Displaying items by tag: wave energy
Marine Notice: Spiddal Wave Energy Test Site Decommissioning Works
#MarineNotice - The latest Marine Notice from the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport (DTTAS) advises of the decommissioning of the wave energy test site in Galway Bay.
The decommissioning of the Marine Institute's wave energy site will involve the removal of four cardinal marks and a wave monitoring data buoy, and the establishment of a new special mark denoting the presence of the Galway Bay Subsea Observatory on the seabed at the site off Spiddal.
The Chateau Thierry (Callsign EIHK6) was scheduled to arrive in Galway Bay this week between Monday 11 and next Monday 18 September. This operation is expected to last two days, depending upon weather or other operational conditions.
It is anticipated that the decommissioning operation will be completed on or before Tuesday 19 September.
The Chateau Thierry will display appropriate lights and markers. The work vessel will be broadcasting and listening on VHF Channel 16 during the decommissioning.
Full details of co-ordinated of the relevant work areas are included in Marine Notice No 38 of 2017, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
Minister for Communications, Climate Action and Environment, Denis Naughten TD, has signed an energy cooperation declaration with nine other EU counties focussing on the development of cost effective offshore wind & wave renewable energy.
Commenting on the cooperation declaration, Denis Naughten said "Ireland has the best off shore energy potential in Europe but we need to work with our colleagues across the EU to turn this potential into electricity"
"While we are at the leading edge ocean energy research, we can always benefit from closer cooperation with our EU neighbours, not just in ensuring that we use the most cost effective solutions to produce off shore energy but also to get this green electricity onto the European electricity grid".
Speaking from Luxembourg at the official signing ceremony he said "As the new Minister with responsibility for both for energy and climate action, I want to ensure that we do all in our power to achieve our climate change targets in a sustainable cost effective manner in the shortest timeframe possible".
It is also important that we have access to a balanced suite of renewable energy options and I believe that this declaration with EU countries adjoining the North Sea and Irish Sea will help us as a country develop a range of cost effective renewable energy solutions" concluded Denis Naughten
Background:
Minister Naughten was one of 10 signatories to the “Political Declaration on Energy Cooperation between the North Seas Countries.” This voluntary declaration, supported by the European Commission, has a particular focus on renewables and smart grid development. The initiative builds on the North Seas Countries' Offshore Grid Initiative (NSCOGI) that Ireland has been successfully involved in in the past.
The key objective of this North Seas energy cooperation is to enhance coordination and integration of national efforts of renewables deployment in addition to grid planning. This aims to reduce the costs of renewable energy and grid development and remove barriers to investment, which contributes to achieving our climate goals and the EU-wide target of 27% renewable energy by 2030. Moreover, it strengthens our security of supply and supports the EU’s long term competitiveness and energy market integration. The long term goal of the cooperation is to attract private investments in the development of the North Seas as a sustainable and regionally optimised energy system.
The signatories to the Declaration are: Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Ireland, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Sweden and the UK and the European Commission.
Galway In Sights Of Wave Energy Firms Seeking Atlantic Power
#SeaPower - The power of the Atlantic Ocean will be put to the test next year as firms are in discussion to place wave energy devices in Galway Bay.
The Irish Independent reports that the Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland (SEAI) is in discussion with "at least" three renewable energy companies to install massive machines to harness the power of the strong Atlantic currents off Galway.
Galway Bay is already a testing site for a number of quarter-scale wave energy prototypes that themselves can measure up to 30m long - and may resemble the enormous wave energy 'harvesters' being tested elsewhere that are changing the face of renewable energy.
It's hoped that wave power could meet up to 75% of Ireland's growing energy needs in the near future, though the technology to achieve this is still very much in development.
Sea Power Projects Could Be Good for Marine Wildlife Says Report
#POWER FROM THE SEA - Marine-based renewable energy projects could be introduced without a damaging impact on marine wildlife, according to a new briefing paper from Friends of the Earth.
Business Green reports on the paper from the environmental campaign group, written by marine ecologist Martin Attrill of Plymouth University's Marine Institute, which draws together research on the biodiversity impact of offshore wave energy, tidal energy and wind power schemes.
Attrill found that the deployment of sea energy arrays could ultimately benefit many marine species by reducing the effects of fishing activity, and even acting as reefs to attract new sea life.
He cites the example of a grey seal colony in Strangford Lough that has steered clear of a nearby tidal turbine over the three years of its operation in the lough.
However, Business Green says the report makes clear that the deployment of such projects "must be done sensitively", noting that any negative impact on biodiversity "would be significantly lower than the damage done to marine wildlife by rising sea levels caused by climate change".
