Displaying items by tag: west cork
Cape Clear Port of Call A First By Cruise Ship
#CruiseLiners - For the first time ever a cruise ship called to the West Cork island of Cape Clear last Thursday morning with a group of 70 bird watchers.
Guests on the cruise ship Ocean Nova, writes the Evening Echo, were escorted by guides from Birdwatch Ireland who have a manned bird observatory on the island, and visited some of the island’s prime birdlife, wildlife, and marine life viewing spots.
While the main focus of the visit was birdwatching, they also took time to visit the island’s museum which depicts life on Cape Clear, past and present, and view its impressive exhibit about the building of the iconic Fastnet Rock.
Upon departure, the ship sailed around Fastnet and entered Schull Harbour, another first.
From there, coaches brought passengers to the Mizen Head Signal Station and Visitor Centre where they enjoyed not only the scenery, but observed the bird and marine life in this area.
To read more on the story, click here.
Buoy Change At Castletownbere Fishery Harbour Centre
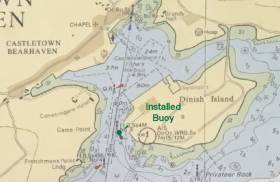
#MarineNotice - Marine Notice No 13 of 2018 advises that the No 3 Green Perch at the entrance to Castletownbere Fishery Harbour Centre in West Cork has been removed due to damage.
The No 3 Green Perch has been replaced by a 1.5m green buoy in position 51° 38’ 49.387” North, 09° 54’ 27.41” West.
The light characteristic is a green flash every five seconds. This buoy will remain in position until further notice.
For safety reasons, mariners are requested to proceed slowly and with caution when in the vicinity of the green buoy.
For further information, contact the Castletownbere Harbourmaster’s Office at +353 27 70220.
Baltimore Lifeboat Launches To Broken Down Trawler
#RNLI - Baltimore RNLI were called out in the early hours of yesterday morning (Friday 23 March) to a fishing trawler with five people on board which had broken down close to shore.
The volunteer lifeboat crew launched their all-weather lifeboat at 5.20am after the Irish Coast Guard requested assistance for a 22m fishing trawler that had suffered engine failure close to the shoreline off the West Cork harbour’s mouth.
Arriving on scene six minutes later, the lifeboat found the casualty vessel had an anchor shot and the crew, all in lifejackets, were working to resolve their mechanical difficulties. Weather conditions at the time had a south-westerly Force 5 wind and a 1.5m sea swell with good visibility.
Within 20 minutes, the trawler was underway by its own power, under escort of the Baltimore lifeboat, to the safety of Baltimore Harbour.
Speaking following the callout, Baltimore RNLI volunteer lifeboat press officer Kate Callanan said: “If your boat is in danger close to the shoreline, always remember to try not to panic.
“Use the resources available such as deploying an anchor, ensure all people aboard are in lifejackets and seek assistance as soon as possible. If you get into difficulty at sea or on the coast, call 999 or 112 and ask for the coastguard.”
The volunteer crew on this callout were coxswain Kieran Cotter, mechanic Cathal Cottrell, Pat Collins, Davie Ryan, Colin Whooley, Aidan Bushe, Emma Lupton and Don O’Donovan. Sean McCarthy assisted at Baltimore lifeboat station.
Elsewhere on the Irish coast, Skerries RNLI launched to reports of individuals in distress on two separate occasions earlier this week.
Shortly after 4am on Monday morning (19 March), Skerries volunteers launched their Atlantic 85 inshore lifeboat after Dublin Coast Guard received a call that a person in distress had entered the water near Laytown.
The lifeboat, with Emma Wilson at the helm and crewed by Steven Johnson, JP Tanner and Paddy Dillon, had just launched the boat when they were stood down as a garda had managed to help the person ashore to a waiting ambulance.
The lifeboat launched again on Tuesday evening (20 March) shortly after 11.30pm, this time helmed by Peter Kennedy with volunteers Jack Keane, JP Tanner and Paddy Dillon on board.
Concerns had been raised about a person who was in danger of entering the water near Bettystown. Again the lifeboat was stood down shortly after launching as shore-based emergency services had taken the person into their care.
Speaking about the callouts, Skerries RNLI volunteer lifeboat press officer Gerry Canning said: “It’s been a restless start to the week for our volunteers, but they are always ready to answer any call for help.
“The most important thing is that there wasn’t a tragic outcome in either case and we hope that the casualties make a full and speedy recovery.”
