Displaying items by tag: Aran Islands
Arklow RNLI’s volunteer crew launched their lifeboat within minutes of receiving a report that a sailing vessel was in danger and aground at Clogga Bay last Tuesday afternoon, 20 April.
Upon entering the bay south of Arklow Harbour, the crew on the Trent class lifeboat Ger Tigchlearr quickly identified the casualty vessel — a 24ft sailing yacht with one person aboard — and made best speed to the area.
Coxswain Ned Dillon and crew made their way up as close to the casualty vessel as possible. Given it was aground in shallow waters, the lifeboat’s inflatable XP boat was deployed for the crew to check the casualty vessel and pass on a towline.
The lifeboat then proceeded to slowly pull the sailing vessel to deeper water. Once it was established the boat was dry and not taking on water, it was taken under tow back to Arklow within 40 minutes.
Following the callout, Dillon said: “Thanks to our crew, this was an excellent successful service, where we got to deploy and use very many of the safety critical tools and lifesaving equipment we carry aboard the lifeboat.
“In all my years I’ve never seen all these items being deployed at once and never so successfully. It’s a real testament to our crew and the excellent training we get from RNLI.”
 Bringing the casualty vessel ashore in Arklow Harbour Credit: RNLI/Mark Corcoran
Bringing the casualty vessel ashore in Arklow Harbour Credit: RNLI/Mark Corcoran
In other recent RNLI news, the Skerries lifeboat was tasked on Monday evening (26 April) after a report of a person stranded on Shenick Island and trying to make their way ashore in the rising tide.
On approach to the island, the lifeboat crew were notified by the coastguard that the individual has made it safety to the beach at Skerries.
But as a number of other people were spotted on the island, the lifeboat put two crew ashore to check on their wellbeing and confirmed they were not planning on returning to shore until the next day.
It followed a busy weekend for Skerries RNLI which saw the North Co Dublin volunteers rescue nine people in two separate incidents.
In the Aran Islands, meanwhile, a late-night medevac for a woman on Inis Mór saw the local lifeboat crew paged in the early hours of yesterday, Tuesday 27 April.
The patient was transferred safely aboard the lifeboat by the volunteer crew, following all strict COVID-19 health and safety guidelines. The lifeboat then headed straight for Rossaveal Harbour and the waiting ambulance.
Speaking after the callout, Aran Islands RNLI coxswain John O’Donnell said: “Time is always of the essence and the volunteer crew are ready to go when called upon. We would like to wish the patient well.”
School Tours Can Take Place to Islands Within County Boundaries Amid Mixed Feelings Among Islanders
Irish offshore islands may have mixed feelings about hosting school tours, but the Department of Education says they can take place within Covid-19 guidelines.
As The Times Ireland edition reports, The department says that “educational trips” by both primary and post-primary schools are a matter for “each individual school authority”.
Transition year students visited the largest Aran island of Inis Mór on two consecutive days last week.
The transition students from Presentation College, Athenry travelled by ferry from Ros-a-Mhíl in south Connemara to Inis Mór, and hired bikes on the island.
All activity on the island was outdoors, with students wearing masks, and cycling, swimming and sending a postcard home, the principal said. The students took a picnic with them.
The school enjoys a close relationship with the Aran Islands, and sent first-year pupils in four separate groups to the Aran Islands during the first term of 2020, the school confirmed.
These first-year trips are designed as a familiarisation exercise, and as an educational experience of an Irish-speaking community, the school explained.
In a statement, the Department of Education said it has “published guidance for schools that provide various teaching and learning approaches, including bringing pupils/students outdoors and to local amenities to enhance learning, support social distancing, promote physical activity and help positive wellbeing”.
“Decisions in relation to educational trips are a matter for each individual school authority and it is the responsibility of each school authority to ensure that appropriate safeguards are in place while pupils/students are participating in school trips and that all such activities are in line with public health guidelines,”a department spokesman said.
However, there has been some confusion among schools, and it is understood that the education unions met department officials last week and raised concerns about the "lack of clarity" in the wording of the guidelines.