Business Green has more on the story HERE.
Tall Ships, Galway Volvo Ocean Race, European Tour, Sharks and More
An unforgettable experience on a tall ship, Galway and the Volvo Race, the MOD70 European Tour in Dublin, protection for seafarers after 92 years, Wi-Fi and sharks, topics in your TIN this week.
Read on ....
UNFORGETTABLE EXPERIENCE" ON A TALL SHIP
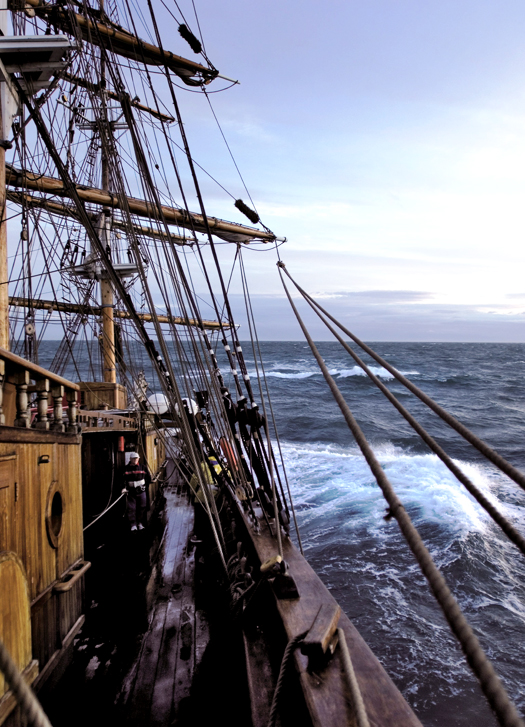

Sailing the Jeanie Johnston
With the Tall Ships Race in Dublin, Captain Michael Coleman has answered my question as to what it is like to command one of these vessels:
"Sailing in good weather on a clear and starry night is an unforgettable experience. The distractions of the land are left far behind and you become at one with nature and the elements."
Captain Coleman of Cobh sailed the Jeanie Johnston in the 2005 Tall Ships Race out of Waterford. "An unforgettable experience never to be repeated," he says and he is right, because at the start of that race Ireland had three tall ships and they led the fleet down the Waterford Estuary to the sea – Asgard, Dunbrody and Jeanie Johnston.
"The distractions of the land are left behind and you become at one with nature and the elements," aboard a tall ship says Capt. Coleman. "No TV or mobile phones or the pressure of modern living, just the ship, the wind and the sea and yourself."
His description is in a new book about the tall ship from Kerry, published by Collins Press of Cork to mark the Tall Ships Race in Dublin. Michael English, who was born in Liverpool and studied art in Cork, then worked in advertising in Dublin, made a photographic record of his voyage aboard the Jeanie Johnston in 2005. This forms the new book: 'Jeanie Johnston – Sailing the Irish Famine Tall Ship.'
The Jeanie Johnston has been berthed for some years as a floating museum on the Liffey in Dublin. As tall ships from around the world gather this week in the capital, while there will be smaller Irish vessels taking part, this island nation does not have an active, sailing tall ship providing training for Irish young people.
VOLVO RACE AND GALWAY
Will we see another race village in Galway again?
Applications from ports around the world to stage the next Volvo Race must be lodged with Volvo by next month and the 'Let's Do It Global' group which ran the event in Galway is not, so far, preparing one it seems, despite the great success of twice staging the event there, this year and in 2009.
Raising the money needed is the problem.
900,000 people attended the race festival in Galway this year, the organisers said and there was a major economic spin-off for the city. A study of the 2009 stopover estimated the economic impact at €55.8 million with more than 650,000 visitors.
The €4 million fee for hosting this year's event was paid directly to the Volvo Ocean Race organisation as the price for bringing it to Galway by Fáilte Ireland. The Galway organisers found it difficult to secure sponsorship in the current economic climate. Galway Harbour Company, which closed the port for the nine-day festival and Galway City Council were major backers. The event had huge voluntary effort. A number of State agencies hosted events and provided logistical support.
Galway Chamber of Commerce called on the Government to provide the necessary support to secure a third successful bid for Galway.
John Killeen one of the leading forces in getting the race to Galway has said the event would have to be underwritten by a bigger entity than just a voluntary group.
As a host port in this year's event, Galway received an automatic invitation for inclusion in the next race in 2014/2015, with the final decision on port selection to be made by the race organisers in December.