Baltimore Lifeboat On 11-Hour Callout To Assist Trawler
#RNLI - Baltimore RNLI were called out on Monday afternoon (26 February) to a fishing trawler that had broken down 50 miles south of Baltimore in West Cork.
The volunteer lifeboat crew launched their all-weather lifeboat at 2.12pm after the Irish Coast Guard requested that they go to the assistance of a 24m French-registered fishing trawler, with five people on board, that had suffered engine failure.
Arriving on scene at 4.25pm, the lifeboat crew had a tow established to the casualty vessel and were proceeding back to Baltimore within 10 minutes. One of the lifeboat volunteers, Youen Jacob, is fluent in French and was able to communicate with the trawler crew for the duration of the callout.
Weather conditions at the time were difficult, with an east southeasterly Force 6-7 wind and a four-metre sea swell, but visibility was good.
During the return to Baltimore Harbour, the tow proved difficult at times due to the weight of the casualty vessel and sea conditions, and at one point, shortly before 11pm, the tow disconnected for a short time.
Due to conditions in the harbour and the size of the casualty vessel, lifeboat coxswain Kieran Cotter decided that Baltimore’s inshore lifeboat should be launched to assist in bringing the trawler alongside the pier in Baltimore.
The smaller boat launched at 11.45pm to meet the all-weather lifeboat at the harbour’s entrance and escorted the two vessels to the pier, arriving at 12.20am, and the trawler was finally manoeuvred alongside and tied up at 1.15am.
Speaking following the callout, Baltimore RNLI volunteer lifeboat press officer Kate Callanan said: “It was helpful that the Irish Coast Guard notified us in advance of launching that the fishing trawler crew had no English as we were able to choose a fluent French speaker as one of our lifeboat volunteers.
“Thanks to Youen being able to communicate between the fishing vessel and the lifeboat both crews knew what was required throughout the rescue.”
The six volunteer crew onboard the all-weather lifeboat were coxswain Kieran Cotter, mechanic Pat Collins and crew members Aidan Bushe, Sean McCarthy, Youen Jacob and Jim Griffiths. Three volunteer crew onboard the inshore lifeboat were helm Micheal Cottrell, Ryan O’Mahony and Paul Synott. Assisting at Baltimore lifeboat station were Marty O’Driscoll, Ronnie Carthy, Pat O’Driscoll, Cathal Cottrell, Kieran Collins, Colin Whooley and Simon Duggan.
Project To Tackle ‘Ghost Fishing’ Scourge Coming To Ireland This Summer
#Fishing - Marine wildlife worldwide continues to fall victim to ‘ghost fishing’, trapped in lost or abandoned fishing gear.
The situation prompted a group of experienced divers, who often come across discarded nets and other debris, to form the Ghost Fishing Foundation — which co-ordinates cleanups in the US, the North Sea coast and the Mediterranean.
And this summer, as Coast Monkey reports, the initiative is coming to Ireland with the Big Ghost Net Removal Project.
Organisers are currently crowdfunding for the week-long cleanup which will see as many as 17 divers removing nets from the waters of West Cork, a popular location for dolphins and whales.
Coast Monkey has more on the story HERE.
Baltimore Lifeboat Provides Medevac From Sherkin Island
#RNLI - Baltimore RNLI launched yesterday afternoon (Sunday 7 January) to provide a medical evacuation from Sherkin Island.
The volunteer lifeboat crew launched their all-weather lifeboat following a request from the Irish Coast Guard at 3.50pm to provide medical assistance and evacuation for an elderly man on the West Cork island.
Once on scene, the volunteer lifeboat crew administered casualty care before transferring the patient back to the all-weather lifeboat, which returned to Baltimore lifeboat station at 4.20pm to transfer the patient to the care of the waiting HSE ambulance crew.
There was a north-easterly Force 4-5 wind at the time but sea conditions within the harbour were calm.
Speaking following the callout, Baltimore RNLI volunteer lifeboat press officer Kate Callanan said: “The RNLI and other rescue/emergency agencies provide a vital service to those living or staying on islands around the coast of Ireland. If you are in difficulty on or near the coastline call 999 or 112 and ask for the coastguard.”
There were eight volunteer crew onboard the lifeboat: coxswain Kieran Cotter, mechanic Cathal Cottrell and crew members Brendan Cottrell, Jerry Smith, Don O’Donovan, Kieran Collins, Micheal Cottrell and Eoin Ryan. In attendance at the lifeboat station was Kate Callanan.