Comhdháil Oileáin na hÉireann, the Irish Island Federation, said that once school tours were to islands within the same county and within current guidelines, its members have no issue.
“Mayo pupils can visit Mayo islands, Galway pupils can visit Galway islands, since county-wide travel has been permitted,” federation secretary Rhoda Twombly said.
However, businesses are still very restricted on many of the islands, she pointed out.
Most offshore islands were restricted to “essential visits” only during several phases of the Covid-19 lockdown from Spring 2020.
Early last year, a vote by residents on the Aran islands was overwhelmingly in favour of restricting visits – at the expense of tourist revenue.
When the National Public Health Emergency Team’s approved an early lifting of travel restrictions from June 29th last year, island communities were thrown into confusion – having planned for a re-opening on August 10th.
In Mayo, the island of Inishturk opted to keep guesthouses closed and host day-trips only.
The cautious approach largely paid off, with only one or two cases on some islands.
However, relaxation of national restrictions over Christmas resulted in an outbreak on Mayo’s Clare island, with 20 positive cases reported in January.
Large numbers of elderly and vulnerable island residents have now been vaccinated, as the roll-out of vaccines continues on offshore communities.
Read The Times here
Aran Islands RNLI’s volunteer crew were asked to launch their all-weather lifeboat from Inis Mór last night (Sunday 21 March) for a local man on the neighbouring island of Inis Meáin who sustained a facial injury and was in need of further medical attention.
The lifeboat launched under coxswain John O'Donnell and a full crew and headed straight for Inis Meáin. Conditions at the time of launching were good, with calm seas, a slight breeze and clear visibility.
Once at the pier in Inis Meáin, the patient was transferred safely aboard the lifeboat by the volunteer crew.
Following all strict Covid-19 health and safety guidelines, the lifeboat then processed straight for Rossaveal Harbour on the mainland and the waiting ambulance.
Speaking after the callout, O’Donnell said: “There was a quick response time by the volunteer crew to get the patient to the medical attention needed. The crew never hesitate to answer their pagers when they go off.
“We would like to wish the patient a speedy recovery.”
The callout came just days after the lifeboat crew were tasked with a double medevac amid poor visibility last Monday, as previously reported on Afloat.ie.
Senior citizens living offshore on the Aran islands have marked St Patrick’s Day with a Jerusalema dance challenge video.
Residents and staff of Áras Rónáin Community Nursing Unit on the largest Aran island of Inis Mór opted to rise to the occasion and mark a “difficult year”, having received their Covid-19 vaccinations.
The choreographed dance routine performed to the South African gospel hit 'Jerusalema' went viral in Ireland after the Garda recorded a video in response to a challenge by Swiss police.
Last month, the Irish Coast Guard stopped units from participating in it after Dingle Coast Guard posted their own version.
Coast Guard management has said individuals can participate in line with public health guidelines.
Two Aran islanders assisted with the drone footage and editing of the final video clip, posted on YouTube today.
“This project has demonstrated excellent teamwork and has provided a new sense of hope and optimism among both staff and residents that there will be some resolution to this Covid-19 pandemic,” the unit’s person in charge Theresa Powell said.
“One thing this pandemic has thought us is that we are we are very fortunate to be living and working on a beautiful Island that provides vital services to our elderly population across the three Aran Islands,” she said – adding “Go mbeirimid beo ar an am seo arís...
The video can be viewed below
Aran Islands Lifeboat Launches for Double Medevac from Inis Mór
Aran Islands RNLI was tasked for a medevac from Inis Mór as a scheduled patient transfer by air was cancelled due to poor visibility yesterday morning, Monday 15 March.
Due to poor visibility, a scheduled patient transfer by air was unable to go ahead. The crew were requested to transfer the patient to Rossaveal.
Following all strict Covid-19 health and safety guidelines, the patient was transferred safely aboard the lifeboat to Rossaveal by both the RNLI crew, under John O'Donnell, and the Inis Mór Fire Service.
Having just launched on the return leg, the lifeboat was called back to Inis Mór as another patient on the island needed further medical attention.
The second patient was safely transferred aboard the lifeboat by the volunteer crew at the pontoon on Inis Mór, and the lifeboat then headed straight for Rossaveal Harbour and the waiting ambulance.
