Displaying items by tag: Cruiser Racer
ICRA Sponsor Offers 'Free Model Truck' As Entry Incentive for Royal Cork National Championships
As ICRA ramps up its promotion for the Cruiser–Racer National Championships at Royal Cork Yacht Club in June, fleet sponsor WD40 is offering a free 'collectors item' model truck to the next six entries received.
The RCYC entry list is certainly hotting up. 2016 ICRA National Class Champions Jump Juice, Joker II, Checkmate XVII and Cartoon will all be back defending their national titles in Crosshaven in June.
Red more about how the coming season is shaping up in Class zero and one here and class two here.
Enter online for the ICRA Nats here.
ORC Interest From Ireland at the ICRA Conference
At the annual meeting of the Irish Cruiser Racing Association (ICRA) in Limerick last weekend, past president Norbert Reilly invited representatives from the Offshore Racing Congress (ORC) to address the assembled crowd of over 60 delegates on features of ORC’s rating systems. Here the ORC's Dobbs Davis gives an overview of the Irish presentation.
The interest from ICRA is in response to the recent growth and popularity the ORC system has seen in recent years around the world: the system issued over 10,000 certificates in 2015 in some 40 countries, has been growing yearly while other international systems are struggling, and yet its not in use at all in Ireland.
What the delegates saw was a presentation on the history of the organisation, which goes back over 40 years into the IOR era, over a decade in IMS, and is now emerged as an improved and accessible science-based system suited for a wide variety of boat types that generates three distinct styles of rating certificates: ORC Club, ORC International, and ORC Superyacht. Of the 15,000 measurement-based certificates issued around the world, two-thirds are issued by ORC in one of these three formats.
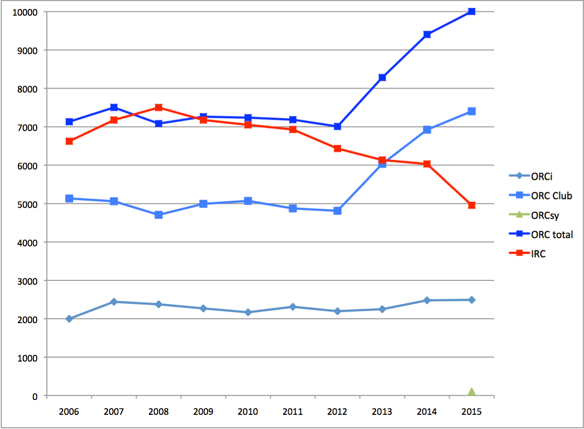
A plot of the growth of ORC contrasted to IRC in the last 10 years
There are five salient features of the system: that it is objective and science-based, it is open and transparent to use, it is accessible online, it is flexible with a variety of scoring styles suited for different types of racing, and that its affordable.
The objectivity comes from use of a sophisticated Velocity Prediction Program (VPP) which through input of measurements of a boat’s hull and appendage profiles, its rig and sail dimensions and other inputs, can calculate the boat’s theoretical speed in a variety of conditions of wind speed and wind angles. To remain relevant to modern designs and improve the methods used in the VPP calculations, it is developed continuously by experts on the International Technical Committee (ITC), which includes talent such as Andy Claughton from the Wolfson Unit at Univ. of Southampton (and now the BAR AC programme), designers Jason Ker, Shaun Carkeek, and others from Farr Yacht Design, Judel/Vrolijk and others.
In fact, the ITC is meeting soon in Annapolis USA to discuss improvements in a variety of areas in response to inquiries from users. This is an important feedback loop that ORC has to continually seek to improve the accuracy of its system. The ORC VPP and its rules are not secret, and are available for download at the ORC website (www.orc.org).
Because the system is open and transparent, ORC has worked hard to make it as accessible as possible to its users. All valid ORC Club and ORCi certificates issued since 2009 are available from ORC’s unique portal to its rating system, the ORC Sailor Services. After registering for a free log-in credential, anyone can access these certificates for free, as well as some 88,000 measurement records that date back 20 years into the IMS era. The searchable database can be used to research the measurements and ratings for any boat in the system, run a test certificate on the current ORC VPP, run a Speed Guide report of the polar performance of the boat or a Target Speed report of the boat’s polar speed targets on a windward-leeward course.
The system also has an edit function that allows a boat’s measurements sails, spars, or crew weight to be changed so that test certificates can be run to explore the effects of these changes on rating. Test certificates are not valid for racing, but can give the user insight on how to optimise their boat for performance…most systems discourage this with limits and high costs placed on test certificates, but ORC’s open approach allows this to better educate its users on their set-up options.
