Displaying items by tag: The Big Picture
Half Tonners Hit The Spot for Irish Sailing
With the confirmation that Kinsale Yacht Club will be hosting the Half Ton Classic Worlds from August 14th to 18th 2017, Irish interest will intensify further in a class which already attracts much favourable attention. W M Nixon tells us more about a popular boat type which will have a defending champion from Ireland when the Worlds get under way in Falmouth in Cornwall in a week’s time.
If today’s newcomers to sailing find the resurrection of old offshore racing classes which are apparently only identified by specific weights a bit bewildering, then they can blame the first Commodore of the National Yacht Club in Dun Laoghaire.
The first Commodore of the NYC in 1931 was the Earl of Granard. The club had been founded in 1870 as the Kingstown Royal Harbour Boat Club, and in 1901 it became the Edward Yacht Club in honour of one of Queen Victoria’s many offspring. But with the new mood of the times after Irish Independence in 1922, such a name just wouldn’t do. Nevertheless it was a very sporting gesture when one of the landed aristocracy proposed the new no-nonsense name in 1930, giving it a fair wind by agreeing to be Commodore the following year.
Thus the big change to becoming “The National Yacht Club” was made respectable. But then, the Earl of Granard was a well-respected sailing man in his own right, despite the fact that his ancestral pile in County Longford was about as far from the sea as you can get in Ireland.
Admittedly there was sailing nearby with the North Shannon Yacht Club on Lough Forbes, which incidentally is named after the earl’s family – they were connected to the Forbes of the famous business magazine in America. However, despite the joys of sailing on Lough Forbes, the Earl had long been into bigger things on the international scene, though his interest still had an inland waterways aspect. In 1899 he’d presented a magnificent silver cup to the leading French sailing club, the Cercle de la Voile de Paris (CVP) for an international competition, to be sailed on the River Seine near Paris or on the Solent at Cowes, with the racing between boats which weighed one ton.
Although the trophy’s official name was the Coupe Internationale du Cercle de la Voile de Paris, it soon became known as the One Ton Cup, and continued to be so named even when racing was between yachts of the International 6 Metre Class, despite their weighing several tons apiece.
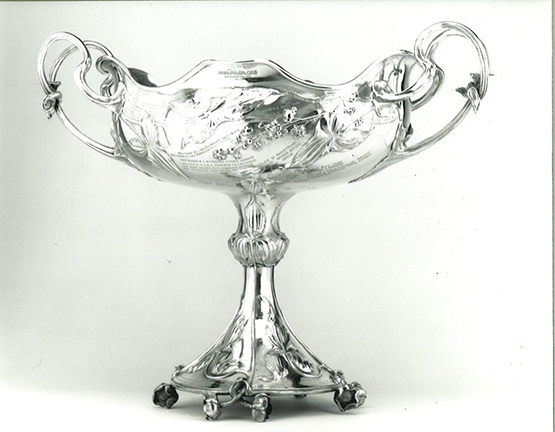 The cause of all the trouble – the One Ton Cup was presented to the CVP by the Earl of Granard, future Commodore of the National YC, in 1898, and was first raced for in 1899.
The cause of all the trouble – the One Ton Cup was presented to the CVP by the Earl of Granard, future Commodore of the National YC, in 1898, and was first raced for in 1899.
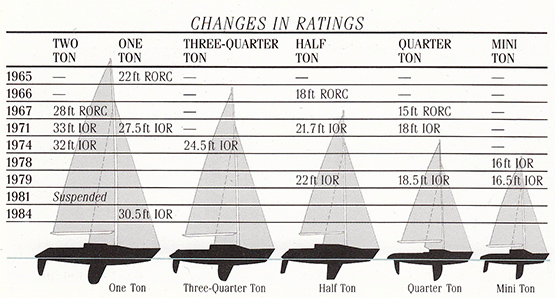
The magnificent cup remained as beautiful as ever, but with World War II it became almost forgotten until 1965, when the CVP proposed using it for an inshore-offshore international series for yachts rating at 22ft under the RORC rule, which worked out to be boats around the 36-37ft mark. The idea took off like a rocket - level-rating racing among diverse boats was an idea whose time had come. Very quickly, a whole range of additional international rating levels arose, with Two Tonners around 40-42ft, Three Quarter Tonners around 34ft, Half Tonners around 30ft, Quarter Tonners around 25ft, Mini-Tonners around 21ft, and they even had Micro-Tonners at about 18ft.
 The Ton Classes at their peak
The Ton Classes at their peak
It all worked very well for twenty years and more in some cases (the last Half Tonner was built in 1992), with the boat sizes staying broadly the same size range, but with the ratings changed to accommodate the RORC rule being replaced by the IOR. And Irish sailing certainly had its moments in this continuing circus of various offshore racing acts. In 1974 the Ron Holland-designed, Cork–built 36ft Golden Apple somehow became more famous than the winner by being runner up the One Ton Worlds. But then in 1976, Harold Cudmore and a youthful crew from Cork put all questions aside by managing to get the new race-prepared Ron Holland-designed 30ft Silver Shamrock to Trieste for the Half Ton Worlds, and he won in style, famously celebrating by sailing up the Grand Canal in Venice with spinnaker set.