Speaking after the callout, Aran Islands RNLI coxswain John O'Donnell said: “The volunteer crew responded quickly and two patients are safely on their way to further medical attention — we would like to wish them both a speedy recovery.
“Poor visibility can be very dangerous on the water. Should you get into difficulty or see someone else in trouble, call 999 or 112 and ask for the coastguard.”
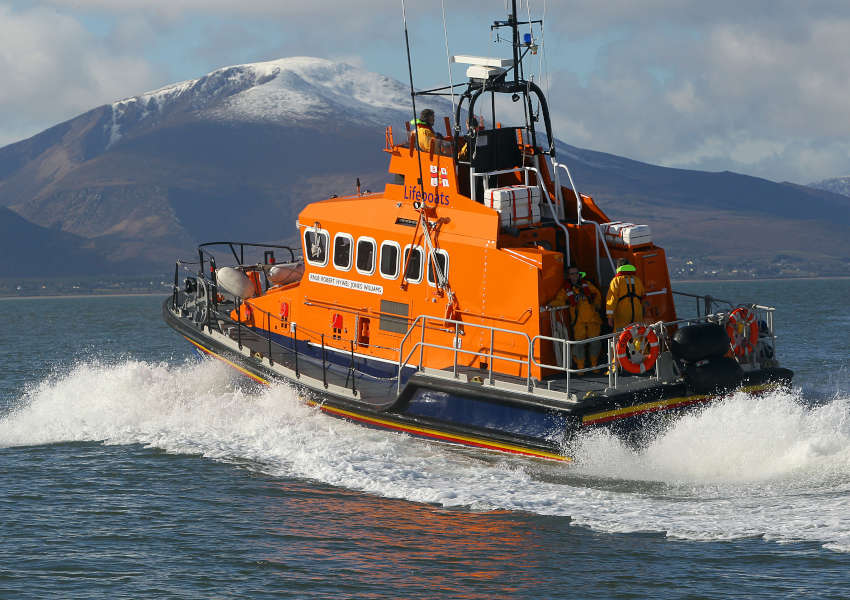 File image of Fenit RNLI’s all-weather lifeboat | Photo: RNLI/Fenit
File image of Fenit RNLI’s all-weather lifeboat | Photo: RNLI/Fenit
Elsewhere, Fenit RNLI’s volunteer crew responded to a report of concern for a windsurfer in the Maharees Islands area early on Sunday evening, 14 March.
The all-weather lifeboat launched with a full crew on board and headed to the location near Castlegregory, on the north side of the Dingle Peninsula.
The Irish Coast Guard’s Shannon-based helicopter Rescue 115 also attended the scene in a search co-ordinated by Valentia Coast Guard.
A search of the given location was under way when word was received that the windsurfer had safely made his way ashore.
Speaking following the callout, Fenit RNLI coxswain Finbarr O’Connell said: “Fenit RNLI are delighted with a safe and positive outcome for all concerned. As always this is an opportunity to remind all users of the sea to be as prepared as possible when going to sea.”
Aran Islands Aims for Own Microgrid in Offshore Renewable Energy Project (PODCAST)
The Government’s ambitious plans for renewable energy off the Atlantic coast should involve communities as active stakeholders and not just recipients of compensation, an island energy co-op has said.
Dara Ó Maoildhia, chairman of Comharchumann Fuinneamh Oileáin Árann, the Aran islands energy co-op, says his group is “campaigning hard” to ensure local communities will have a central role.
“One of our main ambitions is that the three Aran islands will have their own microgrid,” he told this week’s Wavelengths podcast.
 Dara Ó Maoildhia, chairman of Comharchumann Fuinneamh Oileáin Árann, the Aran islands energy co-op. Screenshot courtesy: Comharchumann Fuinneamh Oileáin Árann
Dara Ó Maoildhia, chairman of Comharchumann Fuinneamh Oileáin Árann, the Aran islands energy co-op. Screenshot courtesy: Comharchumann Fuinneamh Oileáin Árann
The co-op is also collaborating in research on hydrogen energy, which may have applications for island ferries as well as businesses, transport and residences.