Because the “rating” for a boat is in fact a matrix of speed values generated by the VPP, ORC’s scoring options are varied for use by race organisers: they can be very simple, where all wind angle and wind speed predictions are condensed into a single number, or quite complex, where inputs of wind angle and course length are used to model the boat’s speed around the course, and their corrected time is calculated based on their relative performance to their competitors on this course.
There is also a hybrid approach, called Triple Number, where for either an inshore or offshore course the ratings are expressed as a function of Light, Medium or Heavy wind speeds. This is a very common scoring style used in ORC Club fleets.
Because ORC uses numerous measurements of a boat’s hull, rig and sails, and there are a variety of scoring options available for race managers, there is less tendency for type-forming rating bias in specific designs such as seen in other single-number systems. This allows the system to be more fair across a wide spectrum of boat types and styles, and the test fleet used to evaluate the system is comprised of some 1500 different designs. It’s thus less relevant to label a boat as being “an ORC design” like is typically seen in other systems.
Proof of this can be seen in the results of the highest-level ORC Championships, the Worlds and the Europeans: recent podium finishers have been not only top-level pro teams sailing on full-race boat types, like TP 52’s, GP 42’s, etc, but well-prepared teams racing production dual-purpose designs as well, such as Swan 42’s, Swan 45’s, X-41’s, X-37’s, etc. The racing at ORC championships is popular – over 100 entries from over 20 countries in the last 5 years at the Worlds – and its close: races are often won and lost by mere seconds in corrected time.

The ORC 2015 World Championships off Barcelona
This year’s ORC World Championship will be in Copenhagen at the Royal Danish YC over July 15-23, and the ORC European Championship will be over July 3-10 in Porto Carras, Greece. There are already 130 entries are signed up for the Worlds, which promises to be another great week of inshore and offshore racing.
The ease and affordability of ORC certificates is determined by the policies and prices set by national rating offices, who are not centrally controlled but have all the tools needed to generate their own ORC certificates for their local customers.
Response to the talk on ORC was generally well-received by the ICRA audience, with particular interest from the fleet in Dublin Bay to try some ORC Club certificates and look at some dual-scoring exercises in the coming season. The attraction expressed to use of ORC is being able to have multiple scoring options to differentiate more fairly across varied boat types in the same race, and the general openness and objectivity of the system.
Dobbs Davis is ORC Media Consultant
Read also: Crazy But It Works: ICRA's Success Is a Highlight of Irish Sailing Scene
ICRA Commodore Appeals for Cruiser Conference Support this Saturday
#icra – ICRA Commodore Nobby Reilly has issued a last minute appeal for support for Saturday's ICRA conference at the Royal Irish Yacht Club, urging cruiser sailors to help recruit more people to the sport of cruiser racing. It follows a campaign launched in 2013 where ICRA recruited up to 300 for day sails at Howth Yacht Club last April.
The day long conference on Saturday will hear from keynote speaker Matt Sheahan on foiling at the America's Cup and Philip Bendon and his Irish Match Racing Irish Team who earlier this season won the U23 European match racing championships.
There will also be news on a Commodore's Cup Team Up Date, Crew Training Programme: Comprehensive Modules for all clubs, a Crew Point: Plan to link Crew to Boats in your club and an ICRA Club Rep Role.
New ICRA Commodore Aims to Recruit New Crews to Boost Sailing
#ICRA – The Irish Cruiser Racing Association's (ICRA) new Commodore seeks to increase participation in cruiser racing during his five year term in office. In his opening address to delegates at the ICRA conference on Saturday Norbert Reilly said he believes the expansion potential for Irish sailing – up to three or four time its existing size – is huge compared to other sports as participation in competitive sailing can be much longer than in other sports.
Experienced keelboat campaigner Reilly, the new man at the helm of cruiser racer sailing in Ireland, said that as well as building on the successes of his predecessors in 2013 ICRA wants to recruit new people into sailing to replace those lost during the recession.
A new ICRA crew training programme will be introduced and the initiative will be club based. It will run to uniform ICRA standards at a number of sailing centres with a programme drawn up by former national sailing coach Dave Harte now based in Schull. The aim is to train crews, such as the role of bowman, to a quality standard for local, national and international events.
The ICRA conference was told quality training for new people would produce a valuable supply of crews to help sail the existing fleet. It will provide a 'route to the boats' for newcomers that can also boost flagging yacht club memberships.
Reilly currently races the Dublin based Mills 36 Crazy Horse and has been running cruiser racer campaigns from Howth since the 1980s including the well known Comanche Raider.
































