 The 1976 Half Ton World champion Silver Shamrock, getting an end-of-season lift-out at her current home port of Penzance in Cornwall
The 1976 Half Ton World champion Silver Shamrock, getting an end-of-season lift-out at her current home port of Penzance in Cornwall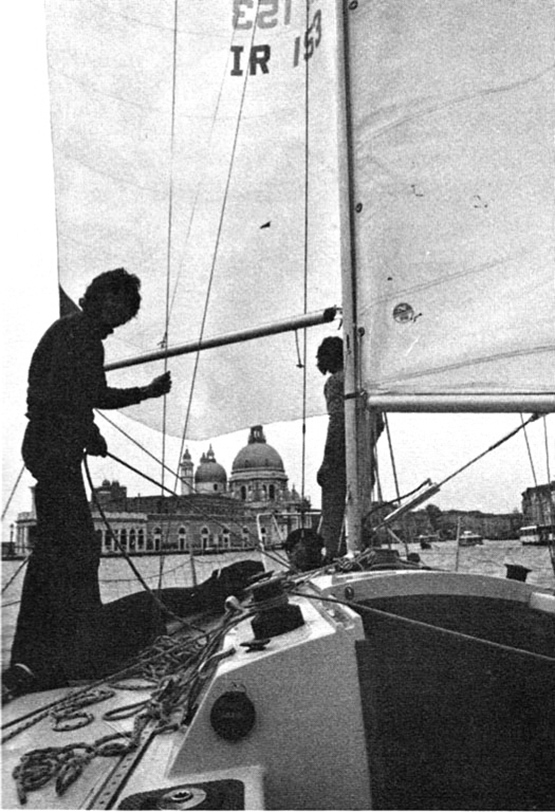 See the conquering heroes come…….Silver Shamrock sailing up the Grand Canal in Venice after winning the Half Ton Worlds 1976 in Trieste under Harold Cudmore’s command. Ronnie Dunphy on left, Killian Bushe on foredeck
See the conquering heroes come…….Silver Shamrock sailing up the Grand Canal in Venice after winning the Half Ton Worlds 1976 in Trieste under Harold Cudmore’s command. Ronnie Dunphy on left, Killian Bushe on foredeck
In 1981 he was back on top again, winning the One Ton Worlds at Crosshaven with the Castro-design Justine IV owned by Frank Woods (NYC). But by this time the boats involved were very different in form from those skinny-sterned designs which had dominated in the earlier 1970s, as a fresh wave of New Zealand designers like Bruce Farr and Laurie Davidson had been showing what could be achieved with broader sterns and better offwind performance.
The Half Ton Worlds was won in 1977, ’78 and ’79 by Kiwi boats of this type. But though she was not the overall winner, Ian Gibbs’ Farr-designed Swuzzlebubble was the one everyone remembered best, as she was on the podium one year as a centreboarder, and back there in the top three the year after, but this time as a keelboat.
 The new wave arrives from New Zealand – Swuzzlebubble in 1979
The new wave arrives from New Zealand – Swuzzlebubble in 1979
The following year she arrived in Ireland in the ownership of Bruce Lyster of Royal St George in Dun Laoghaire, and he won the ISORA Championship in 1980, plus ISORA Week and just about everything for which the boat was eligible in Cowes Week.
He had an exceptional crew of all the talents with Robert Dix, Drewry Pearson and Des Cummins, and Dixie remembers her as one of the most wonderful boats he ever sailed: “She found her own way to peak performance so effortlessly that you’d almost be scared to do anything which might adversely effect the trim” he quips.
He continues to say that even though Bruce Lyster sold Swuzzlebubble to Greece at season’s end, as you simply couldn’t improve on a season like they’d had in 1980. The Three Musketeers meanwhile transferred aboard Ken Rohan’s 40ft Regardless, with which they won their class big time in the 1981 Fastnet.
Regardless would be on most people’s short list for the greatest Irish racing yacht ever, yet Robert Dix remembers the previous season with Swuzzlebubble with even more enthusiasm. So it’s intriguing that at next week’s Henri Lloyd Half Ton Classics Worlds, the new wave of Irish Classic Half Ton sailors will be taking on Swuzzlebubble for the first time.
The story of her re-birth is typical of the modern revival of the very best of the old Ton Cup boats, with the One Ton Championship itself being revived for its Golden Jubilee in New Zealand in 2015 with a classic fleet. As for Swuzzlebubble, she was discovered in a very poor way indeed in a Greek boatyard in 2012, but was brought back to life by the King of Cowes, Peter Morton, who duly won the Half Ton Classics Worlds in Brittany in 2014 with her.