A consortium of islands led by Kerry’s Valentia Island Co-op and Rathlin, Co Antrim has been examining the feasibility of combining offshore wind with electrolyser technology to convert water to hydrogen.
Meanwhile, researchers at the NUIG Ryan Institute Energy Research Institute are also collaborating in a five-year project that will generate, distribute and use at least 300 tonnes of hydrogen per year produced from solar energy on the Balearic island of Mallorca.
 Dr Thomas van Rensburg
Dr Thomas van Rensburg
The NUIG team in the Green Hyslands project involves Dr Pau Farràs Costa, Dr Rory Monaghan and Dr Thomas van Rensburg, and they say it will reduce CO2 emissions by 20,000 tonnes per year.
The NUIG team will assess the economic impacts of the green hydrogen on Mallorca, as well as on other island communities involved in the project, including the Aran Islands.
Dr van Rensburg also spoke to Wavelengths and you can listen below
Double Lifeboat Callout For Medevacs From Aran Islands
Aran Islands RNLI’s volunteers were called twice in succession to aid two people in need of medical attention in the Galway Bay islands yesterday morning, Monday 19 October.
The lifeboat crew were tasked to launch their all-weather vessel David Kirkaldy from Kilronan on Inis Mór at 11.31am, to assist an elderly man on the neighbouring island of Inis Meáin.
A second call came in quick succession when a woman on Inis Mór also required medical evacuation.
This second patient was attended to first and safely secured on board before the lifeboat launched for Inis Meáin under coxswain John O’Donnell and a full crew.
Weather conditions at the time of launching were moderate with poor visibility, but with calm seas and a south-east wind blowing Force 4–5.
Once alongside the pier at Inis Meáin, the male patient was transferred safely aboard and under the supervision of the volunteer crew, observing all coronavirus safety guidelines.
The lifeboat then headed straight for Rossaveal Harbour on the mainland and an awaiting ambulance.
Speaking later, O’Donnell said: “A double callout to start the week — the volunteer crew members train regularly to make the minutes count and get to the incident and patient as fast as possible.
“We would like to wish both patients a speedy recovery.
“Never hesitate to call 999 or 112 if you see someone in trouble and ask for the coastguard.”
Marine Notice: ADCP Deployment Off Inis Mór For Highwave Project
University College Dublin have been set to deploy an Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP) off Inis Mór in the Aran Islands between today, Thursday 15 October, and next Wednesday 21 October as part of the Highwave project.
The university previously deployed an ADCP in February as par of the same ocean wave data modelling project.
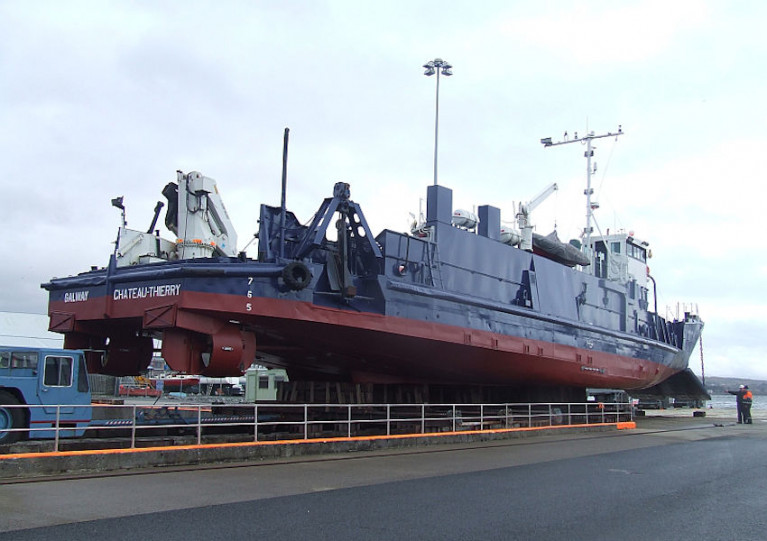
Thos latest deployment, from the MV Chateau-Thierry (callsign EIHK6), will be some 0.6 nautical miles from Rock Island lighthouse — at 53°08’57.4” N, 009°52’23.4” W. The vessel will display appropriate lights and signals.