Last weekend, Baltimore RNLI launched twice in the same day for a medevac from Heir Island and to assist bodyboarders reported in difficulty at Barleycove, as previously reported on Afloat.ie.
#RNLI - Baltimore RNLI launched twice in the space of a few hours yesterday (Friday 29 December) — firstly to provide a medevac from Heir Island, and later to assist bodyboarders in difficulty at Barleycove.
The volunteer crew launched their all-weather lifeboat Alan Massey following a request from the Irish Coast Guard at 11.16am to provide medical assistance and evacuation to a woman who fell on Heir Island off the coast of West Cork.
Once on scene, the crew administered casualty care before transferring the patient to the all-weather lifeboat and returning to Baltimore to meet a waiting HSE ambulance crew.
Conditions at sea during the shout had a north-westerly Force 6-7 wind and a one-metre sea swell, heralding Storm Dylan’s approach this weekend.
The crew launched a second time, at 4.18pm, after a member of the public alerted that three bodyboarders were in difficulty off Barleycove, near Mizen Head in West Cork.
The wind had eased considerably since the first callout, with a south-westerly Force 3-4, but there was a rough sea state with a swell of 3-4m.
At 4.45pm, with the lifeboat four miles west of West Calf Island, the crew were asked to stand down by the Irish Coast Guard after the three bodyboarders had made it safely ashore.
Speaking following the callouts, Baltimore RNLI volunteer lifeboat press officer Kate Callanan said: “With strong winds forecast over the coming days, the Irish Coast Guard strongly advises to exercise caution in coastal areas and reminds people to ‘Stay Back, Stay High and Stay Dry’.
“If you see someone in difficulty in the sea of along the shore call 999 or 112 and ask for the coastguard.”
The volunteer crew on the first callout were coxswain Kieran Cotter, mechanic Jerry Smith and crew members Aidan Bushe, Don O’Donovan, Simon Duggan and Kieran Collins. Ay the lifeboat station were Kate Callanan and John O’Brien. Crew on the second callout were Cotter, Smith, Bushe, O’Donovan, Eoin Ryan and David Ryan.
Crew Leaves Roach-Ridden Trawler Detained In West Cork
#Fishing - A UK-registered fishing boat detained in West Cork last week had to be fumigated twice to remove an infestation of cockroaches.
And according to the Irish Examiner, the Indonesian crew of the trawler Christian M have now walked off the vessel as arrangements are made for their voluntary return.
The Christian M was towed into Castletownbere on Wednesday 8 November after breaking down off the West Cork coast.
A subsequent inspection by the Marine Survey Office (MSO) led to its detention over a number of issues, including the cockroach infestation.
Ken Fleming, a co-ordinator with the International Transport Workers Federation (ITF), visited the boat yesterday (Friday 17 November) along with gardaí and an Indonesian embassy official.
“When I went onboard the vessel, I witnessed cockroaches still on surfaces,” said Fleming. “The accommodation is unfit for purpose.”
The Irish Examiner has much more on the story HERE.
Courtmacsherry Lifeboat Rescues Four On Trawler In Trouble
#RNLI - Courtmacsherry RNLI’s all-weather lifeboat was called out at 7pm on Saturday night (11 November) to go to the aid of an 80ft fishing boat that got into difficulties 15 miles south of the Seven Heads in West Cork.
The Trent class lifeboat, under coxswain Ken Cashman with a crew of five, launched immediately and proceeded at full speed to the distress area as the large trawler with four crew onboard sought assistance.
The stricken vessel was located by the lifeboat at 7.45pm and an immediate tow was put in place, proceeding at low speed back to the safe haven of Kinsale.
Weather conditions in the area at the time were misty with Force 3-4 winds and a strong swell.
Courtmacsherry RNLI lifeboat operations manager Brian O’Dwyer praised the crew for carrying out the rescue with great speed and professionalism.
He also thanked them and all station personnel for skipping Ireland’s important soccer battle in Copenhagen in order to help others in distress.
The crew of the lifeboat were coxswain Ken Cashman, mechanic Stuart Russell, Ciaran Hurley, Conor Dullea, Denis Murphy and Evin O’Sullivan.
Attempt to Refloat West Cork Yacht This Morning
Attempts to recover a 32–foot that went aground in Schul, West Cork during Storm Ophelia get underway this morning.
A recovery team is expected to slide the yacht down the rocks and back into the water using inflated rubber bags.