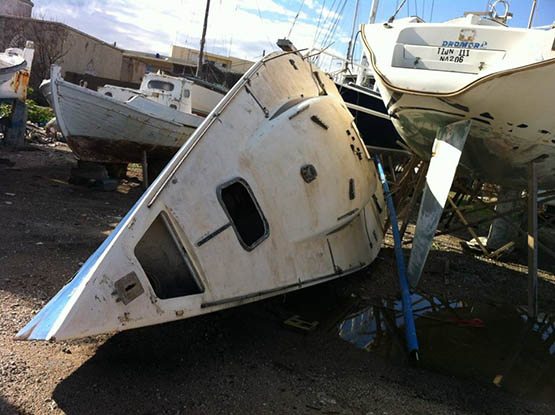 Next stop, the landfill site? Swuzzlebubble as she was found in Greece in 2012
Next stop, the landfill site? Swuzzlebubble as she was found in Greece in 2012 Swuzzlebubble restored, on her way to winning the Half Ton Classics in Brittany in 2014
Swuzzlebubble restored, on her way to winning the Half Ton Classics in Brittany in 2014
However, Swuzzlebubble wasn’t campaigned in the 2015 series in Belgium, when Dave Cullen took the trophy for Ireland with Checkmate XV. So there has been an air of unfinished business about these two rather special boats floating about the ocean without actually locking horns, but that’s all going to be changed in Falmouth.
 Dave Cullen on the helm as Checkmate XV makes a start to die for at the Half Ton Worlds in Belgium, 2015
Dave Cullen on the helm as Checkmate XV makes a start to die for at the Half Ton Worlds in Belgium, 2015 Winners take all – Dave Cullen and his crew with the trophy after victory last year
Winners take all – Dave Cullen and his crew with the trophy after victory last year
In fact, it has become Howth versus Falmouth, as Swuzzlebubble is now Falmouth-owned by Gregory Peck who, in a very varied sailing career, was one of the crew with Dickie Gomes aboard the 83ft catamaran Novanet when a new Round Ireland Record was established in November 1986, but that’s another story altogether.
However, in Falmouth there’ll be other boats involved too, as the word is they might muster as many as 30 entries, which is as big a fleet as anyone could reasonably wish for. The remarkable Howth/Fingal contingent will be there in full strength, as Checkmate XV will be taking the road with Jonny Swann’s Harmony, Michael and Richard Evans’ The Big Picture, and the David Kelly and Patrick Boardman team from Rush SC with King One, Half Ton World Champion in 1981.
It’s an intriguing mixture of nostalgia and modernity, as the boats get revamped to new ideas, yet they always carry their history lightly but definitely with them. In the case of the Howth boats, much of the technical work in revamping is done by ace boatbuilder Alan Power of Malahide, who appropriately is a powerboat nut himself, but his ability to think outside the usual boat-building box makes him the ideal man to undertake crazy notions for addicts of old but still potent offshore racers.
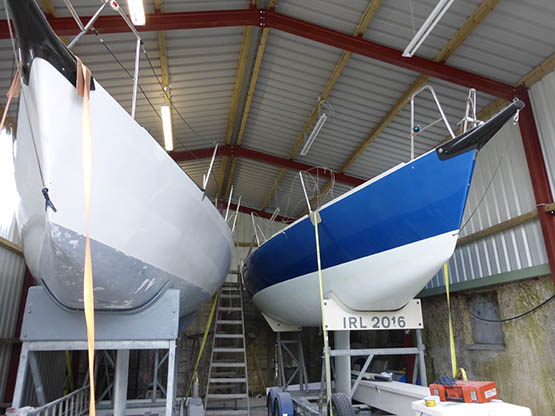

In line with this aim of maximising performance, the Howth/Fingal crewing lineup will include some formidable talent from all over Ireland, with Dave Cullen leading the charge with his 2015 crew of Johnny Murphy, Gary Cullen (no relation), Aidan Beggan, Mark Pettit, James Hynes and Andy George.
The crew on The Big Picture meanwhile have roped in Mark Mansfield of Cork, who is having a great year of it in a variety of boats, while the jockey for King One is young Marty O’Leary, one of the bright new talents to emerge in recent years from Courtown in County Wexford.
Down Falmouth way, it’s going to be Classic Half Ton Racing at its classic best. And if you wonder why it is that the Half Tonners seem to have been the most successful of all the Ton classes in reviving themselves after more than fifty years, perhaps the answer is that at 30ft they’re big enough as boats to be taken seriously, yet small enough to be a manageable proposition for keeping in top order and raced keenly.
 The contemporary Half Ton Classics lineup – the boats are big enough to be taken seriously, yet small enough to be manageable
The contemporary Half Ton Classics lineup – the boats are big enough to be taken seriously, yet small enough to be manageable





























