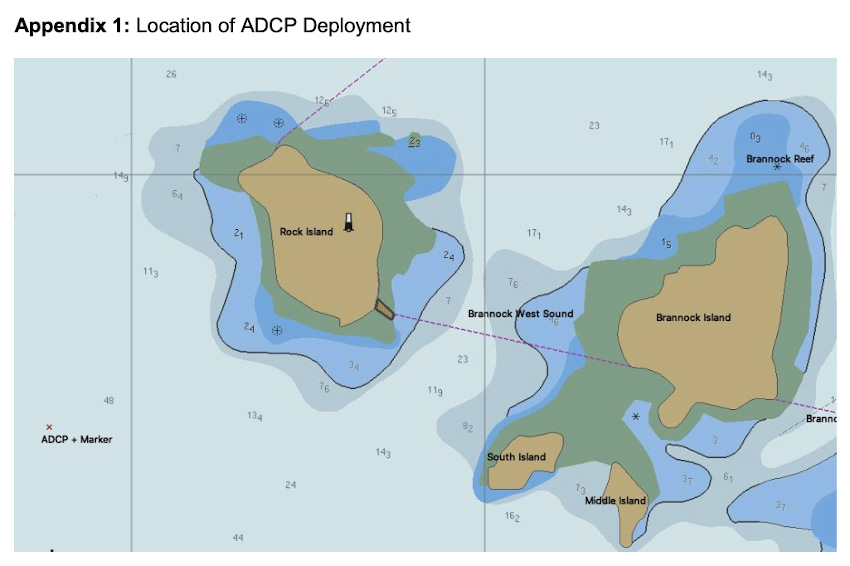
Navigational warnings will be issued by radio when the deployment of the marker buoys takes place. These buoys will be yellow spherical markers, 40cm in diameter and flashing yellow every five seconds.
Fishing Vessel Adrift Off Connemara Rescued By Aran Islands Lifeboat
Aran Islands RNLI’s volunteer crew launched their all-weather lifeboat at 4.43pm yesterday (Thursday 8 October) to assist a 38ft fishing vessel that was drifting “dangerously close” to Eagle Rock, just off Golam Head in Co Galway.
Under coxswain John O'Donnell and with a full crew, the lifeboat headed straight for the fishing vessel amid moderate conditions, with a two-metre sea swell.
Once on scene, lifeboat crew found that both people aboard the fishing vessel were in good health and observing coronavirus guidelines.
A tow line was set up and the lifeboat brought the casualty vessel to the safety of Rossaveal Harbour in Connemara.
Speaking after the callout, O’Donnell said: “This was a good outcome as the vessel was drifting dangerously close to Eagle Rock after losing the use of their engines.
“Our volunteer crew members never hesitate to get to the call as quickly as possible. If you see someone in trouble, call 999 or 112 and ask for the coastguard.”
Aran Islands RNLI has encouraged the public to always call for help when they believe they’ve seen someone in distress at sea.
The message follows a callout across Galway Bay to Rossaveal in Connemara last night (Monday 5 October) that turned out to be a false alarm with good intent.
The volunteer crew launched their all-weather lifeboat at 7.45pm to reports of a flare sighting near Great Mans’ Bay, amid choppy seas with a two-metre swell and 22-knot northwesterly winds.
The crew were joined in the search by Costello Bay Coast Guard and the Shannon-based Irish Coast Guard helicopter Rescue 115.
But after an extensive search of the area by all three rescue services working together, the operation was stood down.
“Thankfully the call out was a false alarm with good intent,” said Aran Islands RNLI press officer Lena O’Connell.
“It is always better to be safe than sorry. The volunteer crew members didn't hesitate to get the lifeboat to the search area as quickly as possible.
“We would remind everyone if you see someone in trouble or see a distress signal, don’t hesitate to call 999 or 112 and ask for the coastguard.”


































