EUROPEAN TOUR FOR IRELAND
The MOD70 is coming to Ireland
Ireland continues to gain a reputation as one of the best sailing locations in the world. The new global sailing championship series, the MOD70 European Tour will be in Dun Laoghaire from Wednesday, September 5 to Sunday, September 9, hosted by the National Yacht Club and Dun Laoghaire Harbour Company. Many of the world's top sailing events have been held in Ireland this year.
The high speed MOD70 class of trimarans are a new innovation in sailing. Each MOD70 is identical, built from the same moulds. That should reflect the skills of the sailing crew in performance and not technological advantage.
The MOD70s coming to Dublin Bay will be - Race For Water, FONCIA, Groupe Edmond de Rothschild, Spindrift Racing and Musandam Oman Sail.
On Friday, September 7 and Saturday, September 8, they will sail the Dublin City Race and Speed Match Races. The trimarans will leave Dun Laoghaire at 3 p.m. on Sunday, September 9, for the start of the second leg of the European Tour from Dun Laoghaire to Cascais.
AFTER 92 YEARS – SEAFARERS TO GET WORK PROTECTION
The labour rights of the world's 1.2 million seafarers are to be protected in a new charter – the Maritime Labour Convention. Following its ratification by 30 countries it will go into effect in a year's time – ninety-two years after it was first proposed.
The International Labour Organisation is the United Nations' agency for internationally-recognised labour rights. The Convention was adopted back in 2006 but could not be put into effect until 30 countries adopted it. They represent nearly 60 per cent of the world's shipping tonnage, meaning that seafarers working on more than 50 per cent of the world's international shipping will be covered by the new Convention. Ireland is a member of the ILO but has not yet signed the Convention.
• A safe and secure workplace that complies with safety standards
• Fair terms of employment
• Decent working and living conditions on board ship
• Health protection, medical care, welfare measures and other forms of social protection
TRACKING WHITE SHARKS

Marine researchers are using "ocean WiFi hotspots" in their latest attempts to track the movements of white sharks. The species is under threat. Sharks take several years to reach maturity and spawn. An unmanned 'Wave Glider' robot is the latest development in ocean technology. It has been deployed near San Francisco in US waters. The self-propelled solar-powered glider is part of a new network including data receivers on fixed buoys that will pick up signals from acoustic tags on animals passing within 1,000 feet and transmit the data to a research team on-shore at Stanford University Marine Sciences Department. These are the result of 12 years development of fixed and mobile ocean transmitters to follow thousands of species. They increase scientific capacity to observe the oceans and marine populations, improve fisheries management models and monitor animal responses to climate change.
• The tracking can be followed in real time on a smartphone and tablet computer app "Shark Net" available free of charge at the Apple app store.
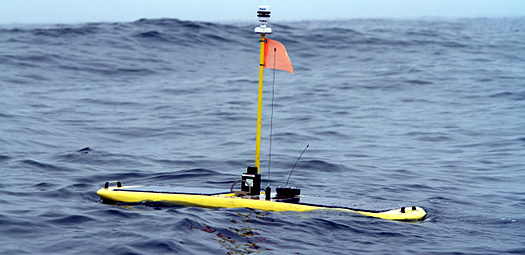
White shark tracking robot
FIRST USA WAVE POWER PLANT
Approval has been given for the building of the first commercial wave-power plant in the USA. The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission has issued a 35-year licence to Ocean Power Technologies Inc. to build the plant, intended to produce 1.5-megawatts of power, 2.5 miles off the coast of Reedsport, Oregon.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
• Email your maritime comments to TIN: [email protected]
Follow me for more maritime news and comment on Twitter: @TomMacSweeney
• And on Facebook – THIS ISLAND NATION page:
Experts Weigh In on Ireland's Wave Energy Future
#POWER FROM THE SEA - When will Ireland make the most of its wave energy? That's the question Journal.ie last week posed to experts in the field.
Some studies claim that up to 75% of Ireland's energy needs could be met by the same wave power that's a driving force behind Ireland's growing reputation as a top surfing destination.
But the industry also points out that the "very difficult technology" involved has yet to be perfected.
“It is perfectly possible to design the necessary equipment,” sats Carnegie Wave's Kieran O’Brien. “But it has to be able to withstand force 9 gales.
“We need something in the water that will extract that energy but will still be there when those storms hit."
Development of the sector is a catch-22 situation, as investors are cautious of putting in funds when no one is yet producing grid-connected power at scale, yet obviously such production requires serious capital.
Ireland in particular faces the problem of being what the industry describes as the Saudi Arabia of wave energy, yet having "no short term opportunities for R&D funding".
