice No 5 of 2017, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
The survey will be conducted by the RV Celtic Explorer (Callsign EIGB), which will display all appropriate lights and signals during the survey and will also be listening on VHF Channel 16.
The vessel will be towing a Jackson demersal trawl or two 4m beam trawls during operations. The Marine Institute requests that commercial fishing and other marine operators to keep a 3nm area around the tow points clear of any gear or apparatus during the survey period outlined above.
While there is no statutory provision for the loss of gear at sea, the Marine Institute will make every effort to avoid gear adequately marked according to legislation that may be encountered in the notified areas.
In the event that an operator has static gear or other obstructions within 3nm of the points listed, it is the responsibility of the owner to notify the survey managers or vessel directly.
This should be communicated by identifying specifically which ‘station’ is of concern using the appendix and contact details provided in the Marine Notice. It is not required to provide positional details of commercial operations beyond 4nm of the survey points provided.
Specifics of any fishing gear or other obstructions that are known and cannot be kept clear of these survey haul locations can be notified using the contact details provided.