Journal.ie has more on the story HERE.
UCC Wave Energy Trials Central to New Maritime Cluster
#POWER FROM THE SEA - A €9 million Europe-wide wave energy trial programme is one of the key elements of a new Government programme designed to transform Ireland as a maritime nation.
According to The Irish Times, University College Cork's Hydraulics and Maritime Research Centre will run testing of wave energy, tidal energy and offshore wind energy devices across a network of sites in 12 European countries participating in the new marine renewables infrastructure network Marinet.
Irish test sites in the network include the national ocean test facility in Cork and centres operated by the Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland (SEAI) at Galway Bay and Belmullet.
The UCC centre also forms part of the new Irish Maritime and Energy Resource Cluster (IMERC), launched last Friday by Taoiseach Enda Kenny.
The cluster comprises UCC, the Irish Naval Service, Cork Institute of Technology and the National Maritime College of Ireland with the initial aim of creating 70 new research jobs by 2014 in the areas of wave energy, green shipping and sustainability of ocean resources.
IMERC director Dr Val Cummins said: “The aim of IMERC is to promote Ireland as a world-renowned research and development location that will unlock Ireland’s maritime and energy potential."
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
- Irish Naval Service
- maritime
- Cork
- Galway Bay
- Belmullet
- National Maritime College of Ireland
- wind energy
- UCC
- Cork Institute of Technology
- renewable energy
- wave energy
- sustainable energy
- tidal energy
- network
- testing
- Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland
- Taoiseach Enda Kenny
- SEAI
- Hydraulics and Maritime Research Centre
- Marinet
- devices
- Irish Maritime and Energy Resource Cluster
- IMERC
- Dr Val Cummins
New Scheme to Measure Noise Pollution from Wave Energy
#POWER FROM THE SEA - The Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland (SEAI) is teaming with IBM in a new project to assess the noise levels of wave energy devices off the Irish coast.
The scheme will see an array of noise sensing equipment such as hydrophones deployed in Galway Bay to monitor the noise levels of wave energy conversion devices in real time, as well as map patterns of marine life in the area.
According to AOL Energy, noise pollution at sea is a chief concern, having a disturbing effect on fish migrations among other marine ecosystems.
The west of Ireland will prove an important case study in this regard, as it hosts one of the world's largest wave energy infrastructures.
"Underwater noise is a global environmental issue that has to be addressed if we are going to take advantage of the huge potential of ocean energy," said EU Commissioner for Research, Innovation and Science, Maire Geoghegan-Quinn.
AOL Energy has more on the story HERE.
New Machines Changing the Rules for Wave Power
New Scientist has highlighted some of the latest technologies being developed to harness power from the sea.
Companies such as Pelamis Wave Power and Aquamarine Power are already testing prototypes of their so-called wave energy 'harvesters' - enormous machines that can capture the massive potential energy stored within ocean waves.
Pelamis' huge P2 is filled with state-of-the-art computers that allow programmers to control and update its operations on the fly, quickly taking advantage of changes in sea conditions to maximise energy production and increase efficiency.
The proof is in the pudding, as P2 can produce 750 kilowatts of power - twice as much as earlier prototypes.
Aquamarine's Oyster 800, meanwhile, can generate an incredible 800 kilowatts by way of a giant hinged flap that juts out of the water. Each passing wave closes the flap shut like a clamshell, with the resultant hydraulic pressure driving an onshore turbine.
"If you can get that sort of level of performance improvement then the economics suddenly start to look a lot more favourable," says The Carbon Trust's Stephen Wyatt.
New Scientist has more on the story HERE.
Ireland Risks Missing Out On Renewable Energy Benefits
Ireland must do more to develop its port and shipping services or risk missing out on the benefits of the growning renewable energy sector.
That was the message from a new analysis compiled by the Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland and the Irish Maritime Development Office, as reported by Renewable Energy Magazine.
The current lack of supply services and equipment for renewables in Irish ports could threaten the country's promise in the fields of offshore wind, tidal and wave energy, the report states.
It is estimated that the total value of such renewable energy sectors could be as much as €16 billion.
The east coast has been identified as the best location for offshore wind and tidal projects, while the south and west coasts were best for wave power and wind farms.
“We now need to look at the investment in infrastructure required if we are to properly capitalise on the current opportunities in this area," said the report.
Renewable Energy Magazine has more on the story HERE.






































































